1. Introduction
1.1 The Growing Importance of Precision in Lamination Manufacturing
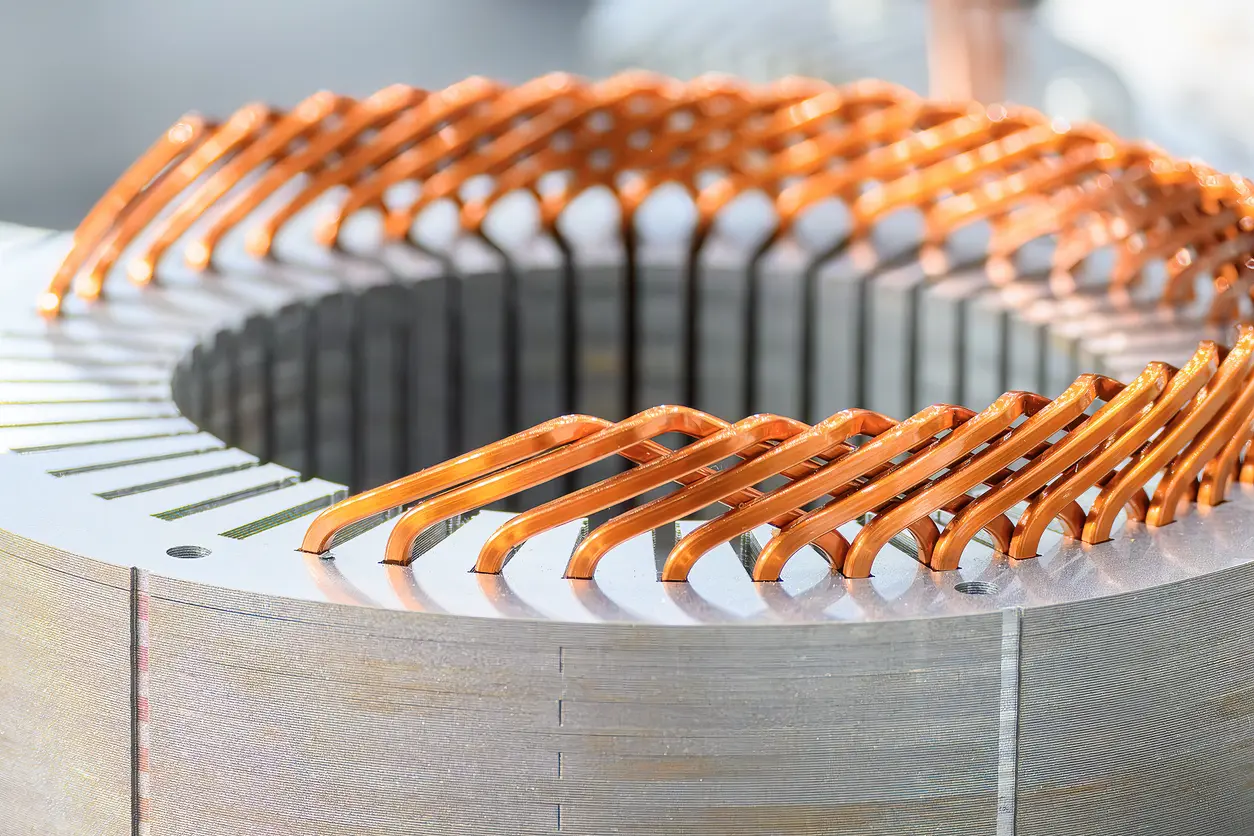
Precision has long been a key focus in the production of electric motor components, but advances in motor technology have elevated these requirements even further. In lamination manufacturing, the slightest dimensional discrepancy can affect magnetic performance and lead to higher energy losses over time. Consequently, many manufacturers are now reevaluating their cutting methods to meet stricter quality demands. By ensuring each lamination is produced with minimal deviation, organizations can enhance motor efficiency and reliability—benefits that ultimately help them remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
1.2 What Is Wire EDM Cutting?
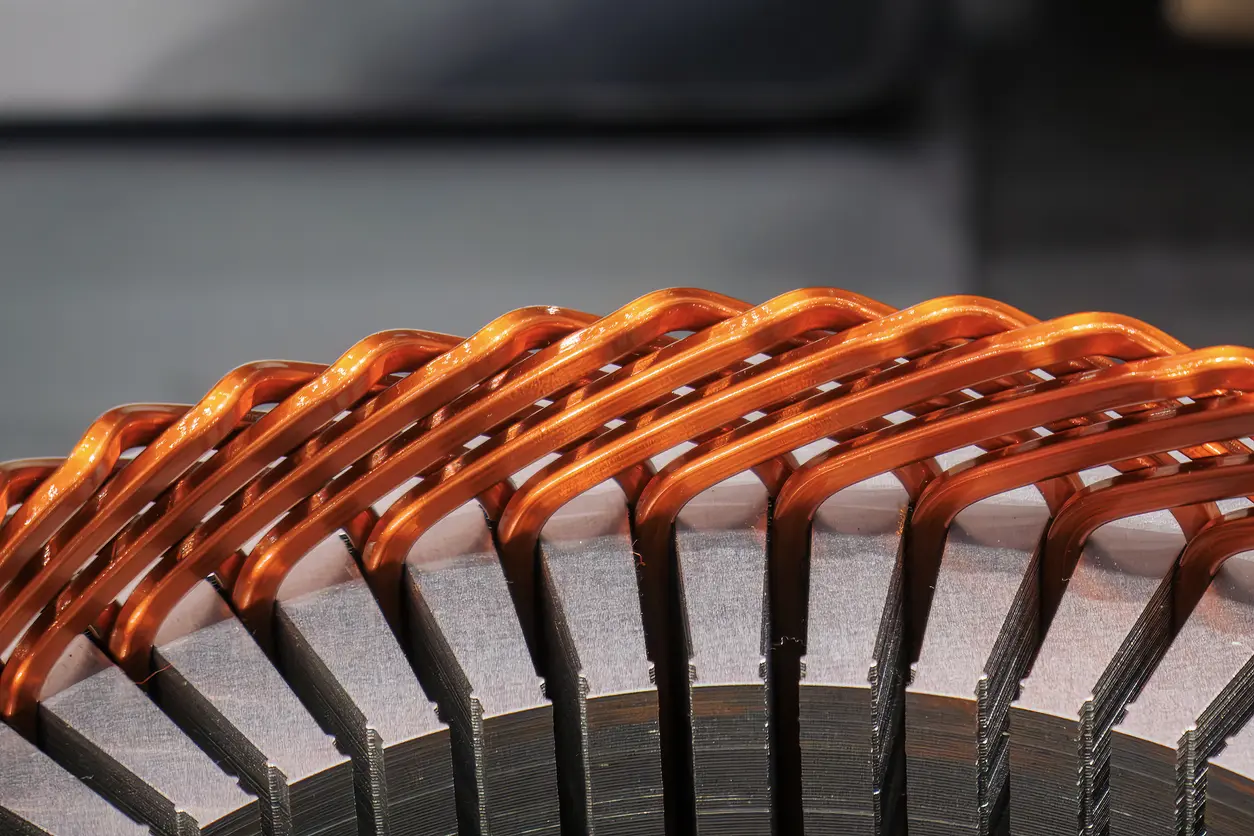
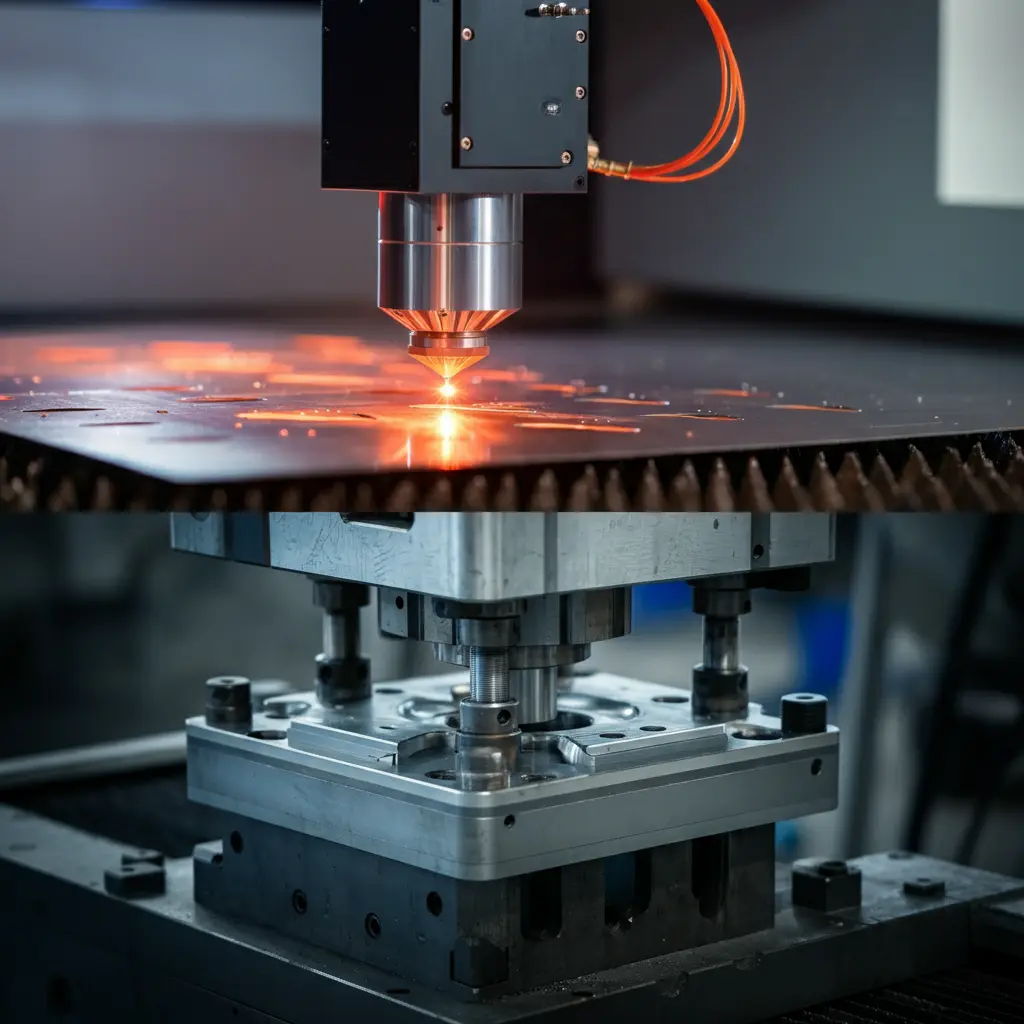
Wire EDM cutting, short for Wire Electrical Discharge Machining, is a non-traditional process that employs a thin, electrically charged wire to erode material with remarkable accuracy. Unlike conventional machining, there is no direct physical contact between the cutting tool and the workpiece. Instead, controlled electrical discharges remove material in a highly precise manner. This approach is particularly valuable when working with delicate laminations, as it minimizes mechanical stress and reduces the chance of part distortion. While wire EDM cutting has been widely adopted in industries like aerospace and medical device manufacturing, it is increasingly recognized as a strong contender for motor lamination applications where precision and part integrity are crucial.

1.3 Purpose of This Blog Post
This blog post aims to present a balanced overview of how wire EDM cutting can address the challenges commonly faced in lamination stack assembly. We will discuss key advantages—such as superior accuracy and potential cost savings—while maintaining a conservative perspective on its practical applications. By exploring these points in detail, manufacturers and engineers can form their own conclusions about whether wire EDM cutting aligns with their production goals. Ultimately, the objective is to help industry professionals make well-informed decisions about adopting this technology for enhanced motor core performance.
2. Benefit #1: Unmatched Precision and Tolerances
2.1 Achieving Micron-Level Accuracy
Wire EDM cutting is often regarded as one of the most precise fabrication methods available for motor lamination. By utilizing a thin wire and a series of electrical discharges, this process can remove material in extremely small increments. In many instances, the accuracy can reach down to a few microns, which is vital for electric motor components requiring tight tolerances. Because the wire never physically contacts the workpiece, there is less risk of deforming delicate parts, making this method particularly suitable for creating intricate lamination profiles. Although results may vary depending on material type and operator expertise, this approach generally offers a higher level of precision compared to conventional cutting techniques.
2.2 Consistent Cut Quality
Another advantage of wire EDM cutting is its ability to deliver a uniform cut across an entire production run. Traditional methods such as stamping can see variations over time due to tool wear or heat buildup, but the electrical discharge principle provides consistency in each pass. This stability is supported by the dielectric fluid, which helps to cool the wire and maintain a steady spark gap. For manufacturers, such consistency can lead to fewer rejected parts and improved production efficiency. In addition, the minimal mechanical stress exerted on the material often results in cleaner edges, reducing the need for further finishing steps.
2.3 Impact on Motor Core Performance
In lamination stack assembly, maintaining precise dimensions is crucial to ensure optimal electromagnetic performance. Even small inconsistencies can create unwanted gaps or misalignments within the core, potentially increasing energy losses. While it is not the sole factor influencing motor efficiency, highly accurate cuts do appear to play a meaningful role in improving overall motor performance, making it an option worth evaluating for critical applications.
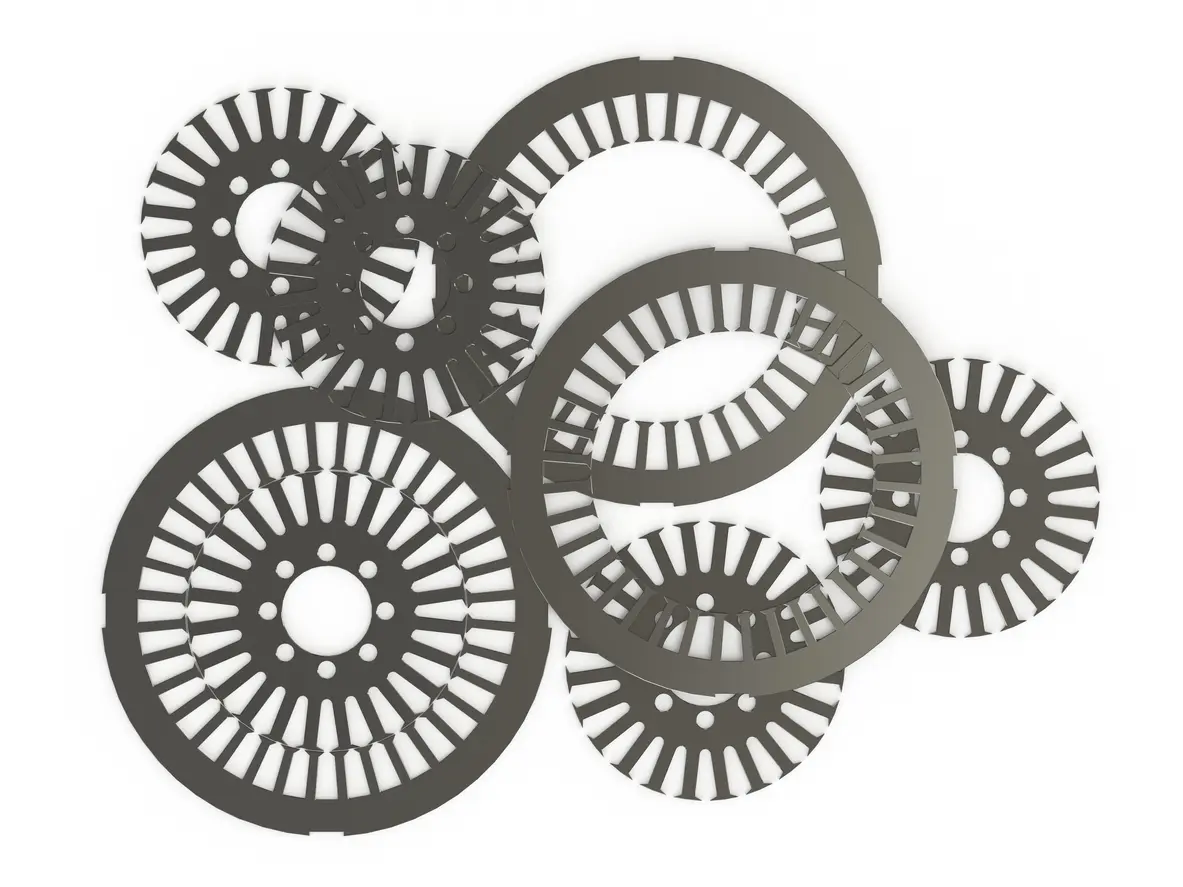
3. Benefit #2: Complex Geometries Made Simple
3.1 Design Freedom for Modern Motors
Many of today’s electric motors feature sophisticated shapes and layouts, often aimed at optimizing magnetic flux distribution or reducing energy losses. Traditional cutting methods can struggle to reproduce these complex geometries consistently, especially when dealing with tight corners or intricate curves. Wire EDM cutting, on the other hand, relies on controlled electrical discharges rather than sheer force to remove material. This approach allows it to produce fine details that might be challenging or even impossible to achieve with more conventional techniques. Moreover, because there is no direct tool-to-workpiece contact, the likelihood of distorting fragile motor laminations is notably reduced.
3.2 Consistent Edge Quality
When creating intricate shapes for lamination stack assembly, the importance of edge quality cannot be overstated. A smooth edge finish helps prevent issues like burrs or uneven surfaces, which could lead to stacking irregularities over time. Wire EDM cutting inherently produces a cleaner edge because the erosion process is highly controlled, minimizing the formation of rough edges. This can be particularly beneficial for motors designed to operate at high speeds or in demanding conditions, where even minor imperfections might affect performance or durability. Still, as with any process, manufacturers may want to conduct thorough inspections to verify that finished parts align with application-specific tolerances.
3.3 Customization and Prototyping
Beyond high-volume production, wire EDM cutting can also be useful for organizations that need rapid prototyping or small-batch fabrication. Designing and testing multiple iterations of a lamination shape can be more efficient when manufacturers are not constrained by expensive tooling changes. This flexibility allows engineers to iterate quickly, potentially improving product outcomes in a shorter timeframe. However, as with all manufacturing decisions, the practicality of wire EDM cutting for prototype work will depend on factors like material costs, operator expertise, and the complexity of the motor design. Overall, for complex or experimental shapes, it remains a process worth evaluating.
4. Benefit #3: No Tool Wear and Reduced Maintenance
4.1 Eliminating Physical Contact
One key advantage of wire EDM cutting is that the process does not rely on direct physical contact between a cutting tool and the workpiece. Instead, a continuously fed wire creates controlled electrical discharges to erode material, effectively eliminating traditional wear-and-tear issues. By removing friction from the equation, manufacturers can avoid many of the challenges encountered in conventional machining methods—such as blade dulling or tool breakage. This absence of mechanical force not only preserves the integrity of delicate laminations but can also contribute to more stable and predictable production cycles.
4.2 Cost Savings Over Time
Although wire EDM cutting does involve the routine replacement of the wire electrode, the overall maintenance demands are relatively modest compared to processes that rely on cutting tools or dies. Traditional tooling may require frequent sharpening, refurbishing, or replacement when used for high-volume lamination stack assembly. Over the long term, these recurring costs add up. By contrast, wire EDM cutting generally experiences more consistent performance over extended periods, allowing organizations to reduce downtime and reallocate resources. Nonetheless, it is advisable to consider both initial investment and long-term operational expenses when assessing the financial implications of integrating wire EDM into production lines.
4.3 Consistent Cut Quality Throughout Production
A further benefit of minimal tool wear is the reliable, repeatable nature of the wire EDM cutting process. Tool degradation can result in fluctuating part dimensions, which can be especially problematic in lamination manufacturing where tight tolerances are crucial. Because the cutting action is governed by electrical discharges rather than mechanical friction, cut quality tends to remain relatively steady from the first part produced to the last. This level of consistency may reduce the need for additional inspections or rework, although prudent quality control measures should still be in place. Ultimately, steady performance and reduced maintenance requirements make wire EDM cutting an appealing option for complex lamination applications.

5. Benefit #4: Minimal Material Distortion or Stress
5.1 Low-Heat, Low-Force Cutting
One notable feature of wire EDM cutting is that it relies on electrical discharges rather than mechanical force to remove material. Because the wire never physically grinds or exerts significant pressure on the workpiece, the process inherently generates less frictional heat. While there is some heat produced at the point of spark erosion, it tends to be localized and dissipates quickly through the dielectric fluid. As a result, the overall temperature of the workpiece remains relatively stable, substantially reducing the risk of warping or thermal damage. This is especially important in the context of lamination stack assembly, where even minor deformations can cause fitment issues or compromise motor efficiency.
5.2 Maintaining Metallurgical Integrity
Beyond limiting thermal strain, wire EDM cutting helps preserve the inherent material properties of the lamination steel or other alloys used in motor manufacturing. With traditional machining methods—like milling or stamping—excessive heat or force can alter the crystalline structure of the material, sometimes weakening it or affecting its magnetic characteristics. By minimizing these stressors, wire EDM cutting can contribute to better overall metallurgical integrity. This becomes particularly relevant for high-performance motors, where consistent magnetic properties across each lamination can make a tangible difference in overall power output and reliability. Of course, the extent to which these benefits manifest may depend on factors like material grade, cutting parameters, and post-processing steps.
5.3 Boosting Longevity of Finished Parts
When material distortion is minimized, each lamination tends to remain dimensionally accurate over its service life. This precision leads to more stable stack assemblies and a reduced chance of alignment issues emerging over time. In turn, the motor core can operate more reliably, helping to prolong its operational lifespan. While wire EDM cutting is not a one-size-fits-all solution, these attributes can be especially appealing for applications where extended durability and consistent performance are highly prized. By preserving the integrity of each lamination, manufacturers may ultimately see greater value and longevity in their finished products.
Conclusion
Wire EDM cutting offers compelling advantages for lamination stack assembly, especially when high precision and minimal material stress are prime considerations. By employing controlled electrical discharges instead of conventional mechanical force, this method can achieve consistent tolerances, support intricate geometries, and reduce tool wear—ultimately enhancing both efficiency and part quality.
Despite these notable benefits, wire EDM cutting may not be suitable for every application. High manufacturing costs, slower production speed compared to progressive-die stamping method, and the expertise required for proper setup and maintenance can limit its appeal in certain manufacturing scenarios. Therefore, organizations must weigh their production needs, budget constraints, and quality requirements to decide if wire EDM cutting provides an optimal balance of cost-effectiveness and performance for their specific lamination stack assembly projects.
Further Reading: