1. Introduction to Brushless Motors
1.1 The Evolution of Brushless Motors
In the early stages of electric motor development, brushed motors dominated due to their straightforward design and ease of manufacturing. However, these motors relied on physical brushes that made contact with a commutator to transfer current, leading to friction, wear, and frequent maintenance. Over time, engineers sought a more efficient alternative that would reduce these mechanical limitations.
This drive for innovation led to the emergence of the brushless motor. By removing the brushes and employing electronic commutation instead, these motors avoid sparking issues and significantly cut down on maintenance. Early adopters found that brushless motors offered better power output relative to their size and generated less heat during operation. Although the initial costs and control complexities were higher, advancements in materials and electronics have steadily reduced these barriers, making brushless motors a common choice in modern applications.
1.2 Why “Brushless Motor” Matters in Today’s World
Today’s industries prioritize efficiency, reliability, and compact design across diverse sectors—ranging from household appliances to cutting-edge robotics. A brushless motor addresses these needs by offering an elevated power-to-weight ratio and reducing the long-term costs associated with replacement parts. In consumer electronics, for instance, brushless motors drive cooling fans that operate quieter and last longer than their brushed counterparts, which is beneficial in gaming consoles or laptops where reliability and low noise levels are essential.
Beyond consumer products, brushless motors also play a critical role in electric vehicles, drones, and industrial automation systems. Their enhanced efficiency contributes to extended battery life in portable devices, while their robust construction allows them to withstand demanding operational schedules in manufacturing lines. Moreover, the internal components—particularly the motor core and lamination—are central to achieving these performance gains. By minimizing eddy current losses and ensuring precise magnetic flux, engineers can further optimize the overall output of a brushless motor, making it an integral part of modern mechanical and electrical solutions.
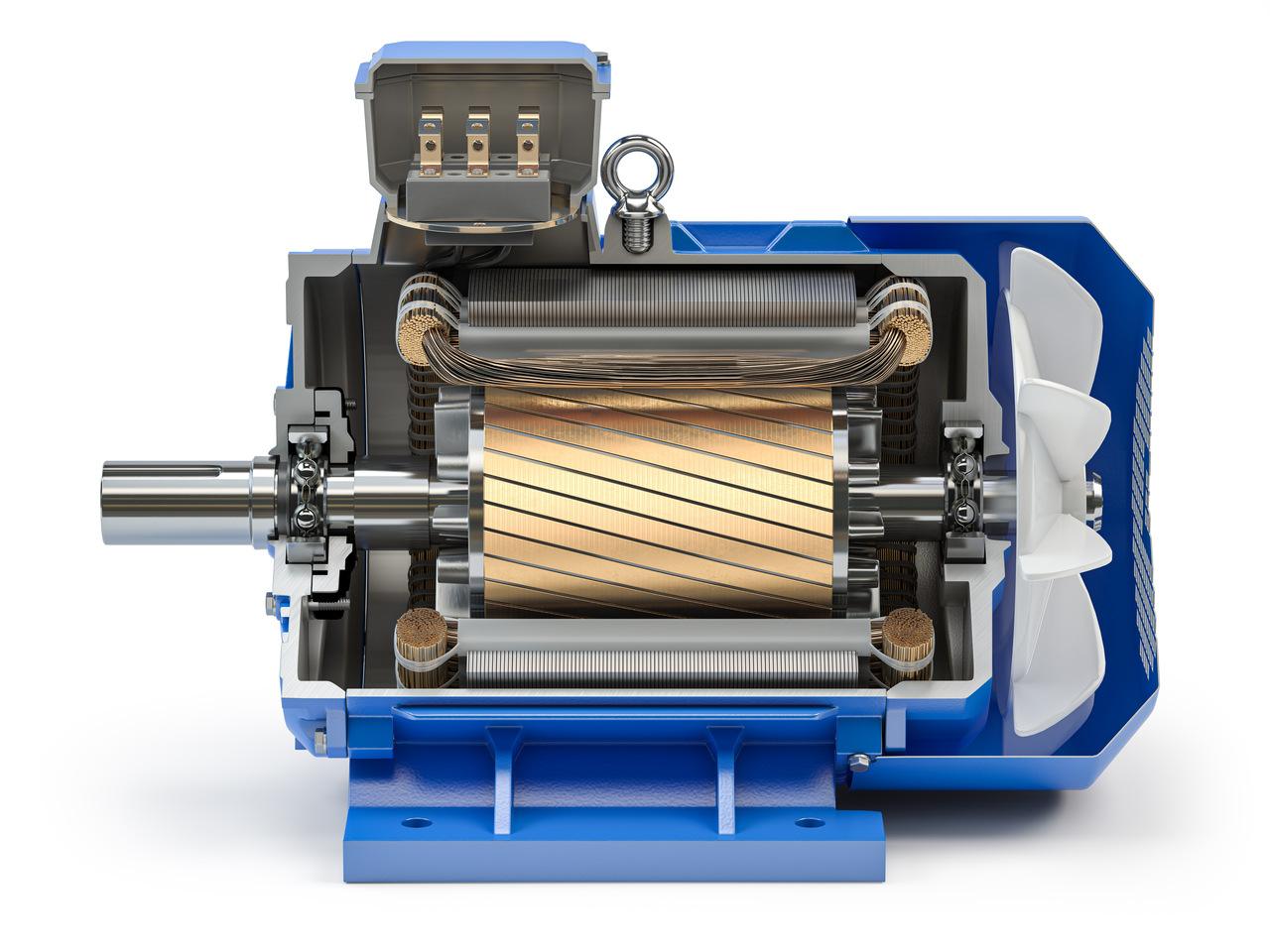
2. Key Components of a Brushless Motor
2.1 The Role of Motor Cores and Laminations
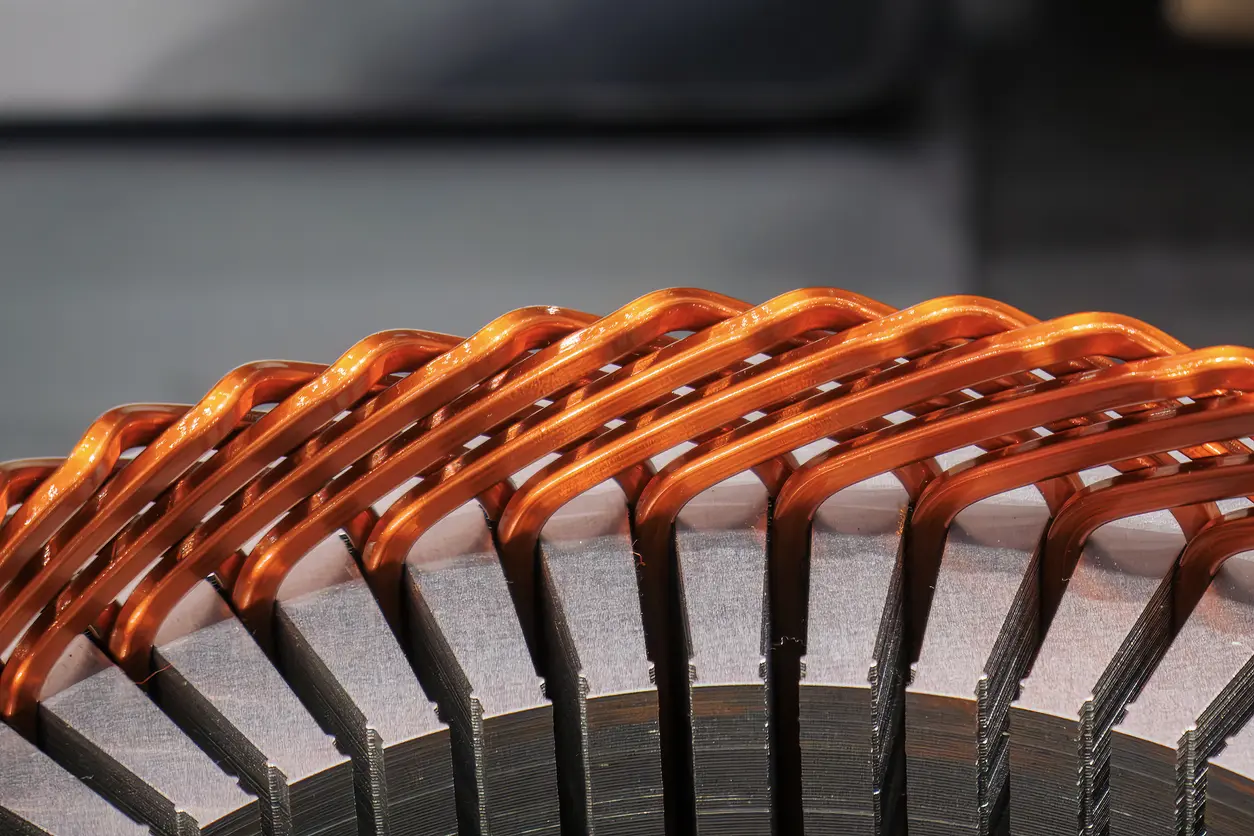
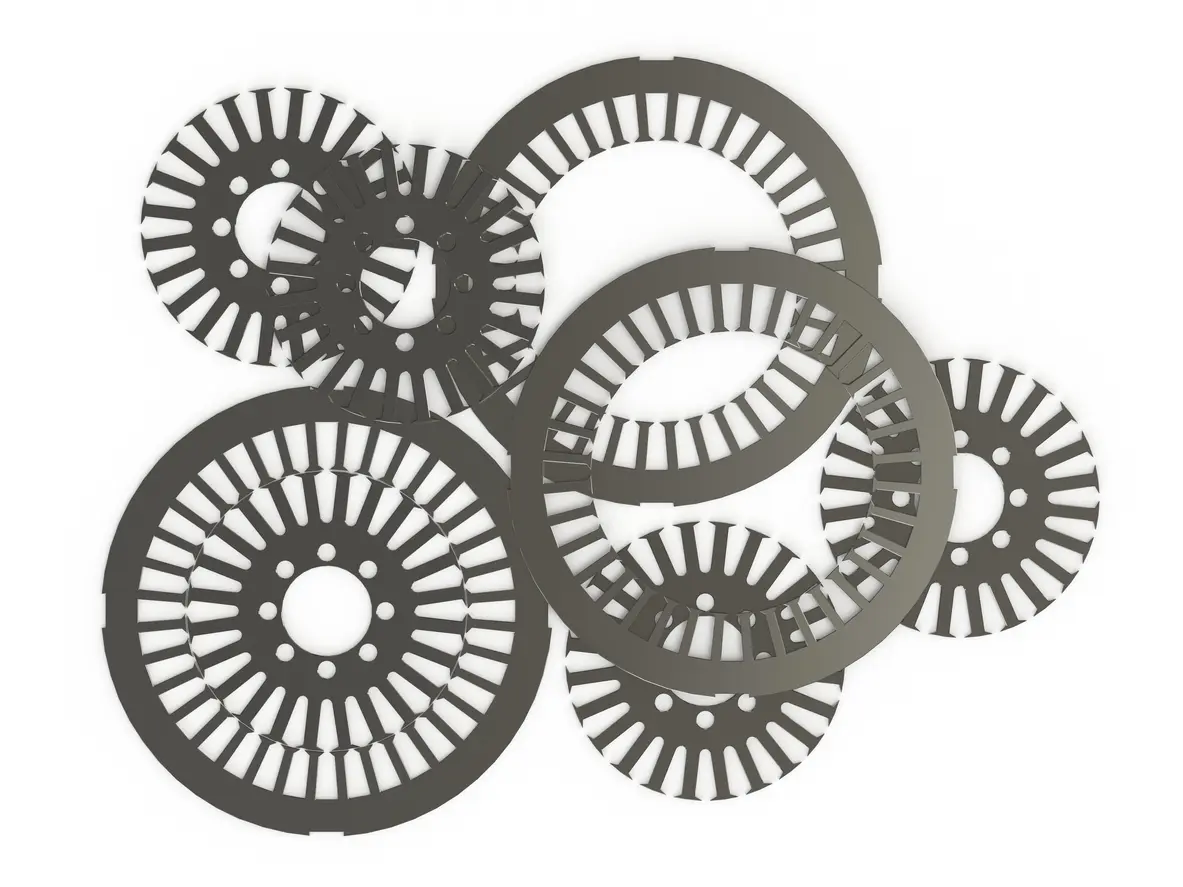
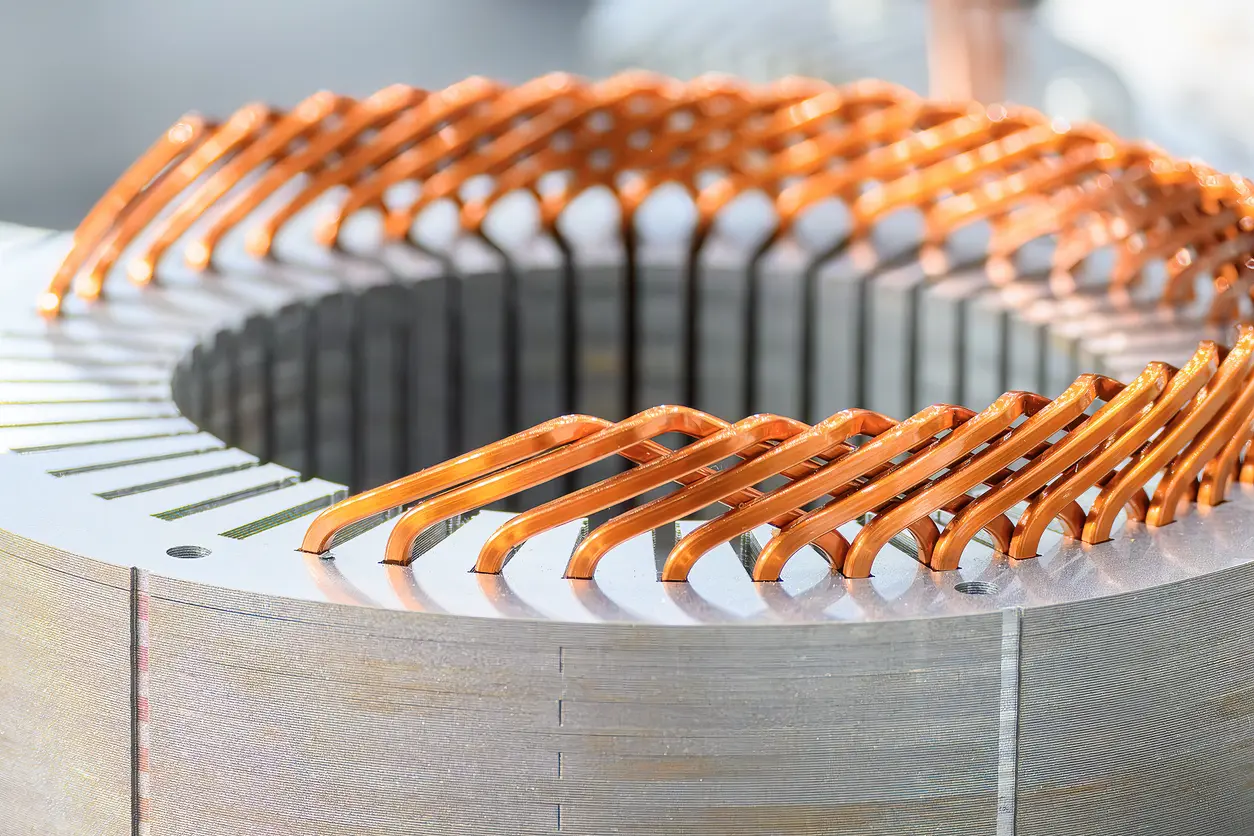
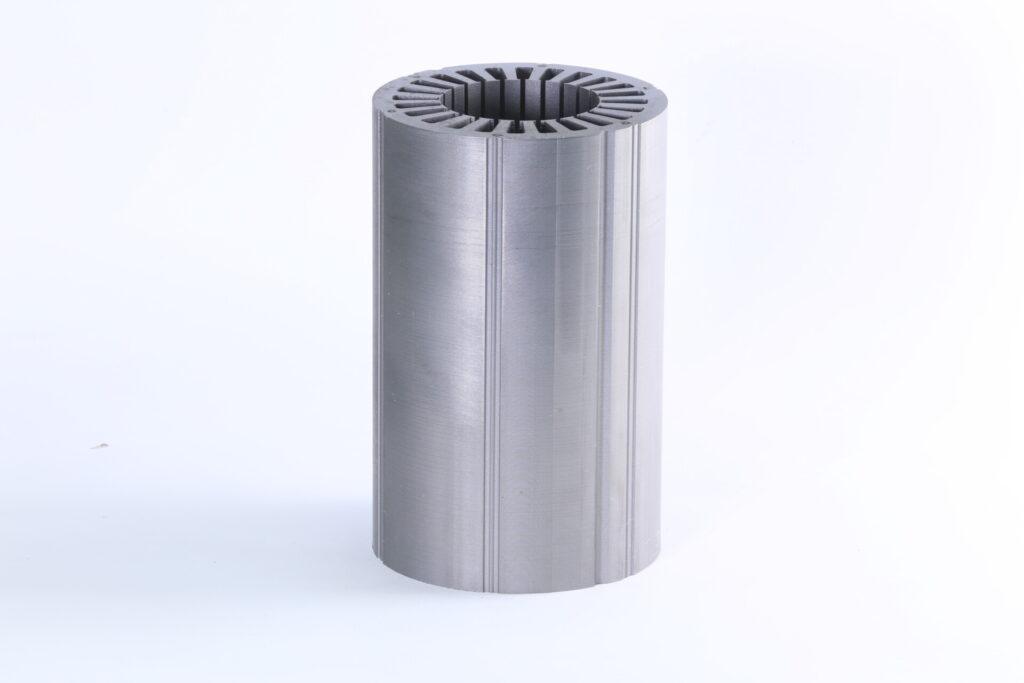
A brushless motor derives much of its efficiency and power from the precision of its internal components—particularly the motor core and its laminations. In essence, the motor core is composed of stacked thin sheets of electrical steel (often referred to as laminations). These thin sheets help minimize eddy current losses by creating barriers that limit circulating currents within the steel. Such control of eddy currents can have a marked impact on overall performance and heat generation.
Quality lamination materials, like high-grade silicon steel, usually undergo specialized processes such as punching or wire electrical discharge machining (EDM) to achieve accurate shapes and tight tolerances. In more advanced production scenarios, progressive die stamping ensures mass consistency for large-scale needs. Manufacturers often emphasize the thickness and coating of each lamination, as subtle variations in these parameters could influence the motor’s magnetic properties. The result is a brushless motor core that can operate at high efficiency under various loads without overheating—a desirable outcome for demanding applications like industrial robotics or electric vehicles.
2.2 Understanding Stators and Rotors
A brushless motor typically consists of two main sections: the stator (stationary part) and the rotor (rotating part). The stator houses wound coils and the laminated steel stack that generates the electromagnetic fields. When electric current flows through these coils, the carefully arranged laminations concentrate magnetic flux paths, allowing the motor to produce torque more effectively. Real-life examples include drone motors, where highly efficient stators enable lighter designs with extended flight times.
The rotor, on the other hand, includes permanent magnets in many brushless motor configurations. These magnets interact with the stator’s rotating magnetic field, causing the rotor to spin. The magnet material and arrangement are critical factors for performance, as stronger magnets can boost torque but may require more precise balancing. Together, the stator and rotor form a coordinated system that, when properly designed and manufactured, delivers the reliable performance for which brushless motors are known.

3. Seven Amazing Benefits of a Brushless Motor
3.1 High Efficiency
A brushless motor is often cited for its ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical output with minimal losses. This high efficiency stems from the absence of brushes, which in brushed motors typically create friction and energy dissipation. In practical terms, industries that rely on continuous operation—like automated conveyor systems—benefit from reduced power consumption. Additionally, the precise magnetic core design in a brushless motor lowers eddy current losses, making these motors well-suited for energy-sensitive applications such as electric drones or battery-powered tools.
3.2 Low Maintenance and Longer Lifespan
By eliminating physical brushes and commutators, the brushless motor significantly cuts down on wear-and-tear components. Traditional brushes erode over time, requiring regular inspection and replacement. In contrast, a brushless design avoids this direct contact, reducing potential points of failure. Industries that demand uninterrupted operation—like medical device manufacturers—find this reliability invaluable. Maintenance costs often decrease, and operational downtime is minimized, leading to a longer useful life for each motor.
3.3 Greater Power Density
Power density refers to how much torque or power a motor can deliver relative to its size. In a brushless motor, carefully engineered rotor magnets and stator laminations contribute to a compact yet potent design. This becomes especially advantageous in portable equipment, such as handheld power tools, where maximizing output while minimizing bulk is crucial. The superior torque characteristics also support heavier loads in smaller form factors.
3.4 Superior Speed Control and Performance
A brushless motor relies on electronic controllers instead of mechanical commutation, giving engineers the flexibility to fine-tune speed and torque with greater precision. This level of control proves valuable in robotic arms, where delicate movements are needed, or in drone flight systems, which depend on rapid and accurate throttle adjustments. Electronic commutation also aids in optimizing performance under variable load conditions.
3.5 Reduced Heat Generation
Because there is no friction from brushes and fewer energy losses in the stator core, a brushless motor generally runs cooler than a comparable brushed motor. Lower operating temperatures can extend a motor’s lifespan and help maintain performance consistency. Heat management is particularly important in continuous-use scenarios such as industrial assembly lines, where even small temperature reductions can enhance overall system stability.
3.6 Less Noise and Vibration
Without the mechanical contact of brushes, a brushless motor typically produces less acoustic noise and vibration. This benefit is clearly noticeable in environments like office printers or medical devices, where noise reduction is paramount. Additionally, the well-balanced rotor and precisely aligned stator contribute to smoother operation, which can improve user experience and reduce structural fatigue in the surrounding machinery.
3.7 Reliability Under Challenging Conditions
Many industrial processes involve demanding conditions—high temperatures, frequent start-stop cycles, or continuous high-speed rotation. The design and material choices of a brushless motor lend it an advantage in such environments, allowing stable and consistent performance. In manufacturing plants where motors may run 24/7, the robust nature of brushless technology and the use of high-grade core laminations help maintain reliability over the long term.
Further Reading:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/brushless-dc-motor