Discover how to enhance efficiency and performance in BLDC motor cores with advanced strategies like superior material selection, precise stamping, progressive die design, and innovative lamination coatings.
1. Introduction: The Growing Importance of BLDC Motor Cores
1.1. Understanding the Basics of BLDC Motor Core
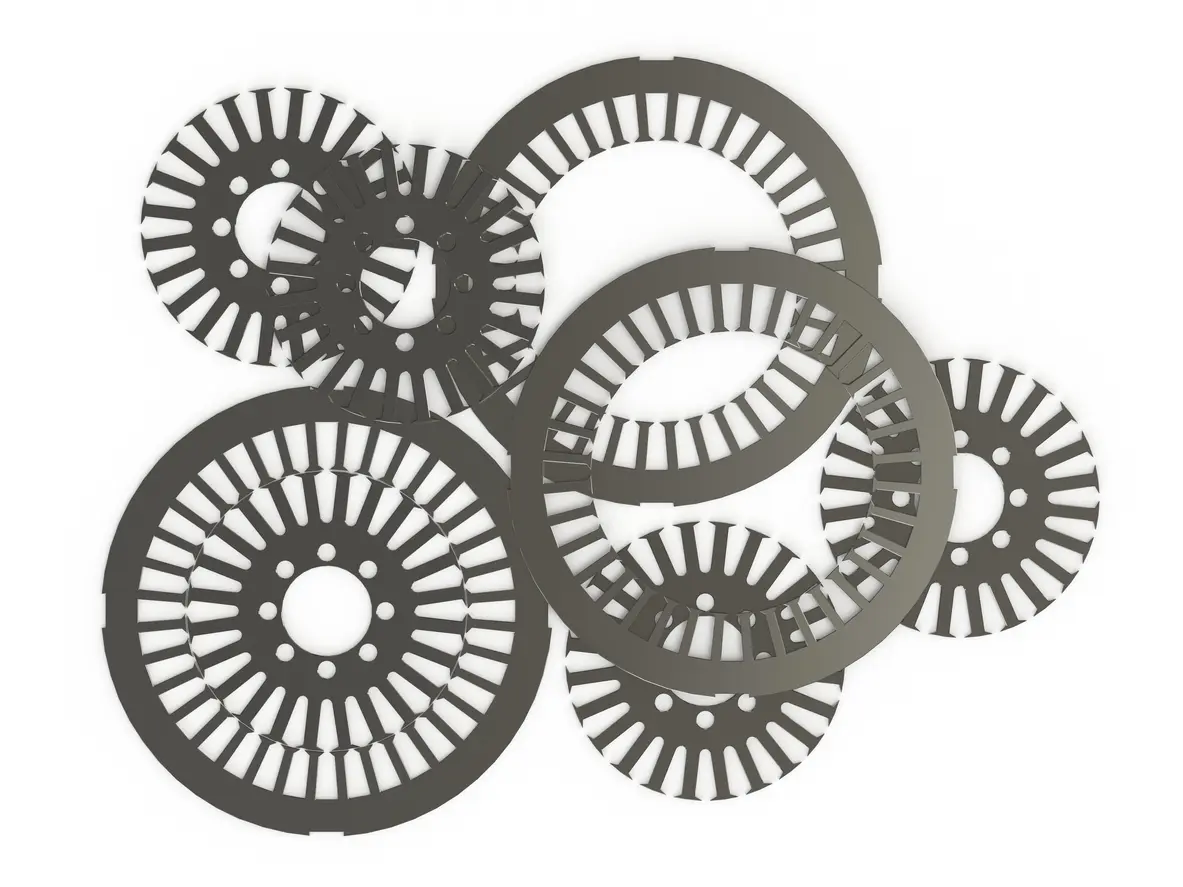
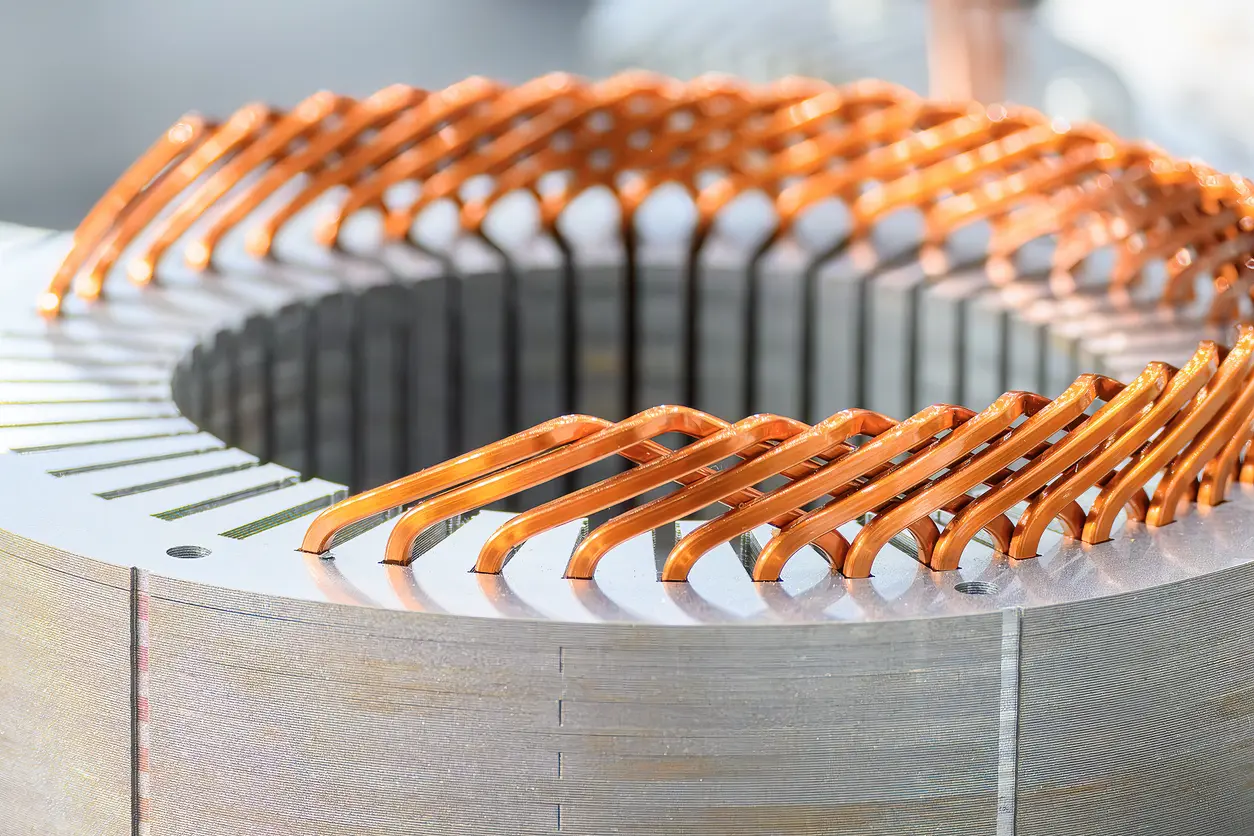
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors have become a significant force across various industries because they eliminate the mechanical limitations seen in traditional DC motors. The BLDC Motor Core—composed of stacked electrical steel laminations—plays a crucial role in translating electrical energy into mechanical output. By reducing friction and wear, these motors often achieve better reliability and durability over time.
In many applications, such as electric vehicles and home appliances, the BLDC Motor Core directly influences efficiency and power density. Each lamination layer is carefully designed to minimize magnetic losses, helping the motor maintain consistent torque output. When the core is manufactured with precise tolerances, these laminations form an optimized magnetic circuit that underpins reliable performance and extended operational life.
1.2. Why Efficiency Matters in BLDC Motor Core Lamination
High efficiency in a BLDC Motor Core hinges on selecting superior-grade materials, such as low-loss electrical steel, and employing precise manufacturing methods. These approaches collectively reduce heat generation and maximize energy transfer, which can lower operational costs and prolong the motor’s lifespan. Although efficiency targets vary among applications, even minor improvements often lead to measurable gains in overall system performance.
Attention to lamination quality also helps address thermal concerns, ensuring the motor can operate under demanding conditions without unnecessary degradation. In many sectors, including automation and e-mobility, businesses value motors that deliver consistent output while minimizing both power consumption and maintenance expenses. Advancements in core design, coupled with emerging fabrication techniques, are therefore central to achieving these goals.
Ultimately, recognizing the importance of efficient lamination practices in a BLDC Motor Core is essential for meeting both performance and sustainability requirements. With careful material selection and proven manufacturing processes, engineers can create robust, energy-saving motors that fit the evolving demands of modern technology.
2. Strategy #1: Superior Material Selection for Maximum Magnetic Performance
2.1. Choosing the Right Silicon Steel and Electrical Steels
Selecting premium-grade silicon steel or other specialized electrical steels is a critical first step toward optimizing any BLDC Motor Core. These materials often possess low core loss characteristics, enabling the motor to operate with greater efficiency under various load conditions. High-grade steel also minimizes hysteresis losses, ensuring stable performance and reducing heat buildup.
In many cases, non-oriented electrical steels (like CRNGO) offer a balanced combination of magnetic permeability and mechanical strength. Grain-oriented steels (CRGO) can also be considered for specific designs such as the transformer core usage that benefit from enhanced directional magnetic properties. However, the exact choice depends on the motor’s operational requirements, such as torque output, speed range, and ambient temperature. A thorough assessment of material thickness, coating quality, and insulation layer is recommended before finalizing the specification.
2.2. Balancing Cost and Quality
While high-end materials can significantly improve a BLDC Motor Core, their premium pricing warrants careful evaluation of long-term benefits. Investing in better materials may result in higher initial costs, but it can also deliver superior energy efficiency, lower operating temperatures, and an extended motor lifespan. In some high-performance applications, these advantages often offset the upfront expenditure.
Nonetheless, a pragmatic approach is advisable. Different market segments may require distinct performance targets, and not all applications demand the highest-grade steel. Balancing cost and quality typically involves working closely with suppliers to identify the most suitable grade based on established performance metrics. Rigorous testing—such as core loss measurements at various frequencies—can further validate the choice of material.
Ultimately, the right balance of cost, quality, and availability contributes to a well-designed BLDC Motor Core. By carefully selecting and evaluating materials, manufacturers can ensure reliable magnetics, reduced energy waste, and a consistent performance profile that aligns with both technical specifications and budget considerations.
3. Strategy #2: Advanced Stamping and Punching Techniques
3.1. Precision Stamping to Reduce Lamination Defects
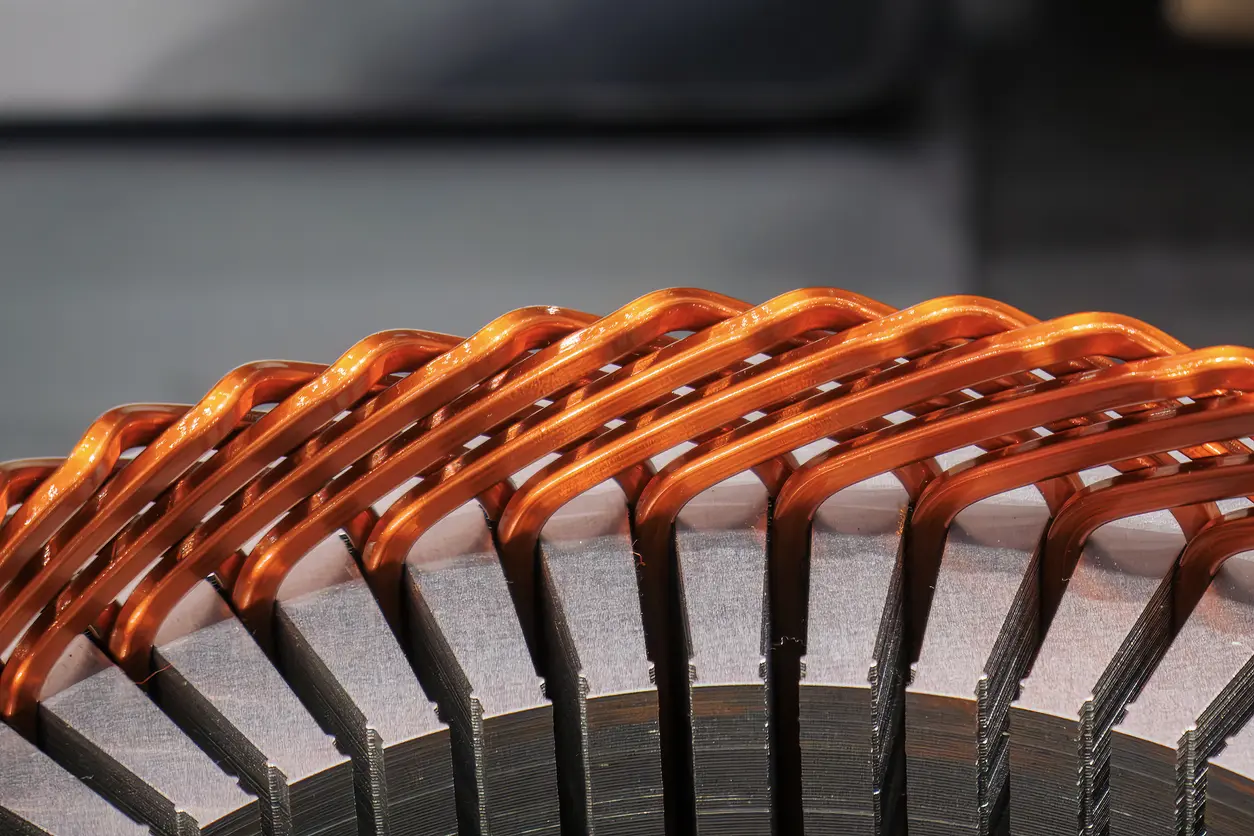
A high-quality BLDC Motor Core starts with precise stamping methods that produce uniform lamination shapes. Progressive die designs, for instance, can help maintain consistent tolerances while minimizing burrs and other defects. Keeping these imperfections in check is critical, as they can increase the likelihood of short circuits between laminations, contributing to higher core losses.
Effective stamping also relies on proper tooling maintenance. Dull or misaligned tooling sets can deform delicate lamination edges, impacting both stack height and overall magnetic integrity. Regular inspections, coupled with quality materials for the dies, reduce the risk of defective parts entering the assembly process. In applications demanding consistent motor performance and extended service life, a well-managed stamping setup can be a decisive factor in achieving optimal results.
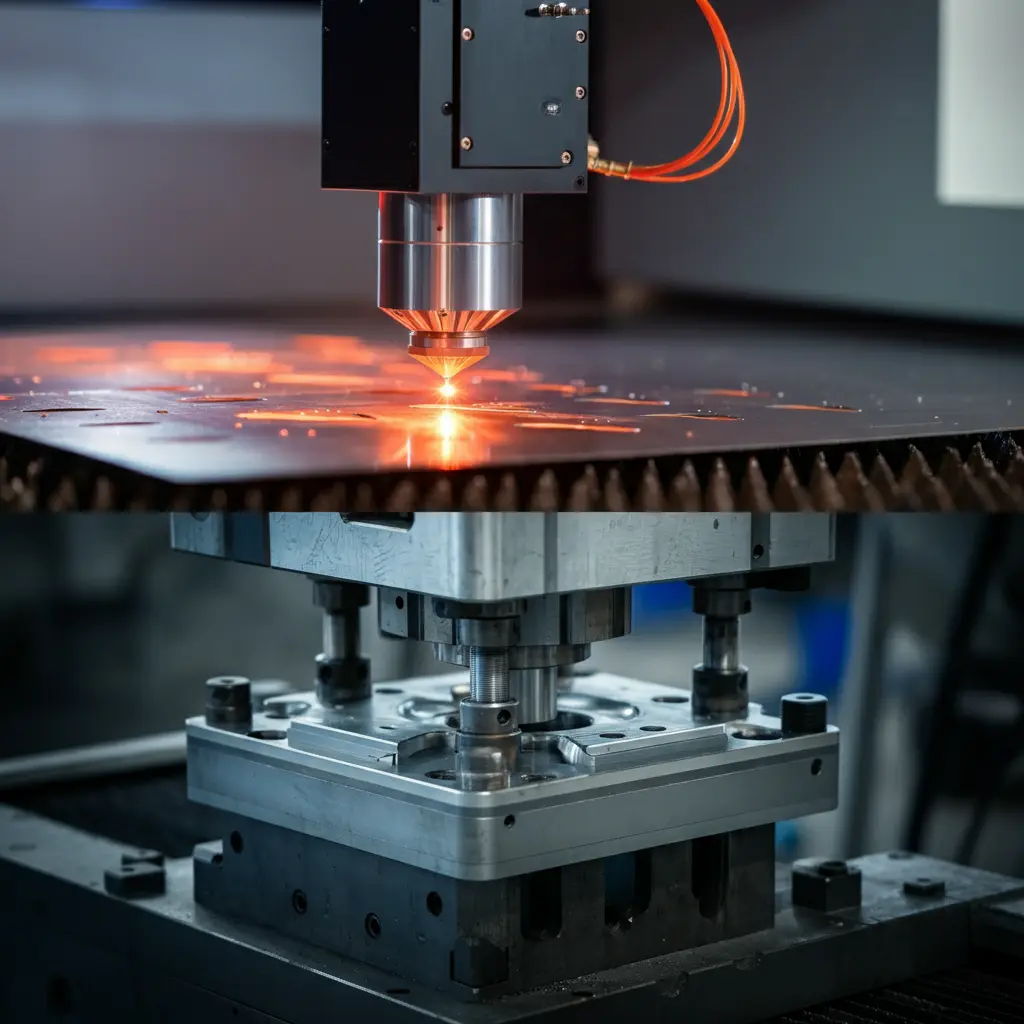
3.2. Laser Cutting vs. Traditional Punching
When producing laminations for a BLDC Motor Core, manufacturers often evaluate both laser cutting and traditional punching to find the best combination of accuracy, throughput, and cost. Traditional punching remains a popular choice for high-volume production because it offers speed and repeatable accuracy when dies are properly maintained. However, setup costs and potential tooling replacements should be considered in long-term budgeting.
Laser cutting, by contrast, excels in applications that require complex geometries or prototypes with fewer parts. Its non-contact nature can reduce mechanical stress on the lamination edges, potentially preserving the steel’s magnetic properties. Yet, this method usually operates at a slower rate compared to punching, which can affect production targets. Balancing these factors—part complexity, batch size, and total cost—ensures that manufacturers select the most suitable cutting technique. Through thoughtful planning and careful process control, advanced stamping and punching methods enhance the quality and efficiency of every BLDC Motor Core they produce.
4. Strategy #3: Progressive Die Design and Tooling Optimization
4.1. Streamlining the Manufacturing Process
Progressive die design is a sophisticated approach that allows manufacturers to handle multiple stamping operations in one continuous process. By integrating functions such as blanking, piercing, and forming within a single die setup, production lines can achieve faster throughput and more consistent results. When producing a BLDC Motor Core, maintaining tight tolerances is essential to preserve magnetic properties and reduce any unwanted gaps between laminations. Properly engineered progressive dies enable each station to perform specific tasks with minimal deviation, decreasing the likelihood of defects.
Additionally, investing in robust tooling materials can prolong tool life and minimize unexpected downtime. Selecting high-quality steel, along with advanced coatings that reduce friction and wear, helps ensure sustained accuracy. The resulting stability contributes to a more uniform lamination stack, ultimately leading to lower core losses in the finished BLDC Motor Core. Furthermore, streamlined processes often yield predictable lead times, which can prove critical when meeting urgent or high-volume orders.

4.2. Minimizing Material Waste and Handling
Optimized tooling design not only accelerates production but also helps lower overall costs by reducing material waste. For instance, careful layout planning—commonly referred to as nesting—allows each lamination to be cut in a way that makes the most efficient use of raw steel sheets. Minimizing scrap is particularly valuable when dealing with higher-grade electrical steels that command a premium price.
Effective handling techniques also play a key role in preserving the integrity of each BLDC Motor Core. Automated transfer systems can prevent scratches, dents, or other damage that might compromise the lamination’s electrical insulation. By controlling the movement and orientation of parts throughout the stamping process, manufacturers reduce the likelihood of burr formation and dimensional inaccuracies. Overall, thoughtful tooling optimization and progressive die design create an environment in which high-volume production of BLDC Motor Cores is both cost-effective and quality-focused.
5. Strategy #4: Innovative Lamination Coatings and Insulation
5.1. Reducing Eddy Current Losses Through Coatings
When it comes to a BLDC Motor Core, every effort to reduce heat and power loss can make a measurable difference in overall efficiency. One such method involves applying specialized coatings to the lamination layers, which serve as barriers preventing excessive eddy currents. These currents, if unchecked, create additional heat and waste energy, potentially reducing the motor’s performance and lifespan. Common coatings include inorganic oxide layers and epoxy-based formulations. Each option offers unique advantages, such as improved electrical insulation, higher thermal resistance, or better adhesion to the steel substrate.
Additionally, adopting a robust coating process that ensures consistent application thickness can help maintain minimal gap spacing between laminations. This approach keeps the magnetic circuit as efficient as possible without introducing unwanted variations. Manufacturers often test different coating chemistries and thicknesses to ensure they are compatible with specific operating temperatures and speed ranges. By using coatings tailored to the demands of each application, a BLDC Motor Core can achieve reduced losses and stable output over time.
5.2. Ensuring Superior Electrical Insulation
High-quality insulation between lamination layers is crucial for preventing electrical shortcuts and preserving the integrity of the BLDC Motor Core. Even minor imperfections in insulation can lead to localized hot spots and reduced motor efficiency. Before finalizing a particular insulation method—be it coating or bonding—manufacturers typically evaluate how well it withstands mechanical stress, thermal cycling, and potential chemical exposure.
Some processes involve inline coating systems that apply insulation layers uniformly on each strip of steel before the stamping phase. Others rely on post-lamination treatments, such as dipping or spray applications. Whichever method is chosen, rigorous testing—like dielectric strength measurements or thermal aging assessments—can help confirm long-term reliability. By employing top-tier insulation techniques and verifying their performance through established quality checks, engineers can create a BLDC Motor Core that balances robust functionality and energy efficiency, supporting more reliable operation across a broad range of use cases.
Further Reading: