“Dive into the three revolutionary breakthroughs of PMSM motor cores in humanoid robotics—from high efficiency to modular design—fully optimizing robotic power and precision. Through professional analysis and case studies, you’ll stay one step ahead in the rapidly evolving world of automation.”
1.1 Basic Concepts and Development Background
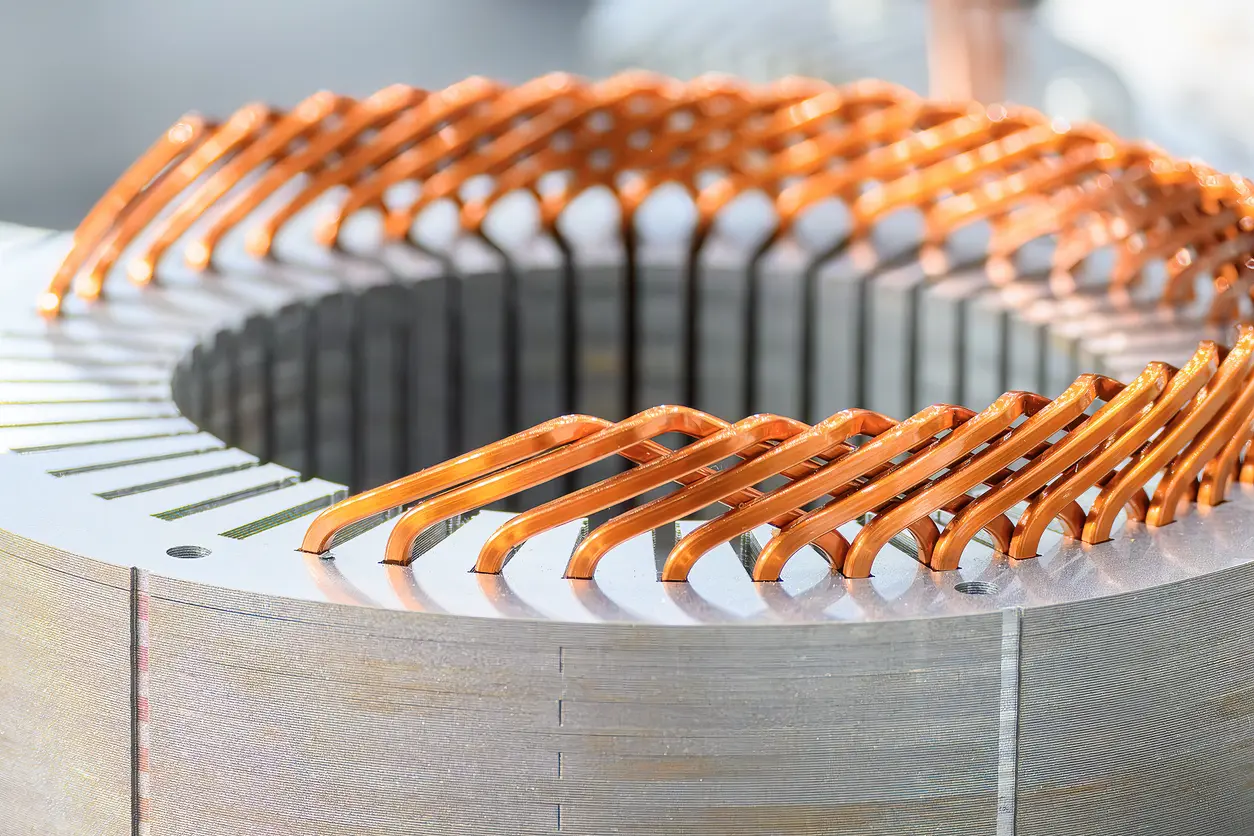
The PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) plays a pivotal role in the field of robotics, especially in humanoid robot applications, where it determines overall motor performance and operational stability. Humanoid robots require both multi-joint coordination and high-precision movement control. With its high efficiency, stable torque output, and relatively low noise, the PMSM motor core has gradually become a widely recognized solution in the market. However, despite optimistic forecasts from experts and industry players, factors such as cooling design, material selection, and system integration must be carefully assessed before actual implementation. Only by addressing these complex considerations can the PMSM motor core truly fulfill its potential.
1.2 Structure and Electromagnetic Principles
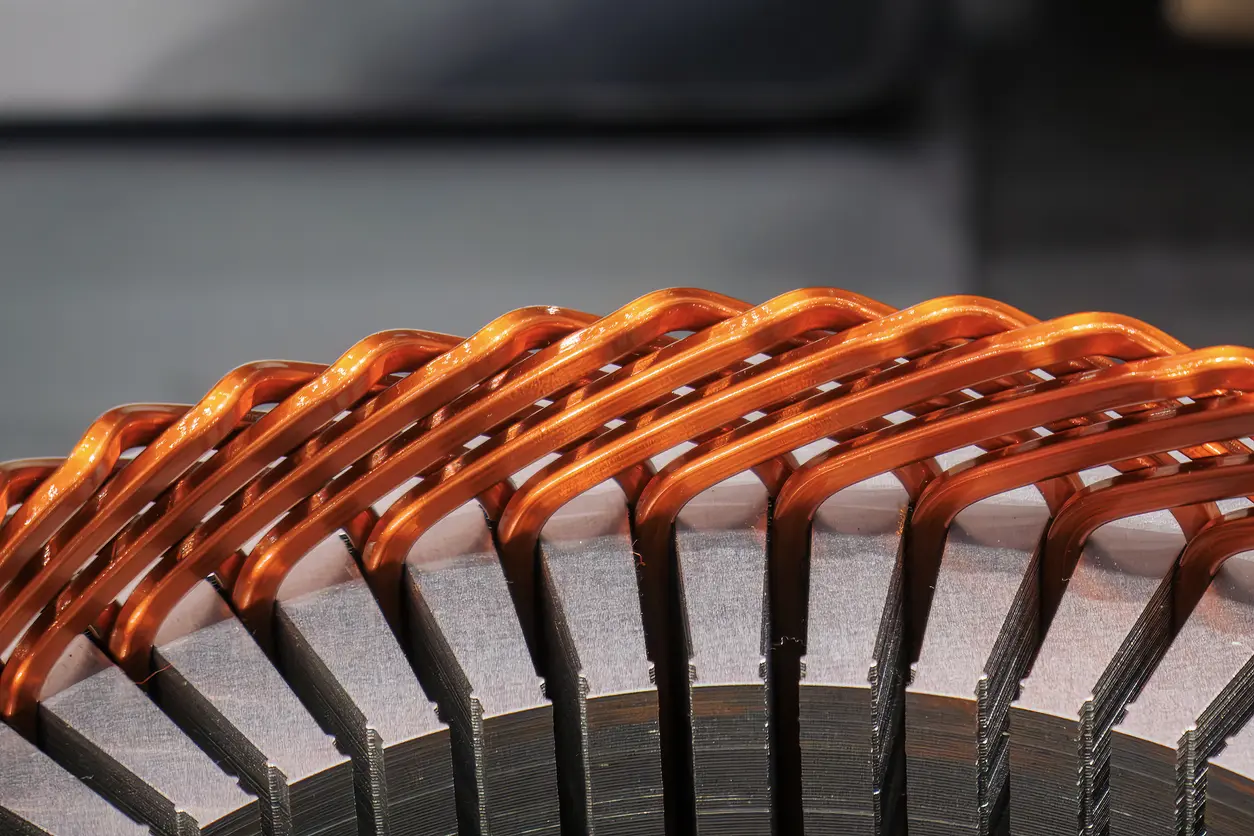
The core concept behind the PMSM motor core involves the electromagnetic interaction between the stator windings and the permanent magnets arranged on the rotor. When current flows through the windings, a rotating magnetic field is formed, causing the rotor to rotate in sync. The iron core itself provides a stable magnetic path, effectively converting electrical energy into mechanical energy. Because PMSM motors stand out in terms of efficiency and torque performance, they are particularly valuable for humanoid robots requiring high-precision movements. Nevertheless, over-reliance on high-end materials or complex processes may drive up costs, so it is crucial to select appropriate specifications and manufacturing methods based on actual needs.
1.3 Positioning and Advantages in Humanoid Robots
Humanoid robots are regarded as a key development trend in future automation industries. They need to run for extended periods and execute diverse tasks, imposing stringent demands on motor reliability and efficiency. Compared to other motor technologies, PMSM motor cores can deliver high torque in a relatively small form factor, alongside rapid dynamic response and energy efficiency—making them a significant advantage for humanoid robots. At the same time, factors like system integration, heat dissipation, and ongoing maintenance should not be overlooked. A thorough consideration of these aspects is essential to unleash the true value of the PMSM motor core in real-world applications and to avoid unnecessary risks or expenses during development.
1. Breakthrough One: High Efficiency and Low Energy Consumption
1.1 Background and Requirements
a. The Trend Toward High Energy Efficiency
Global industries are moving toward greater automation and intelligence, while also placing increased emphasis on overall energy conservation and carbon reduction. For humanoid robots operating over long periods, effectively reducing energy consumption largely determines overall operational costs and application viability. As a result, adopting motors known for high efficiency has become extremely important, and the PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) is widely regarded as one of the most promising options in the industry.
b. Comparison with Other Motor Technologies
Commonly available motors—such as brushless DC, stepper, or induction motors—each have their own advantages in terms of efficiency, torque output, and heat management. However, the PMSM motor core typically demonstrates more favorable performance in both output efficiency and overall energy consumption, while more easily accommodating lightweight designs and high power density. Nevertheless, large-scale production or highly customized requirements must still consider the balance between cost and design complexity.
1.2 Key Design Features of the PMSM Motor Core
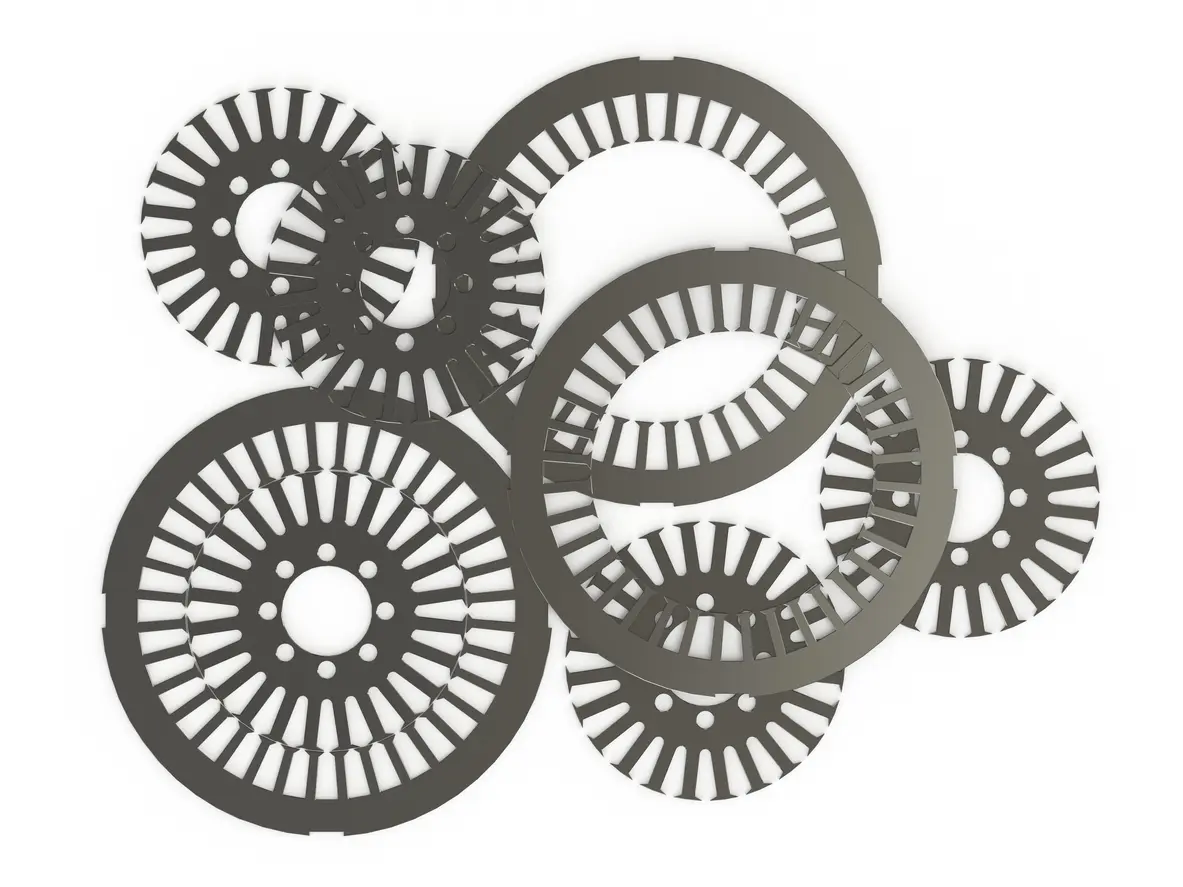
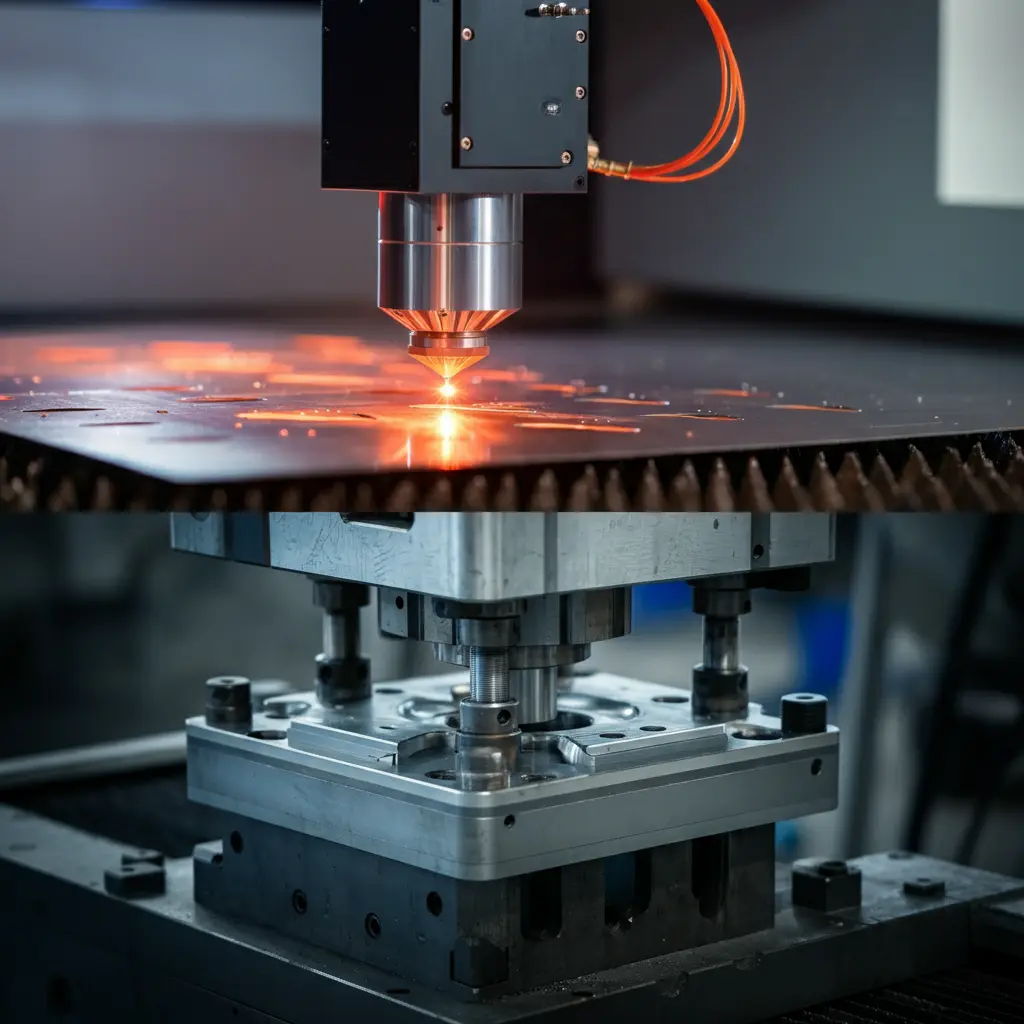
a. High-Silicon Steel Sheets and Lamination Process
To minimize electromagnetic losses, PMSM motor cores generally use steel sheets with a high silicon content, fabricated via precision stamping or laser cutting. Thinner laminations can significantly reduce eddy current losses, thus boosting efficiency. However, both manufacturing precision and material choice can affect overall costs.
b. Electromagnetic Field Optimization
In addition to the materials themselves, electromagnetic field design is crucial to improving efficiency. Through software modeling and empirical data analysis, it is possible to achieve more optimal magnetic flux distribution between the stator and rotor, thus reducing energy loss and enhancing torque output. This gives the PMSM motor core a competitive edge in humanoid robots requiring sustained long-term operation.
1.3 Successful Application Examples
a. Industrial Manufacturing Sector
In highly automated production lines, humanoid robots equipped with PMSM motor cores can reliably handle repetitive tasks. Because of their relatively low energy consumption and consistent efficiency, factories can control operating costs more effectively over long operating periods.
b. Service Robots
In service industries such as hotels, hospitals, or shopping centers, humanoid robots often need to balance a lightweight appearance with long operational time. Thanks to the high efficiency and stable output of PMSM motor cores, robots can extend run times despite limited battery capacity, improving service quality and reducing the frequency of mid-operation recharging.
2. Breakthrough Two: Outstanding Dynamic Response and High-Precision Control
2.1 Importance of Dynamic Response
a. Joint Control and Balance
Every joint’s immediate movement in a humanoid robot can impact overall balance and coordination, making the speed and accuracy of dynamic response critical. If a PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) can provide the necessary torque instantly and adjust angles and speed in real time, the risk of falls or malfunctions from unstable posture can be significantly reduced.

b. Torque Control and Instant Acceleration
When a robot needs to accelerate quickly from a standstill or rapidly change its movement during motion, torque output becomes the key performance indicator. The PMSM motor core excels here by reaching high torque outputs in a short time, thus enhancing overall response speed. However, in practical operations, a high-performance driver and precise sensors are still required to ensure that movements are not overly abrupt in ways that might compromise system stability.
2.2 Elements of High-Precision Motion Control
a. Low Vibration and Low Noise
High-precision control generally depends on a stable environment with minimal interference. Excessive vibration or noise from the motor not only can disrupt sensor data interpretation but may also increase wear on system components. A PMSM motor core that effectively reduces rotor jitter and stator noise is an attractive feature for humanoid robots that run continuously.
b. Integration of Sensors and Controllers
Dynamic response and high-precision control cannot be achieved by the motor alone; sensor and controller integration is also essential. Only through efficient coordination among the motor, controller, and various sensing devices can the fast, precise advantages of the PMSM motor core be fully utilized. Developers must pay attention to hardware connectivity, software algorithms, and real-time communication protocols to ensure overall system coherence.
2.3 Cost and Benefit Evaluation
a. ROI for High Dynamic Response Motors
High dynamic response motors typically require more meticulous design and advanced manufacturing techniques, which inevitably drives up costs. However, in real-world applications, if they enhance production efficiency, reduce downtime, or improve service quality, the long-term return on investment could be quite substantial.
b. Comparison with Other Motor Options
Different types of motors each have their strengths in terms of cost, size, and performance. While the PMSM motor core generally holds an advantage in torque output, efficiency, and vibration reduction, constraints such as budget and system compatibility should be considered during selection. Achieving an optimal balance between dynamic response and spending can pave the way for more precise and reliable motion control in humanoid robots.
3. Breakthrough Three: Modular Design and Future Upgrade Potential
3.1 Advantages of a Modular Motor Core
a. Flexible Upgrades and Maintenance
While aiming for high performance and a long service life, humanoid robot developers also prioritize the ability to adapt as requirements evolve. A PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) can be designed in a modular fashion to minimize interference among components and enable quicker replacement or maintenance when upgrades are needed later. This swappable design approach also allows for local performance enhancements without altering the entire system framework.
b. Compatibility with Other Systems
Humanoid robots generally incorporate multiple sensors and control elements. A modular PMSM motor core can be more easily paired or replaced with other systems. In projects spanning various fields, unforeseen applications sometimes arise in mid or late phases, and adopting a modular strategy allows developers to quickly customize or upgrade the motor module without dramatically altering the robot’s overall design.
3.2 Technology Directions to Meet Future Demands
a. Smart Control and Cloud Management
With the growing maturity of AI and IoT technologies, a PMSM motor core that reserves space for sensor interfaces or communication modules upfront can integrate more easily with smart control and cloud management features. This can enable more precise data analysis for humanoid robots and provide real-time monitoring of motor status, facilitating remote supervision and fault prediction.
b. New Materials and Lightweight Design
Future motor development may move toward new materials offering higher magnetic permeability and lower losses. If lightweight design requirements are factored in from the outset—alongside structural considerations for potential modifications—upgrading or changing materials later becomes much smoother. This, in turn, may usher in a new wave of advancements in volume, efficiency, and heat dissipation for the PMSM motor core.
3.3 Application Prospects in Humanoid Robots
a. Expanding the Realm of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
As collaborative robots continue to rise and increasingly overlap with the scope of humanoid robots, a modular motor core can be flexibly configured for varying safety mechanisms and load ranges. This may spur more cross-domain innovations in robotic design.
b. Long-Term Commercial Value
Embracing modular design and future upgrade potential means companies and research institutions can more quickly adapt their strategies and maintain competitiveness as technology and market demands evolve. Continual incorporation of state-of-the-art materials and control methods in a PMSM motor core will likely see it play an increasingly critical role in upcoming developments for humanoid robots.
4. Technical Selection and Procurement Guidelines
4.1 Performance Evaluation and Testing Methods
Before integrating a PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core), it is advisable to perform multiple assessments, including load testing, operating speeds, and long-term operational stability. Fatigue and accelerated aging tests are especially helpful for gauging durability under high-frequency usage. Additionally, evaluating heat dissipation and operating noise is essential to ensure reliability under extreme environments or extended run times. Having precise core data early on sets a solid foundation for subsequent system integration and maintenance planning.
4.2 Cost and Return on Investment
While high-end PMSM motor cores generally offer impressive performance, they also imply higher procurement or development costs. It is recommended to consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), rather than just focusing on motor price. For example, improved efficiency can lead to lower energy expenses, and better durability can reduce maintenance and downtime costs. If these benefits translate into higher productivity or a superior user experience in actual operation, the return on investment (ROI) may become positive within a reasonable timeframe.
4.3 Supplier Evaluation and Technical Support
When selecting a PMSM motor core, the manufacturer’s R&D capabilities and after-sales support are crucial. First, ensure the supplier can offer customization or technical adjustments based on the project’s requirements and that they have extensive application experience. Second, comprehensive after-sales support, including warranties, technical consultations, and emergency services, provides additional security for humanoid robots in real-world scenarios. Through thorough upfront evaluation and reliable ongoing support, developers can more effectively integrate the advantages of a PMSM motor core into the overall system, maintaining stable, high-performance operation over time.

5. Successful Application Cases and Practical Benefits
5.1 Industrial and Service Sectors
In automated production lines, the high efficiency and stable output of the PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) often ensure reliability in long-duration operations. Some manufacturing firms implement it in humanoid robot assembly units for tasks requiring high precision. The stable torque and low energy consumption offered by PMSM motor cores not only reduce downtime and maintenance costs but may also boost output over a given production cycle. In the service sector—such as hotels or shopping malls—humanoid robots often require a sleek appearance and long operating times. With a PMSM motor core, they can maintain smooth movements despite limited battery capacity, minimizing overheating or noise interference and thereby enhancing user experience.
5.2 Integration with AI and IoT
In recent years, AI and IoT technologies have become increasingly mature in robotics. When real-time sensor data and cloud algorithms are combined, operating parameters of the PMSM motor core can be precisely monitored and adjusted. For example, logging the motor’s operational status and load changes through a cloud platform allows early detection of potential faults, helping engineering teams schedule maintenance and fine-tuning in advance. With such predictive maintenance, humanoid robots can retain greater stability and safety during workflows, while avoiding unplanned production or service interruptions.
5.3 Enterprise Adoption Outcomes
For enterprises, the ultimate aim of choosing a PMSM motor core is to improve overall efficiency, whether that means optimizing production, reducing development time, or enhancing service quality. Since the motor core offers superior efficiency and durability, using it long term can lower labor and energy expenditures. Moreover, enhanced reliability translates into reduced failure rates, thus avoiding additional costs due to emergency repairs and bolstering a company’s competitiveness in the market. Overall, the multiple use cases for PMSM motor cores across industrial and service applications demonstrate strong economic and social value, laying a solid foundation for further humanoid robot development projects.
6. Future Trends and Collaboration Opportunities
6.1 Technical Standardization and Ecosystem
As humanoid robot applications continue to expand, achieving technical standardization during the development process becomes a major concern. Establishing unified hardware and software interface specifications would help the PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) to be integrated more efficiently across different platforms and industries. This would not only shorten development cycles but also reduce supply chain complexities, fostering wider adoption of humanoid robot technologies. For businesses, collaborating broadly and establishing a mutually beneficial ecosystem can confer a greater competitive edge.
6.2 Potential Breakthrough Directions
With ongoing advancements in materials and manufacturing processes, the PMSM motor core could evolve toward higher magnetic flux density, lighter weight, and even lower energy consumption. New composite materials or nanotechnology, for instance, may further reinforce the motor core’s structure, enhancing cooling efficiency and durability. Additionally, if real-time monitoring and intelligent control algorithms can be integrated, the motor’s operating parameters could adjust dynamically based on actual load conditions, further cutting energy use and boosting system reliability. These breakthroughs could redefine the upper limits of humanoid robot performance and spawn new application scenarios.
6.3 Encouraging Industry and Academic Collaboration
Because humanoid robot technology is complex and requires lengthy development cycles, relying solely on enterprises or research institutions is often insufficient. Encouraging government-industry-academia cooperation can more effectively drive research, manufacturing, and market adoption of the PMSM motor core. Through joint laboratories or international R&D initiatives, new technologies can be validated and implemented more quickly, bringing together expertise from diverse fields. This model can also cultivate more specialized talent, ensuring that humanoid robots have robust vitality and competitiveness in the future. By maintaining close interaction among industry and academic entities—and focusing on standardization, innovative materials, and system integration—widespread adoption of PMSM motor cores in humanoid robots is likely to become more feasible, creating deeper impacts on the industry.
7. Conclusion
7.1 Summarizing the Importance of PMSM Motor Cores
In the realm of humanoid robots, the PMSM motor core (Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Core) undeniably demonstrates remarkable potential. From high efficiency and low energy consumption to exceptional dynamic response and precision control—not to mention modular design and future upgrade possibilities—this technology stands out across a variety of scenarios. Even so, when implementing it in practice, it remains necessary to weigh multiple factors, including cost-effectiveness, material choices, manufacturing processes, system integration, and ongoing maintenance. A cautious, pragmatic evaluation ensures that the PMSM motor core truly becomes the driving force in humanoid robots.
7.2 Practical Recommendations
First, developers and businesses planning projects should clearly define the target applications and load requirements of humanoid robots, along with feasible budgets and technical roadmaps. If high torque and low energy consumption are priorities, a PMSM motor core may be an option worth considering. For smaller-scale projects, initial investment must be balanced against ongoing maintenance costs. Next, selecting suppliers or partners with solid R&D capabilities and robust after-sales support is particularly important, as they can assist with customized designs, troubleshooting, and long-term upgrades, thus providing more consistent results.
7.3 Looking to the Future
As humanoid robots gain traction in a wider range of industries and public services, the outlook for PMSM motor cores will also continue to grow. Whether in tandem with AI, smart sensors, or new materials and manufacturing technologies, additional improvements in motor performance could lead to new breakthroughs in functionality and mobility for humanoid robots. Although certain technical and cost-related challenges remain, the combined efforts of various stakeholders can help PMSM motor cores provide a solid foundation for ongoing upgrades and innovations in humanoid robots. This collaboration will likely foster stronger growth and advancements in both industry and research in the years ahead.
External resources: Lyapunov-Based Robust Control for PMSMs in Collaborative Robots
Internal links: 5 Must-See Keys: How to Choose the Most Powerful PMSM Motor Core for Humanoid Robots