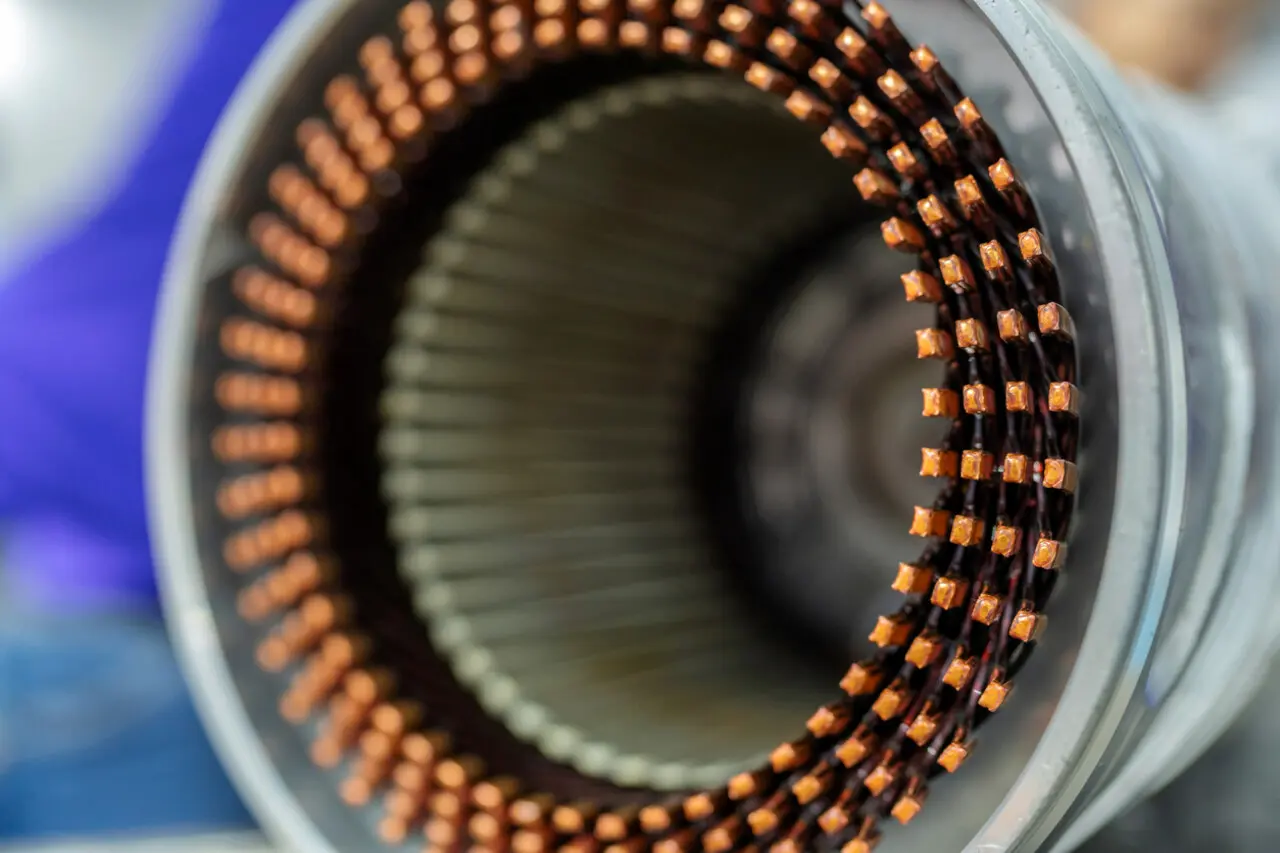
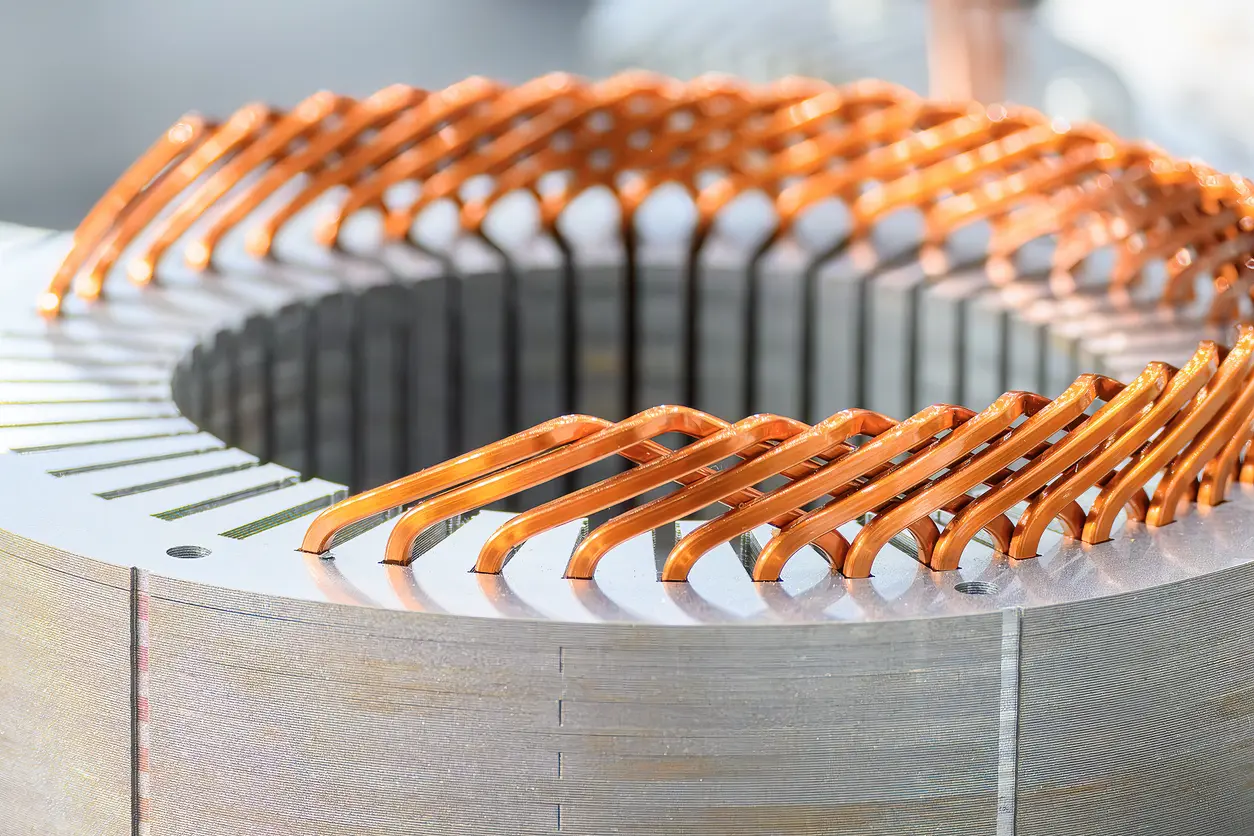
1. Understanding Eddy Current and Its Impact on Motor Performance
1.1 What is Eddy Current?
Eddy currents are loops of electrical current induced within conductive materials when they experience changing magnetic fields. First identified by physicist Léon Foucault in 1851, eddy currents typically arise during the operation of electrical machines such as transformers and electric motors. In electric motor cores, these currents circulate within the iron core and generate heat, which in turn contributes to energy loss and efficiency reductions. Despite their invisible nature, eddy currents significantly affect the overall performance and reliability of electrical motors.
1.2 How Eddy Currents are Generated in Electric Motor Cores
In electric motors, alternating magnetic fields produced by varying electrical currents induce eddy currents in the metallic components of the motor core, typically made from laminated electrical steel. When a motor’s stator winding is energized, it creates rapidly changing magnetic fluxes passing through the iron core. Due to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, these fluctuating magnetic fields induce circulating eddy currents within the steel laminations. The intensity of eddy current generation depends heavily upon material properties, core geometry, frequency of operation, and the thickness of the lamination sheets. For example, thinner laminations generally limit eddy current paths, thus reducing associated losses.
1.3 Negative Impacts of Eddy Current on Motor Efficiency
Eddy currents significantly degrade motor efficiency, mainly by converting valuable electrical energy into unwanted heat. This thermal generation increases operational temperatures, necessitating additional cooling solutions or reducing motor lifespan due to excessive thermal stress. Furthermore, higher eddy current losses directly reduce output torque and efficiency, undermining overall system performance. For instance, in industrial motors running continuously at high frequencies, unmanaged eddy current losses can lead to measurable increases in power consumption, operational downtime, and maintenance costs. Thus, proactively addressing eddy current challenges is crucial for enhancing motor reliability, lifespan, and operational cost-efficiency.
2. Lamination: The Foundation for Eddy Current Reduction
2.1 Role of Lamination in Controlling Eddy Currents
Lamination is widely recognized as a fundamental method for controlling eddy currents in electric motor cores. The underlying principle involves dividing the iron core into thin, electrically insulated layers, thereby restricting the pathways available for circulating currents. Because eddy currents typically flow perpendicular to magnetic flux lines, laminations are stacked parallel to the flux path to minimize the cross-sectional area for current loops. By reducing this area, laminations significantly mitigate the magnitude of eddy current losses. While lamination alone cannot entirely eliminate eddy currents, it remains one of the most effective methods for managing their negative impacts.
2.2 Selecting the Optimal Lamination Thickness and Material
Choosing the correct lamination thickness and material type directly influences eddy current performance. Thinner laminations inherently offer higher resistance to eddy current formation due to smaller loop areas. Typically, electrical steel laminations vary from around 0.20 mm to 0.65 mm in thickness. Although thinner laminations—such as 0.20 mm or even thinner—can effectively minimize eddy currents, their production cost and mechanical handling complexity may increase, posing challenges for certain applications.
Material selection is also critical. Silicon steel (or electrical steel) is commonly preferred due to its high magnetic permeability and relatively low electrical conductivity, characteristics which reduce eddy current losses substantially. For instance, high-grade non-oriented silicon steel, widely used in electric vehicle motors, demonstrates excellent performance by achieving an optimal balance between magnetic permeability, electrical resistivity, and mechanical durability.
In practical applications, motor manufacturers frequently balance between lamination thickness, material quality, and economic considerations. For example, industrial motors operating at standard frequencies (50–60 Hz) might utilize slightly thicker laminations (0.50–0.65 mm), whereas high-frequency motors used in electric vehicles or aerospace often require thinner laminations (≤0.35 mm) to effectively suppress eddy current losses.
3. Proven Techniques to Achieve Significant Eddy Current Reduction
3.1 Technique #1: Using High-Quality Electrical Steel Laminations
One highly effective method to reduce eddy current losses is selecting high-quality electrical steel for motor core laminations. Premium grades of silicon steel, particularly non-oriented types, offer lower electrical conductivity and higher magnetic permeability, limiting energy loss significantly. Materials specifically engineered for high-efficiency motors typically feature optimized silicon content, which reduces energy dissipation caused by circulating currents. For example, motors in electric vehicles (EVs) commonly utilize high-grade silicon steel laminations to maximize driving range by minimizing internal losses. While these materials may involve higher initial costs, long-term energy savings and improved operational reliability often justify the investment.
3.2 Technique #2: Optimizing Lamination Insulation and Coating
Optimizing insulation and coating on lamination sheets is another practical strategy for mitigating eddy current effects. Coatings such as phosphate or inorganic-organic varnishes are applied to electrically isolate each layer, effectively reducing interlaminar conductivity. Insulation quality directly influences long-term reliability, particularly in motors operating under harsh environments or elevated temperatures. A well-applied coating also minimizes risks of degradation over extended use. For instance, industrial induction motors frequently benefit from phosphate-coated laminations due to their robustness and stable insulation properties under prolonged exposure to vibration and thermal cycles.
3.3 Technique #3: Advanced Lamination Stacking Methods and Technologies
Advanced stacking technologies provide additional improvements in reducing eddy current losses by enhancing the integrity and precision of the laminated core. Techniques such as interlocking, adhesive bonding, welding, or self-bonding methods securely assemble laminations while minimizing air gaps and mechanical stresses. These methods ensure consistent magnetic properties throughout the core, thus limiting unintended current pathways. For example, adhesive-bonded laminations, increasingly common in aerospace and medical motor applications, effectively reduce internal friction and vibration, further optimizing magnetic performance. Selecting a suitable stacking technique depends on the application, budget, production volumes, and desired efficiency targets, highlighting the importance of balanced decision-making in motor design.
4. Real-Life Applications and Results
4.1 Application Case Study: Industrial Motors
Industrial motors commonly operate under demanding conditions, running continuously and handling substantial loads. Minimizing internal energy losses, including those caused by eddy currents, significantly impacts overall efficiency and operational costs. In one real-world example, a major manufacturer of industrial pump motors switched from standard-grade steel laminations to high-quality silicon steel with optimized lamination thickness and phosphate-based insulation coatings. As a result, energy efficiency improved measurably by approximately 3–5%, leading to considerable annual savings in energy expenses. Additionally, these motors exhibited reduced thermal stress, resulting in lower maintenance costs and extended service life. Such practical improvements underscore the value of targeted lamination strategies to address inherent efficiency losses.
4.2 Application Case Study: Electric Vehicle Motors
In electric vehicle (EV) motor design, efficiency and thermal management directly influence driving range, battery longevity, and overall vehicle performance. Automotive manufacturers frequently emphasize lamination thickness reduction and advanced stacking technologies to mitigate internal losses effectively. A prominent EV brand implemented extremely thin (0.20–0.35 mm) electrical steel laminations combined with adhesive-bonded stacking methods in their traction motors. This approach significantly reduced heat generation, allowing motors to operate at higher speeds and lower temperatures, ultimately improving battery efficiency and driving range by as much as 5–8%. Real-life tests and on-road analyses demonstrated clear performance enhancements, validating the effectiveness of strategic lamination improvements.
Overall, real-life applications consistently demonstrate that thoughtfully designed lamination solutions and careful material selection significantly reduce internal losses in various motor systems. Although complete elimination of losses is unrealistic, substantial improvements in efficiency, reliability, and sustainability are achievable, reinforcing the importance of proper eddy current management in modern motor engineering.

5. Conclusion and Key Takeaways for Motor Core Lamination
5.1 Recap of Eddy Current Reduction Strategies Discussed
Effectively managing eddy currents remains essential to improving motor performance, energy efficiency, and reliability. Throughout this article, we reviewed several proven methods to address this challenge. Firstly, selecting high-quality electrical steel laminations with suitable thicknesses significantly reduces circulating currents, providing a practical balance between performance and production feasibility. Additionally, optimizing insulation coatings, such as phosphate or inorganic varnishes, enhances electrical isolation between laminations, thereby further controlling unwanted current loops. Lastly, employing advanced stacking technologies like adhesive bonding, welding, or interlocking methods helps ensure structural integrity, reducing internal friction and vibration, and ultimately limiting the conditions that facilitate eddy current formation.
5.2 Importance of Eddy Current Management in Modern Motor Design
In modern motor design, proactively addressing internal losses associated with eddy currents has become crucial. Motors employed in industrial applications and electric vehicles serve as clear illustrations: carefully designed lamination and stacking solutions yield measurable efficiency improvements, extend operational lifespan, and lower overall costs. For example, industrial motors using optimized lamination solutions achieve significant energy and maintenance savings, while automotive traction motors benefit from extended battery range and improved thermal management.
Yet, while substantial progress can be achieved through these strategies, it is important to recognize that complete elimination of eddy currents is impractical. A conservative approach acknowledges inherent limitations and instead seeks to balance improvements against practical considerations such as production complexity and cost-effectiveness. Continuous advancements in material sciences and manufacturing processes will further refine these solutions, underscoring the importance of staying informed and adaptable within the motor design community. Ultimately, diligent attention to lamination materials, insulation techniques, and stacking methods remains essential for engineers seeking consistent performance improvements in today’s demanding electric motor applications.
Further Reading: