1. Introduction
1.1 Understanding Lamination Stamping
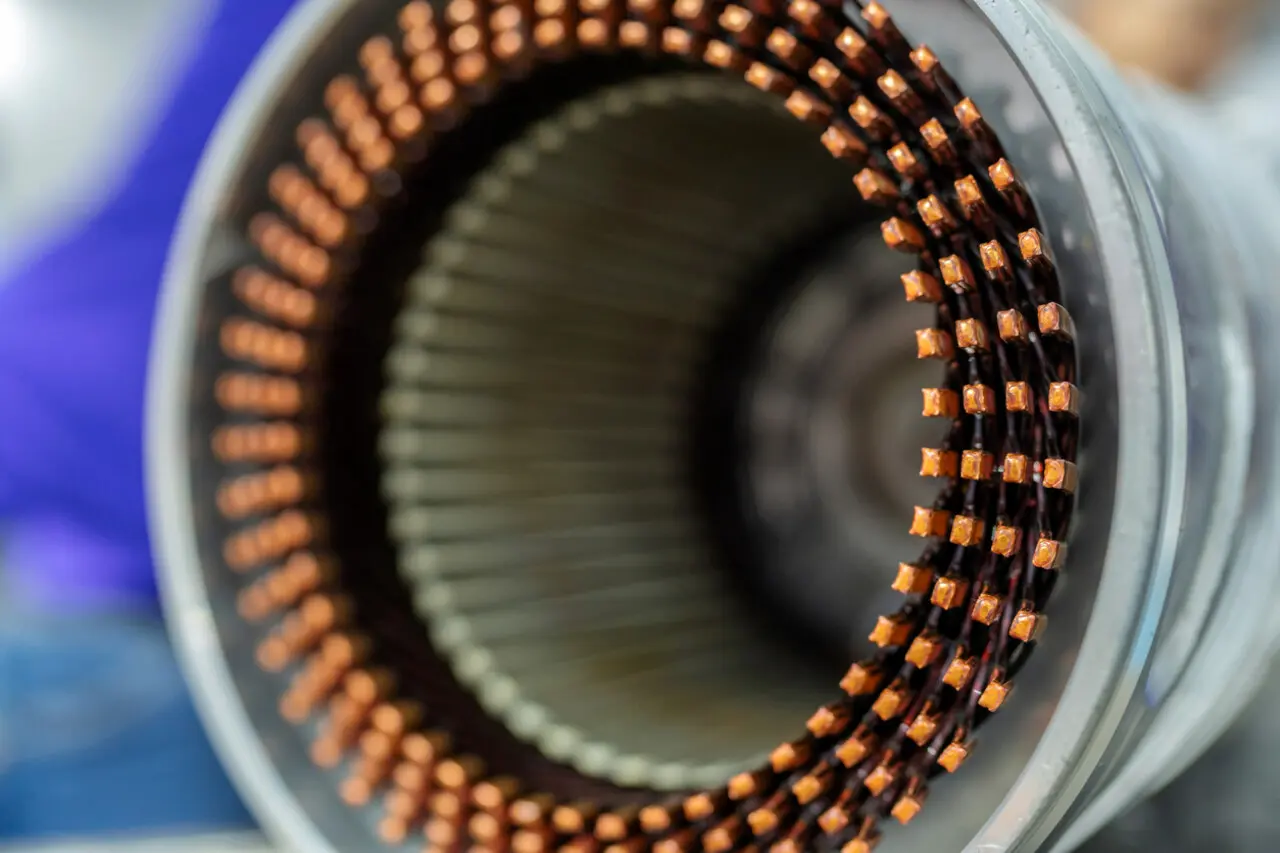
Lamination stamping involves cutting and shaping thin metal sheets—often made from materials like silicon steel—into precise forms that can be stacked to create motor cores. By stacking these laminated sheets, manufacturers reduce energy loss (in the form of eddy currents) and enhance the overall efficiency of electric motors. Although the concept may appear straightforward, maintaining consistent thickness, tolerance levels, and accuracy in each lamination is critically important.
The significance of lamination stamping becomes clearer when considering how even minor imperfections can compromise a motor’s performance over time. In many industries, including automotive and consumer electronics, reliable lamination stamping processes are essential to building high-performing motors that can meet demanding efficiency and durability requirements. While methods such as wire EDM or simple die stamping may offer certain advantages in specific scenarios, they might not always provide the speed or consistency needed for large-scale production.
1.2 Purpose of This Blog Post
The intent of this post is to introduce readers to the fundamentals of lamination stamping and to highlight why progressive die stamping can be an effective method for producing large volumes of high-quality laminations. We will discuss core principles of lamination stamping, examine various manufacturing methods, and delve into the distinct benefits that come with using progressive die technology.
At the same time, it is important to acknowledge that no single solution is universally perfect. Each manufacturing approach has its place, depending on factors like production volume, budget constraints, and specific design requirements. By the end of this blog post, readers will be better informed about how progressive die stamping fits into the broader landscape of lamination stamping methods—and why it could be considered a strong candidate for those aiming to optimize their motor core manufacturing processes in a cost-effective, efficient manner.
2. Fundamentals of Lamination Stamping
2.1 What Are Motor Core Laminations?
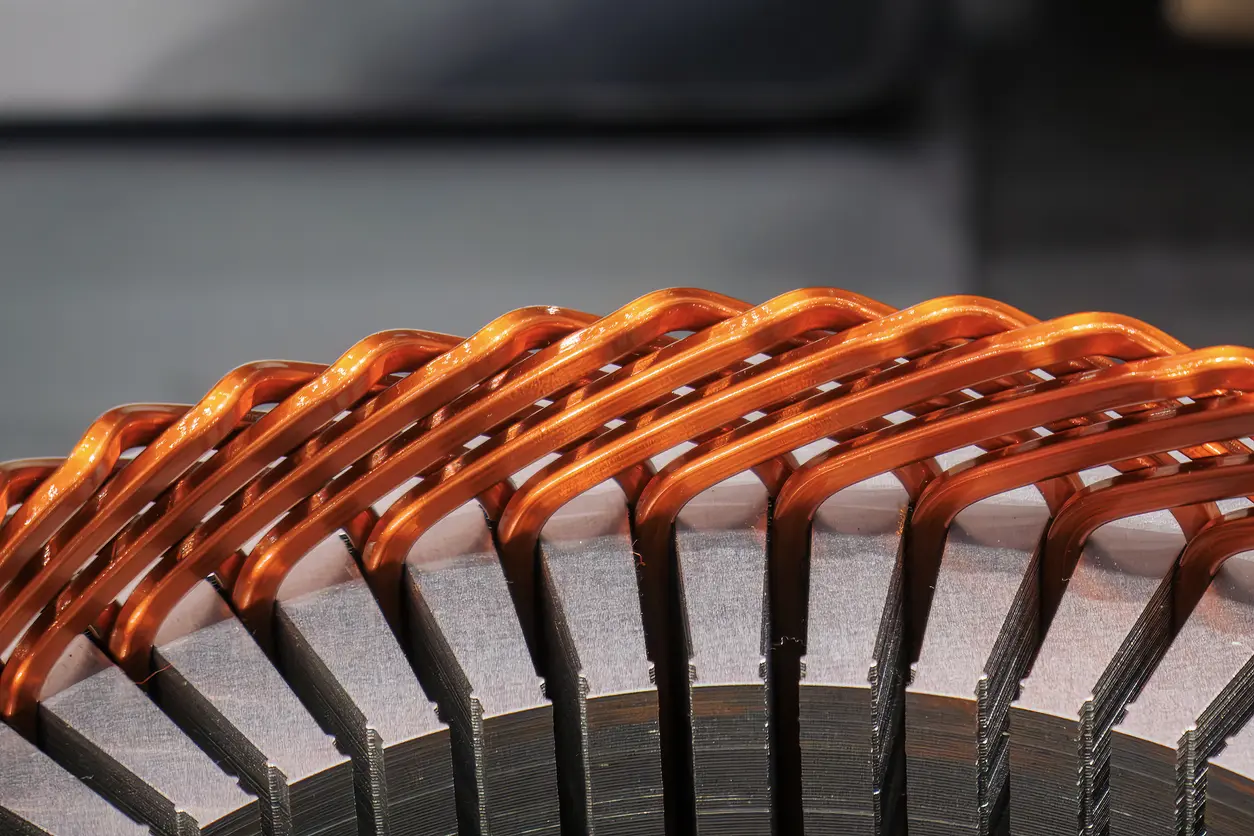
Motor core laminations typically consist of thin sheets of metal—often silicon steel—stacked together to minimize energy loss from eddy currents. By layering multiple thin sheets rather than using a single, thicker piece of metal, manufacturers can improve the magnetic properties of the core and enhance motor efficiency. In many applications, these laminations are held together with methods like interlocking tabs, welding, or adhesive bonding, forming the basis of a wide range of electric motors.
Accurate lamination stamping practices help ensure each sheet meets strict design specifications, which can be particularly important for motors that require tighter tolerances. Although some industries may prefer different stamping methods, such as wire EDM for small batch runs or prototypes, consistent quality often hinges on choosing a process suited for high-volume production. By understanding what motor core laminations are and why they matter, businesses can make more informed decisions about which stamping method best aligns with their performance goals.

2.2 The Role of Stamping Processes
Stamping processes play a pivotal role in shaping and cutting individual laminations. Lamination stamping, in particular, must balance efficiency with precision. Techniques range from simple die approaches, where each operation is performed separately, to more integrated systems like progressive die stamping, which can undertake multiple steps in a single press cycle.
Each process has its own set of advantages and trade-offs. Simple dies may be adequate for modest runs or less complex designs, while high-volume projects often demand a faster, more scalable method. A careful evaluation of production needs—factoring in volume, budget, and design complexity—is advisable when determining which approach to take. In addition, working with an experienced partner can help guide companies toward the stamping method that provides the best combination of performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness for their specific motor core applications.
3. Comparing Different Stamping Methods
3.1 Wire EDM Cutting
Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) uses a fine, electrically charged wire to cut through metal with exceptional precision. In the context of lamination stamping, this approach can be especially useful for creating prototypes or small volumes of complex parts. Because the wire removes material in a non-contact manner, there is minimal risk of material distortion. However, the cutting speed can be relatively slow, and overall production costs may become significant for larger batches. While Wire EDM offers a high degree of accuracy, it may not always be the most economical option for extensive lamination stamping runs.
3.2 Simple Die Stamping
Simple die stamping typically involves a singular or straightforward tool that performs basic cutting or forming operations. This method can be sufficient for lower-volume production or simpler designs. When producing laminations, companies might favor simple die stamping if they need limited quantities or if the motor core design is not overly intricate. Still, each new step or change may require manual intervention or additional tooling. This constraint can slow down production and elevate labor expenses. For businesses aiming for scalability or higher throughput, simple die stamping may not be as efficient in the long run.
3.3 Progressive Die Stamping
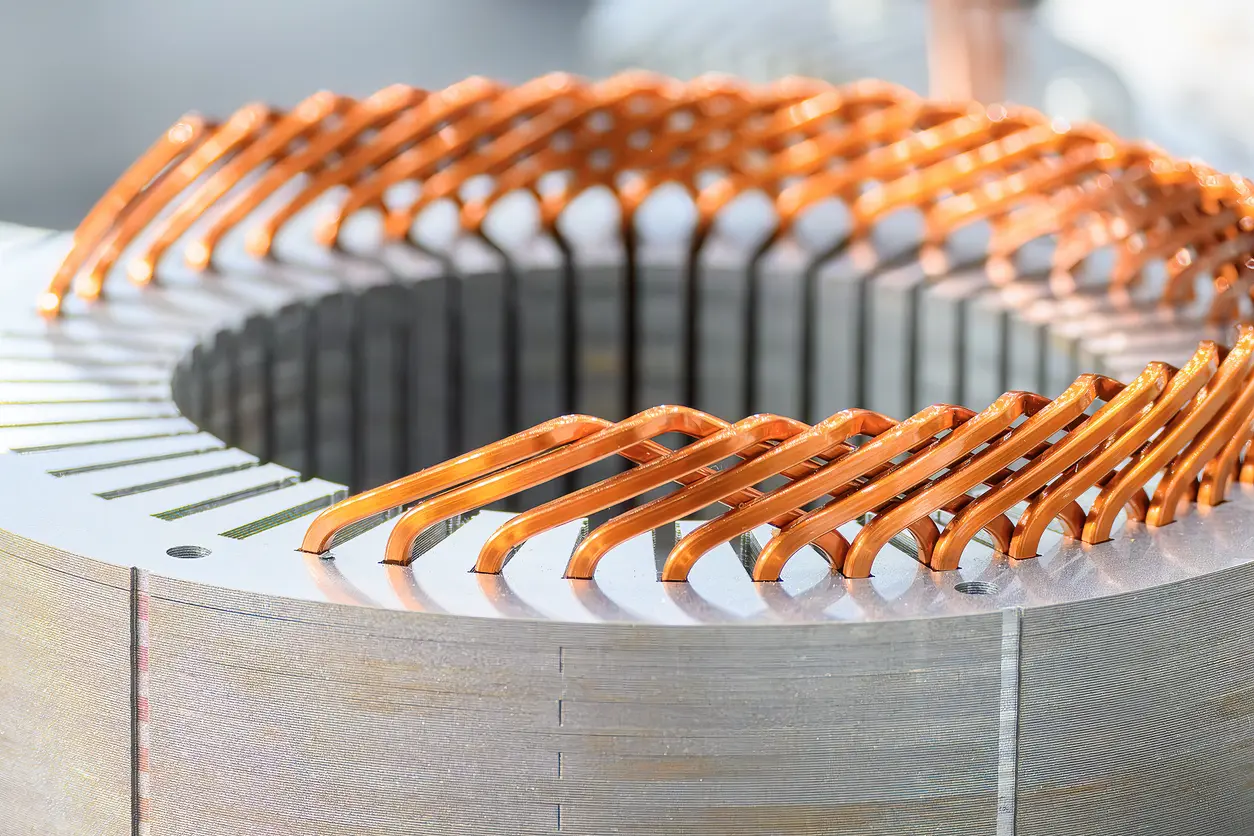
Progressive die stamping consolidates multiple operations—such as punching, notching, and forming—into a single, continuous process. Sheets of metal are fed through a series of stations, each performing a specific operation until the final lamination is complete. While the initial investment in tooling can be more substantial, the per-piece cost tends to decrease significantly with larger volumes. For lamination stamping projects that require consistent quality over high production runs, progressive die stamping is often viewed as a well-balanced option. It allows for better material usage, reduced scrap, and a streamlined workflow—all critical factors for companies seeking an efficient and reliable manufacturing process.
4. Advantages of Progressive Die Stamping for Lamination Stamping
4.1 High Efficiency and Speed
Progressive die stamping streamlines the manufacturing process by combining multiple stages—such as cutting, shaping, and notching—into a single, continuous operation. In contrast to other lamination stamping methods that might require individual setups for each task, progressive die stamping can complete an entire sequence of operations with minimal downtime. This efficiency is particularly helpful for businesses aiming to meet tight production deadlines without compromising on component accuracy, making it a sensible choice for those seeking to balance speed with reliability.
4.2 Consistent Quality and Precision
Maintaining uniformity across thousands or even millions of laminations is crucial in lamination stamping. Progressive die stamping facilitates this consistency by keeping critical tolerances in check throughout the manufacturing run. When each station is purposefully designed to handle a specific task, and the metal strip moves through the press in a controlled manner, the risk of variation between parts is minimized. Although no system can guarantee zero defects, progressive die tooling is known for delivering repeatable results that align well with strict motor core performance requirements.
4.3 Cost-Effectiveness Over Time
Although the initial tooling investment for progressive die stamping can be more substantial than simpler methods, many manufacturers find that this cost is offset by gains in efficiency. Larger production runs often benefit from lower per-piece expenses, as the rapid throughput reduces both labor and operational overhead. Additionally, optimized material utilization can lead to less scrap, further contributing to cost savings. While each situation is unique, the long-term financial benefits may be significant for companies considering progressive die stamping for high-volume lamination stamping projects.
4.4 Scalability for High-Volume Production
Progressive die stamping offers a scalable solution for businesses looking to increase or adjust production without extensive retooling. A single progressive die setup can often produce diverse shapes or sizes of laminations by making moderate modifications to the tooling. This flexibility is advantageous in industries where demand may fluctuate or where multiple motor models need to be supported. In sum, progressive die stamping stands out as a balanced approach that can handle large-scale requirements while maintaining consistency and cost-effectiveness in lamination stamping.
5. Applications in Electric Motor Core Manufacturing
5.1 Automotive and Industrial Motors
In the automotive sector, the shift toward hybrid and fully electric vehicles has increased the demand for highly efficient motors. Lamination stamping is often at the heart of achieving this efficiency, as it helps form the precise core elements that reduce energy loss. When large volumes of consistent laminations are required, progressive die stamping can be a suitable choice, thanks to its ability to maintain repeatable quality in high-output scenarios.
Industrial motors, meanwhile, frequently operate under heavy loads or extended run times. For these motors, lamination stamping not only needs to meet tight tolerances but also ensure long-term durability. By minimizing material inconsistencies and ensuring accurate alignment, manufacturers can help extend motor lifespan while maintaining performance. Although other methods like wire EDM or simple die stamping can still be beneficial for specialized tasks, progressive die stamping is widely recognized for balancing efficiency with reliable output levels in automotive and industrial production lines.

5.2 Consumer Appliances and Electronics
Household appliances—from washing machines to air conditioners—also rely on efficiently stamped laminations to improve motor performance and reduce power consumption. Well-formed cores enable smoother operation, lower energy usage, and can even reduce noise levels. In consumer electronics, smaller motors might require fewer laminations, yet precision remains critical to maintain device functionality and longevity.
Overall, lamination stamping continues to play a pivotal role in electric motor core manufacturing across a variety of industries. By aligning the stamping method with specific production goals—be it large-scale automotive runs or smaller home appliance models—companies can produce reliable, energy-efficient motor cores that meet today’s growing market demands.
Further Reading:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11740-024-01328-5