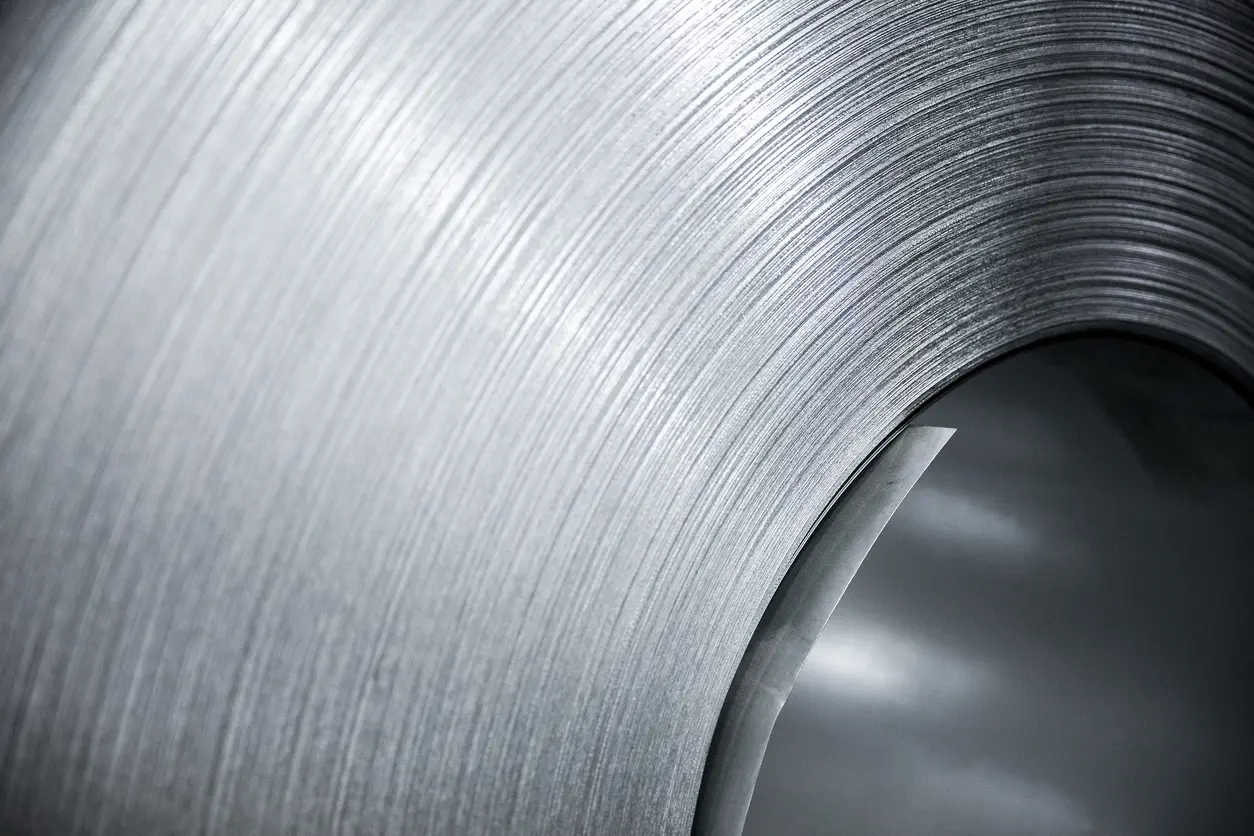
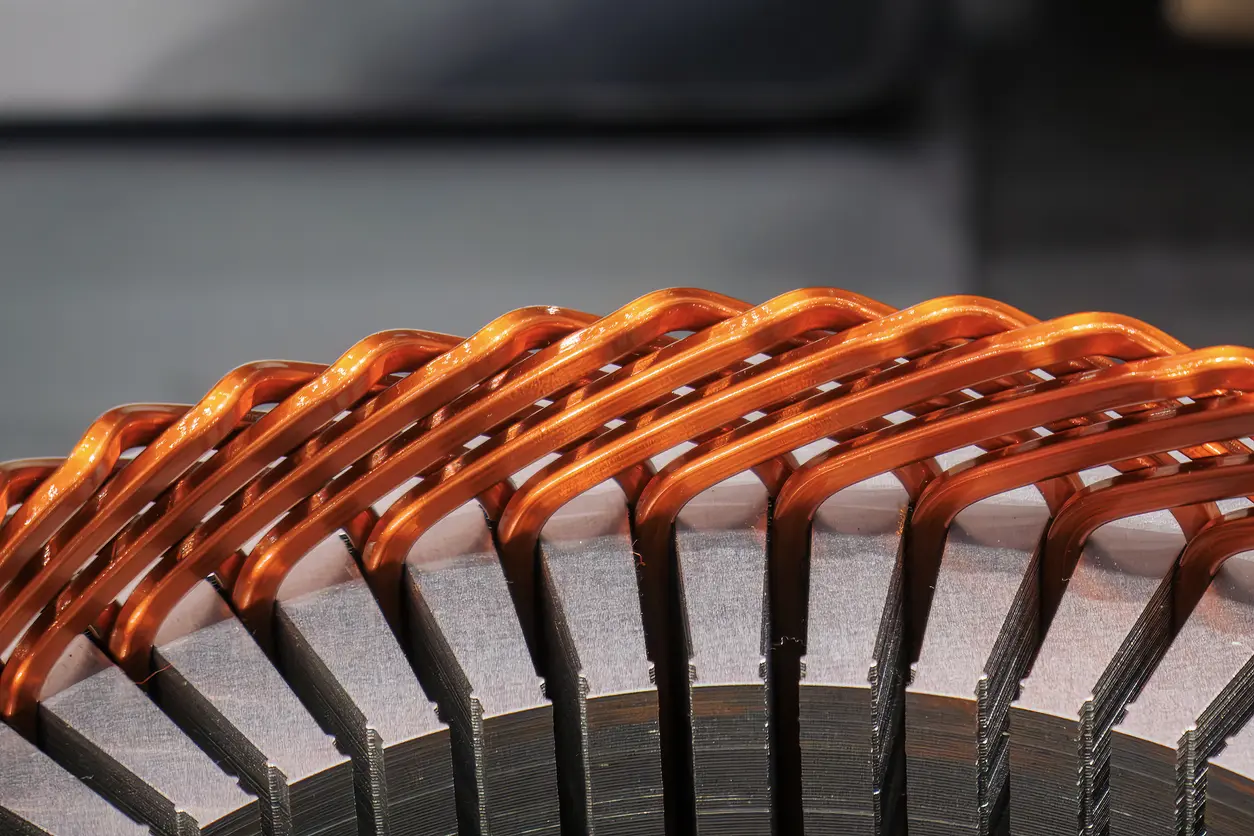
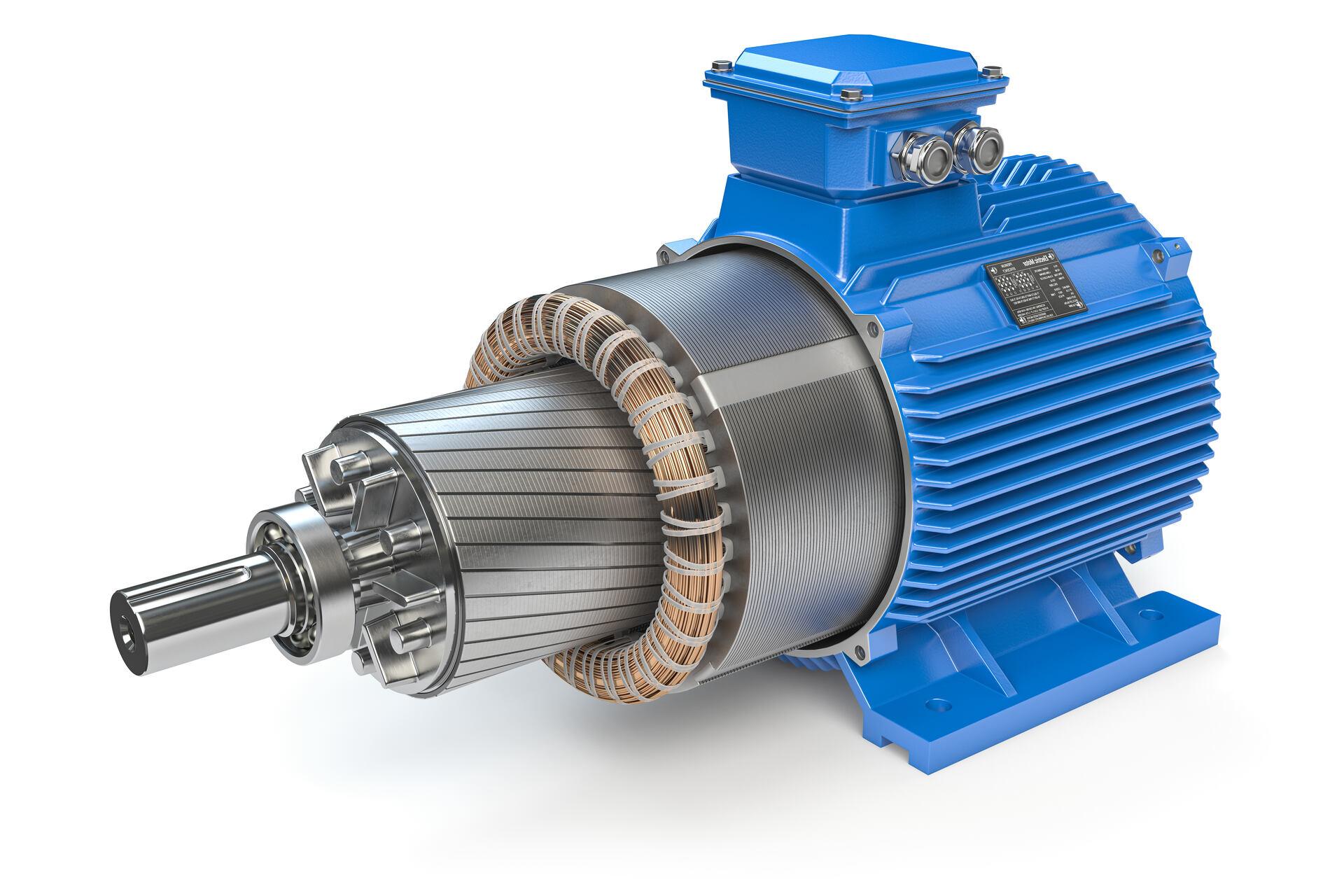
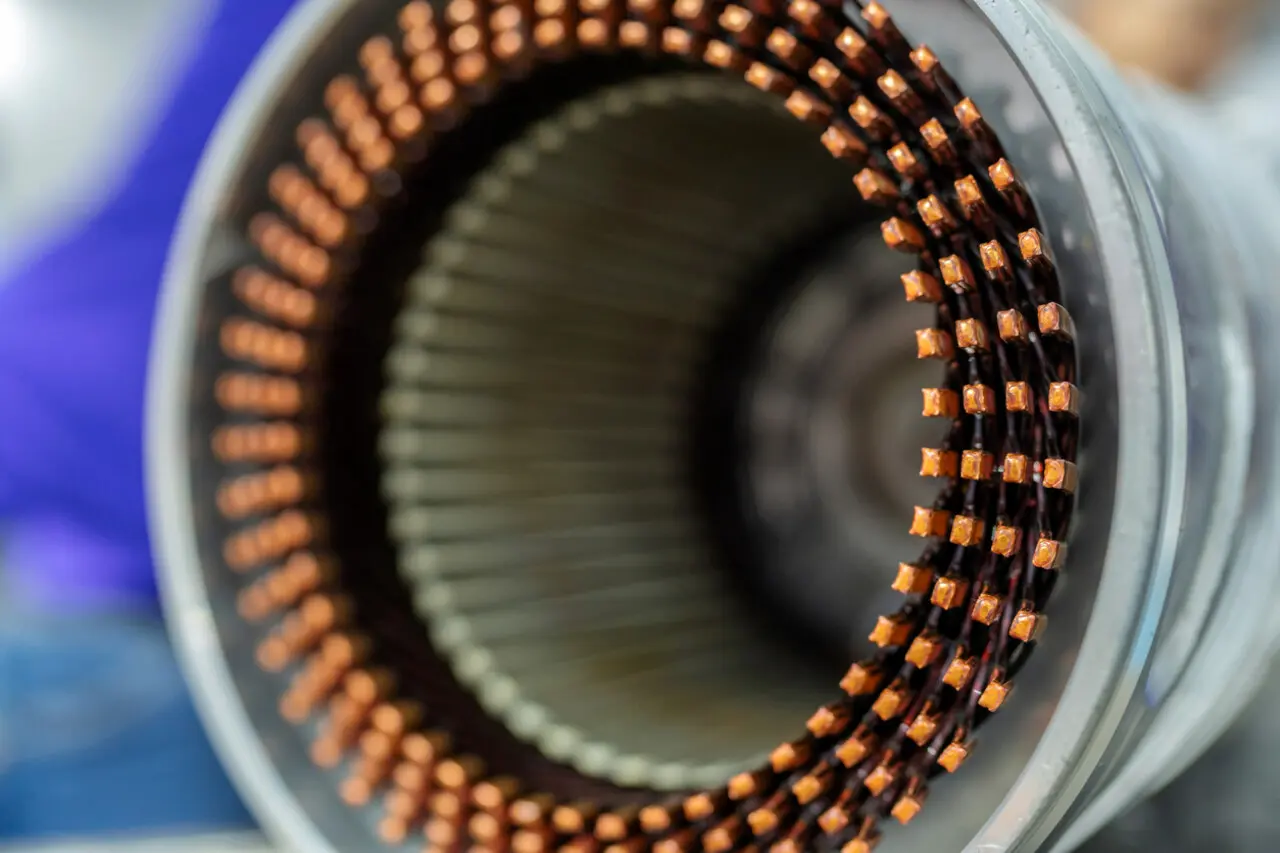
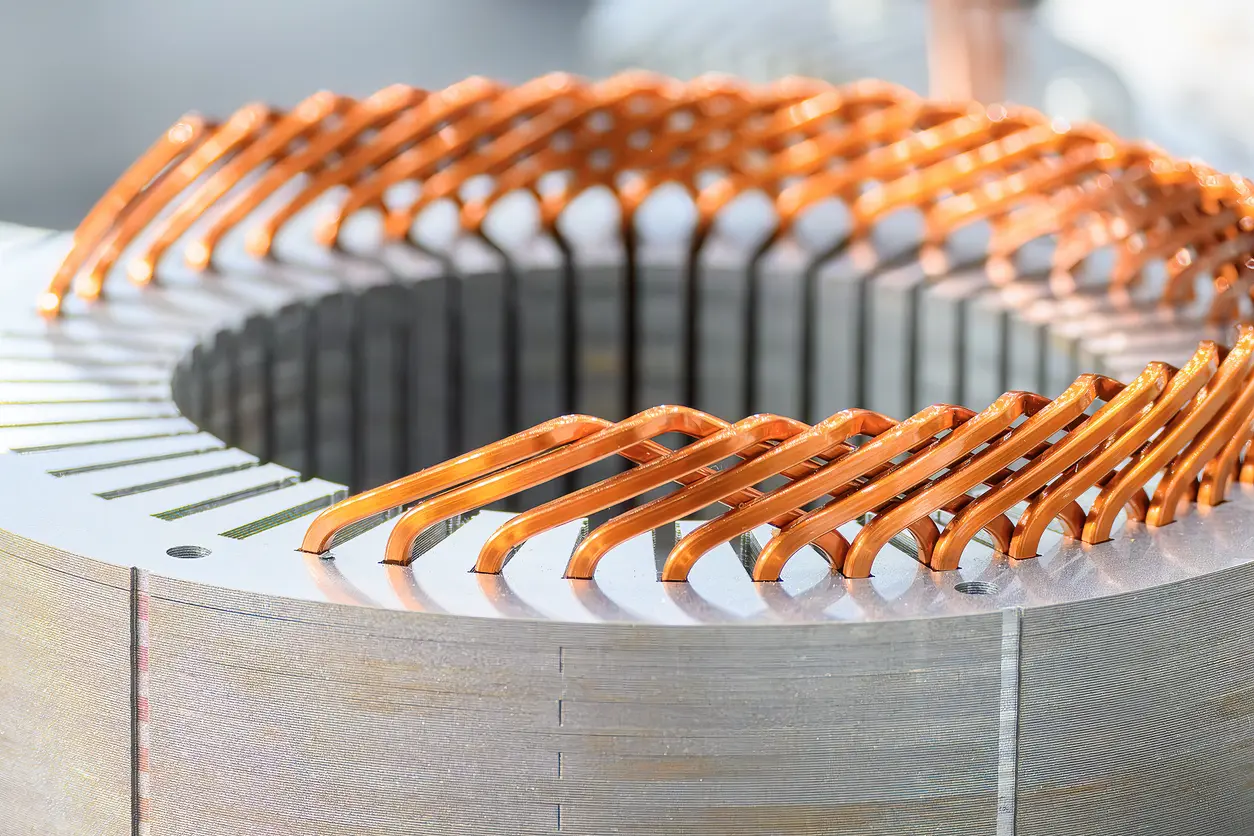
Discover how high-quality motor core materials can significantly improve electric motor efficiency, from controlling eddy current losses to perfecting lamination design. Learn practical strategies for balancing cost, performance, and longevity in an ever-evolving marketplace.
1. Introduction to Motor Core Material
1.1 Basic Concepts and Role
a. What is Motor Core Material
Motor core material refers to the metal or alloy used in the core section of an electric motor, typically assembled after processes such as lamination, coating, and precision cutting. The primary function of this core structure is to establish a stable magnetic circuit that helps the motor operate efficiently. Because different applications vary in their requirements for efficiency, heat resistance, and cost, motor core material has evolved into diverse alloy options such as silicon steel, amorphous alloys, or other low-loss materials.
1.2 Market Demand and Application Scenarios
a. Why the Market Values Motor Core Material
With the rise of green energy and the push for higher efficiency, the scope of electric motor applications has expanded significantly. Household appliances, automobiles, industrial equipment, and even cutting-edge new energy sectors all rely on electric motors for power output. Therefore, the quality of the chosen motor core material directly affects overall performance. When the material’s magnetic permeability and eddy current losses are well-managed, the same input power can yield higher output efficiency. This has led many companies to invest in research and development, aiming to enhance motor core material for improved competitiveness.
1.3 Considerations in Material Selection and Future Development
a. Balancing Cost, Efficiency, and Reliability
When selecting motor core material, factors such as cost and long-term benefits are typically considered simultaneously. Although high-quality materials may involve higher initial costs, they can reduce operational expenses and maintenance requirements over time. In many cases, companies will determine the optimal alloy composition and insulation coatings based on the motor’s operating environment (e.g., high temperature, high-frequency use).
b. Staying Humble and Continuously Innovating
Since technologies and applications are still evolving, future advancements may lead to even newer motor core materials. Although high-quality core materials are generally seen as beneficial for motor efficiency at present, actual usage conditions and professional evaluations are still necessary to find the best fit. In an increasingly competitive market, ongoing research and improvement remain key to steady progress.
2. Fact One: The Critical Impact of Material Purity and Alloy Composition
2.1 Silicon Steel Purity and Eddy Current Loss
When choosing motor core material, the silicon content in the alloy is often seen as a key factor influencing eddy current losses. Generally, increasing silicon content within appropriate limits raises the metal’s electrical resistivity, thereby reducing eddy current loss and improving motor efficiency. However, if the silicon content is too high, the material’s ductility may decrease, making manufacturing more difficult. As a result, manufacturers typically select an appropriate silicon content based on the motor’s specific operational requirements. Additionally, factors like heat treatment and lamination quality also affect eddy current losses, collectively determining the final motor performance and stability.
2.2 Purity and Impurity Control
Apart from silicon, other impurities can also affect the performance of motor core material. For example, if trace elements like aluminum or zinc are not controlled, they can degrade the alloy’s magnetic permeability or accelerate oxidation. Many in the industry believe that higher-purity alloys maintain superior magnetic properties and heat dissipation capabilities during high-frequency operation or extended load periods. However, tolerance for impurities varies by application environment; some specialized motors or high-temperature applications may even incorporate traces of nickel or cobalt to enhance strength. While these techniques show potential, they require more comprehensive testing and may not be universally suitable for mass-produced motors.
In summary, the purity and alloy composition of motor core material have a pivotal influence on motor efficiency. Yet, practical use still demands consideration of multiple factors such as cost, manufacturability, and actual operating conditions. Although many studies suggest that high purity and a well-balanced alloy composition help reduce losses, it is advisable for companies to base decisions on real-world requirements and empirical data, working closely with professional suppliers to ensure that selected materials and manufacturing processes meet an increasingly diverse range of market applications.
3. Fact Two: How Quality Lamination Design and Precision Manufacturing Enhance Efficiency
3.1 Lamination Thickness and Inter-Laminar Insulation

When evaluating the performance of motor core material, lamination thickness and inter-laminar insulation are critical factors affecting efficiency. In general, thinner laminations can effectively reduce eddy current losses, allowing the motor to maintain better thermal management in high-speed or high-frequency conditions. However, overemphasizing extremely thin laminations can increase manufacturing and assembly difficulties and drive up production costs. To strike a balance between performance and economy, many manufacturers choose lamination thickness based on the load characteristics and speed requirements of the application. Equally important is the quality of inter-laminar insulation; if the coating is insufficient or has deteriorated, short circuits or increased losses may occur, affecting overall efficiency and lifespan.
3.2 Manufacturing Precision and Tolerance Control
Beyond the laminations themselves, precise manufacturing and tight tolerance control are vital to the end performance of motor core material. High-precision stamping and cutting processes ensure each lamination has consistent dimensions, minimizing deformation or burrs that could cause pressure drops or localized overheating. Automated assembly technology helps maintain uniform stacking in mass production, reducing the risk of human error. If lamination stacking tolerances are too large, motors may exhibit noise, vibration, or decreased efficiency during operation. Additionally, suitable filling or fastening methods can prevent lamination loosening, ensuring stability at high rotational speeds.
Overall, the combination of quality lamination design and precision manufacturing not only enables motor core material to achieve higher efficiency but also strengthens the durability and thermal management of the entire system. Nevertheless, each company should test and evaluate its chosen production methods based on target applications and remain in close communication with professional suppliers to find a solution that optimally balances cost, quality, and efficiency.
4. Fact Three: Coating and Insulation Technologies Extend Motor Service Life
4.1 Coating Quality and Electrical Protection
a. Differences Between Organic and Inorganic Coatings
Coating technology is often overlooked but plays a crucial role in extending a motor’s service life. For motor core material, the surface protection not only guards against external environmental corrosion but also effectively reduces inter-laminar short circuits and iron losses. Common coating methods fall into two main categories: organic and inorganic coatings. Organic coatings generally offer better flexibility and higher tolerance against impact or vibration but may degrade or peel off in high-temperature environments. Inorganic coatings, on the other hand, provide greater heat and flame resistance but are relatively more complex and costly to apply. Because application scenarios and budgets vary, careful consideration is required to fully leverage the protective benefits of coating technology.
b. Preventing Corrosion and Wear
In prolonged or heavily loaded operating conditions, preventing corrosion and wear is essential for maintaining the performance of motor core material. If a coating develops cracks or peels off in localized areas, this can lead to electrical short circuits or additional losses between laminations, shortening the motor’s lifespan. Regular inspection and maintenance of the coating can preserve efficiency and avoid the high costs of repairs or downtime.
4.2 Insulation Materials and Service Life
a. Heat Resistance and Insulation Class
Apart from the coating, choosing the right insulation components inside the motor also affects overall stability. If the motor core material is paired with an appropriate insulation class and heat-resistant materials, it can maintain solid electromagnetic performance and structural integrity under high temperature or high-frequency conditions. In some scenarios where motors run close to their load limits or in harsh environments for extended periods, ensuring the insulation does not degrade prematurely is essential.
b. Staying Cautious and Continually Improving
Although advanced coating and insulation technologies can significantly prolong a motor’s service life, they still need to be balanced against factors like load analysis and production costs. The industry continues to develop new coatings and insulation materials to handle increasingly complex operating environments. In all cases, evaluating actual needs and collaborating with professional teams can help motor core material deliver its true value over the long term while minimizing risks.
5. Fact Four: Cooling and Mechanical Strength Affect Motor Operational Stability
5.1 Cooling Structure Design
For any electric motor system, cooling design often determines both stability and longevity. When motor core material has excellent thermal conductivity, it can help rapidly dissipate heat in high-speed or long-duty operations, preventing excessive heat buildup in the core. Common cooling methods include providing ventilation channels within the lamination stack, adding cooling fans, or using more advanced techniques like water cooling or oil cooling. It is crucial, however, to maintain a tightly integrated design; overemphasis on cooling at the expense of structural rigidity may introduce unnecessary vibration or energy losses. For companies aiming for efficient and stable motor performance, choosing motor core material with good cooling characteristics and integrating an effective cooling mechanism can greatly boost motor capabilities and reduce the likelihood of breakdowns.
5.2 Mechanical Strength and Vibration Control
Beyond cooling, mechanical strength also affects motor smoothness at high operating speeds. When motors run continuously under high speed or heavy load, if the laminations in the motor core material are not firmly secured or if the material cannot withstand prolonged vibration, structural loosening may occur. This can lead to extra noise and efficiency losses, and in some cases, damage coatings or insulation layers. To avoid such issues, manufacturers should strictly control stacking tolerances and adopt fastening techniques appropriate for the application environment—such as riveting, welding, or high-strength resin bonding. Additionally, regular maintenance checks and dynamic balance tests can help identify potential problems early on and prevent a chain reaction caused by vibrations.
In the overall design assessment, cooling and mechanical strength are not isolated factors but must be considered in tandem. By selecting motor core material suited to the operating conditions right from the design stage, and then applying proper manufacturing processes and structural optimization, a motor can maintain stable efficiency and reliability over a long service life, while also providing a solid foundation for future maintenance and upgrades.
6. Fact Five: Future Trends and Material Selection Strategies

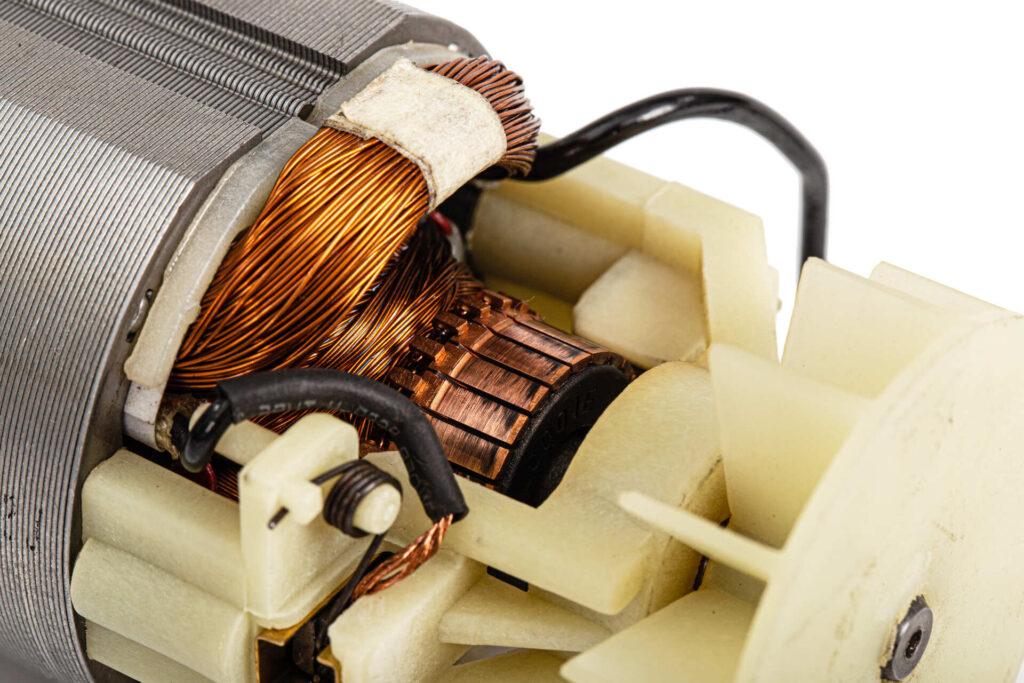
6.1 Emerging Materials and Technologies
Driven by electric vehicles, smart factories, and other high-end applications, the development of motor core material is facing new challenges and opportunities. Another notable trend involves leveraging smart manufacturing through big data and artificial intelligence to enhance production-line automation and precision, thus improving the compatibility between material selection and manufacturing processes. Such digitalized management can track quality changes in real time and improve the overall utilization of motor core material.
6.2 How to Choose the Most Suitable Material
Amid these rapidly evolving trends, companies should remain relatively cautious when selecting motor core material. First, it is advisable to begin by analyzing the actual usage scenario—identifying the motor’s operating environment and load characteristics, such as temperature, rotational speed, and service life requirements. For high-temperature or high-frequency applications, advanced alloys or special coatings may be necessary to ensure adequate magnetic properties and heat management. Meanwhile, for general industrial or household motors, balancing cost and efficiency with mature silicon steel or mid-level alloys may be a good starting point. Additionally, working with suppliers that have proven technical expertise and certifications helps prevent oversight in evaluation. Using scientific data and real-world tests to validate the reliability of the chosen motor core material ensures that businesses can stay competitive and mitigate investment risks in a dynamic market environment.
7. Conclusion and Actionable Recommendations
7.1 Overall Review
From the discussions in the previous sections, it is clear that motor core material plays a pivotal role in electric motor systems. Every aspect—from the purity and alloy composition of the material to lamination design, coating and insulation, and cooling and mechanical strength—ties directly to efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Although the requirements for material performance and manufacturing technology vary across different applications and production scales, one thing is certain: the higher the demand for motor efficiency and longevity, the more crucial high-quality motor core materials become.
7.2 Evaluation and Strategy Recommendations
When assessing which motor core material is best for a given project or product, focusing on “overall benefits” rather than merely the material’s unit price is recommended. If a motor is required to run for extended periods under high temperatures, high rotational speeds, or high-frequency conditions—or if the market places strict demands on efficiency and stability—choosing premium-grade alloys and advanced insulation techniques can lead to substantial long-term cost savings. Additionally, collaborating with suppliers who possess strong technical and testing capabilities, and conducting prototype testing or small-scale pilot production, can help companies detect issues early in product development and refine their solutions.
7.3 Future Outlook
Since energy conservation and environmental protection have become global imperatives, there remains considerable potential for further development and application of motor core material. Advancements in ultra-low-loss materials, new alloys, and smart manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, offering the possibility of further enhancing motor performance. For businesses, appropriately tracking new technologies and staying attuned to market trends can help maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly demanding industry. Of course, any move toward product upgrades or process improvements should be based on careful evaluation and prudent investment, ensuring resources are used effectively and continuing to provide users with reliable, high-performance motor solutions.
External resources: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344664111_Joining_of_the_Laminated_Electrical_Steels_in_Motor_Manufacturing_A_Review
Internal links: 9 Surprising Highlights: How Electrical Steel Is Transforming the Green Energy Industry