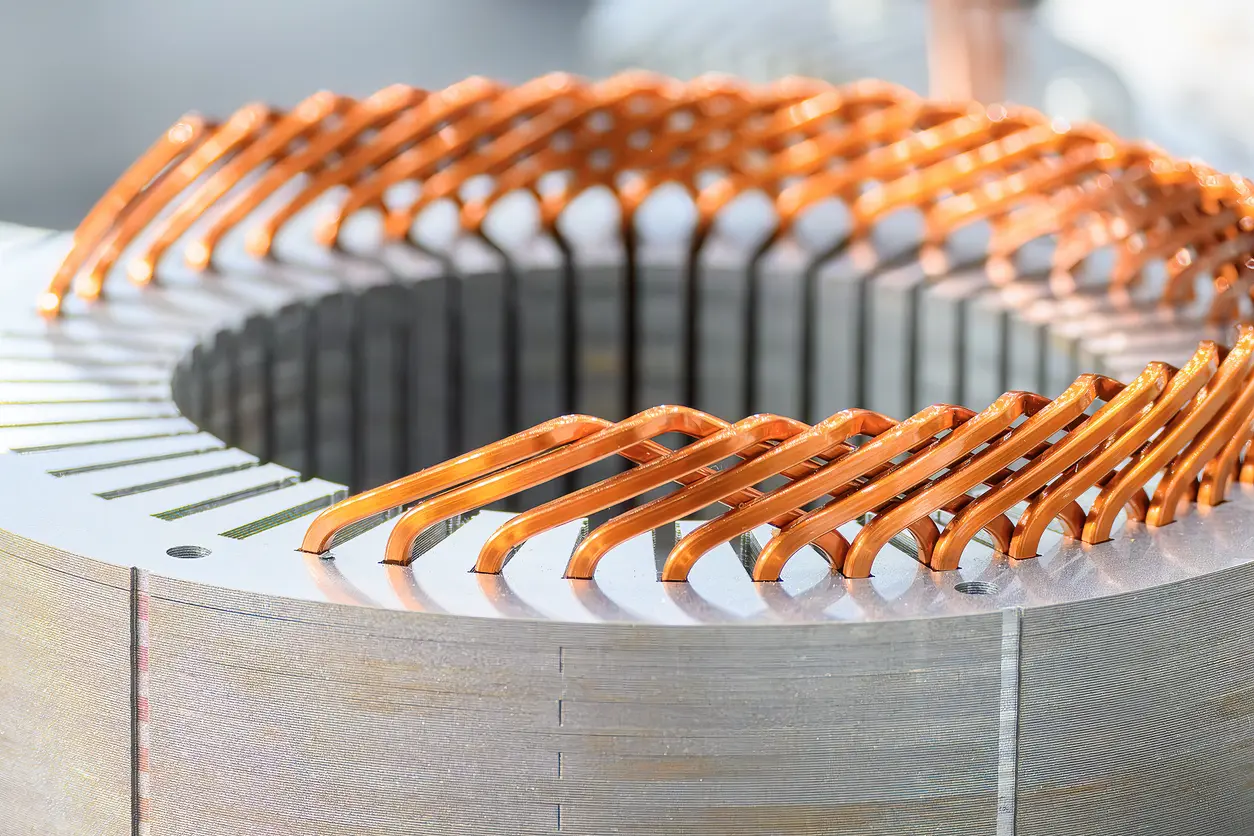
1. Introduction: The Importance of Precision in Lamination Stack Assembly
Lamination stack assembly is a cornerstone of modern electric motor manufacturing, ensuring that every motor core is built to exacting standards. This process, which involves the precise stacking and alignment of thin, pre-cut sheets of electrical steel, is essential for controlling electromagnetic properties, reducing energy losses, and enhancing the motor’s overall performance and durability. Any deviation in precision during assembly can lead to inefficient magnetic flux paths, resulting in increased operational costs and compromised reliability.
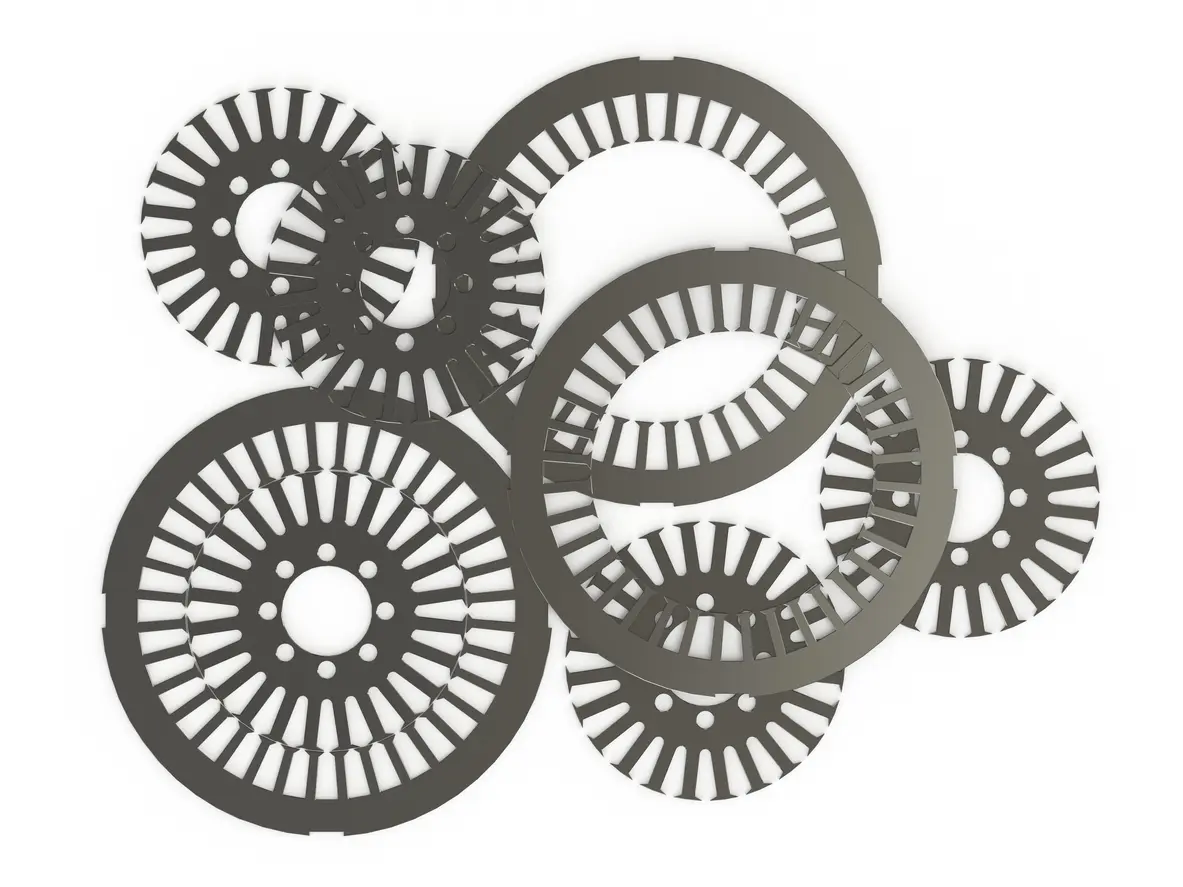
1.1 What is Motor Core Lamination Stamping?
Motor core lamination stamping is the method by which raw electrical steel is transformed into precisely cut laminations. Each stamped piece is engineered to fit perfectly within a larger assembly, forming the motor’s core. The accuracy of these cuts and the subsequent stacking process are critical. Even minor imperfections or misalignments can compromise the core’s integrity, leading to unwanted eddy currents and diminished magnetic efficiency. Thus, achieving meticulous precision in lamination stack assembly is not just a quality measure—it is fundamental to optimal motor performance.
1.2 The Role of Lamination Stack Assembly in Modern Electric Motors
In contemporary motor design, the lamination stack assembly does more than simply support structural integrity; it actively influences the motor’s efficiency and thermal performance. A well-executed lamination stack minimizes energy waste and enhances the electromagnetic characteristics of the motor core. This is particularly crucial in high-performance and energy-sensitive applications where every fraction of efficiency counts. The process underlines the importance of aligning each lamination with exact precision to ensure uniform magnetic flux distribution throughout the core.
1.3 Emphasizing “Lamination Stack Assembly”
The term “lamination stack assembly” has become a key phrase in industry discussions and searches, reflecting its critical role in motor manufacturing. As manufacturers strive for excellence, a thorough understanding and careful implementation of lamination stack assembly processes are imperative. By focusing on precision, companies can secure enhanced motor performance, reliability, and long-term operational success.

2. Mistake #1: Inadequate Material Selection and Handling
A critical aspect of a successful lamination stack assembly process lies in selecting and managing the right materials from the outset. Inadequate material selection can undermine the overall performance of the motor core, leading to increased energy losses and compromised durability.
2.1 Understanding Material Properties for Optimal Laminations
In the realm of lamination stack assembly, the choice of material is paramount. Electrical steels, such as silicon steel alloys, are typically used due to their excellent magnetic properties and low hysteresis losses. These materials must exhibit consistent thickness, high permeability, and proper insulation between laminations to minimize eddy current formation. When the material properties are not rigorously evaluated, even a minor inconsistency can affect the magnetic flux distribution across the stack. This is why detailed material specifications and quality certifications are indispensable. Manufacturers should work closely with suppliers to ensure that every batch meets the stringent standards required for optimal motor performance.
2.2 Common Material Handling Errors in Lamination Stack Assembly
Beyond selection, proper handling of materials is crucial during the lamination stack assembly process. Common errors include exposure to moisture, improper storage, and contamination from dust or oils. Such mishandling can lead to oxidation or surface defects that deteriorate the performance of the assembled motor core. Even when high-quality materials are used, poor handling practices can negate their benefits, leading to uneven stacking or misalignment during assembly. Maintaining a controlled environment, adhering to strict handling protocols, and implementing regular inspections are essential steps. This careful approach not only preserves the material’s integrity but also ensures that the final lamination stack assembly consistently meets the operational demands of modern electric motors.

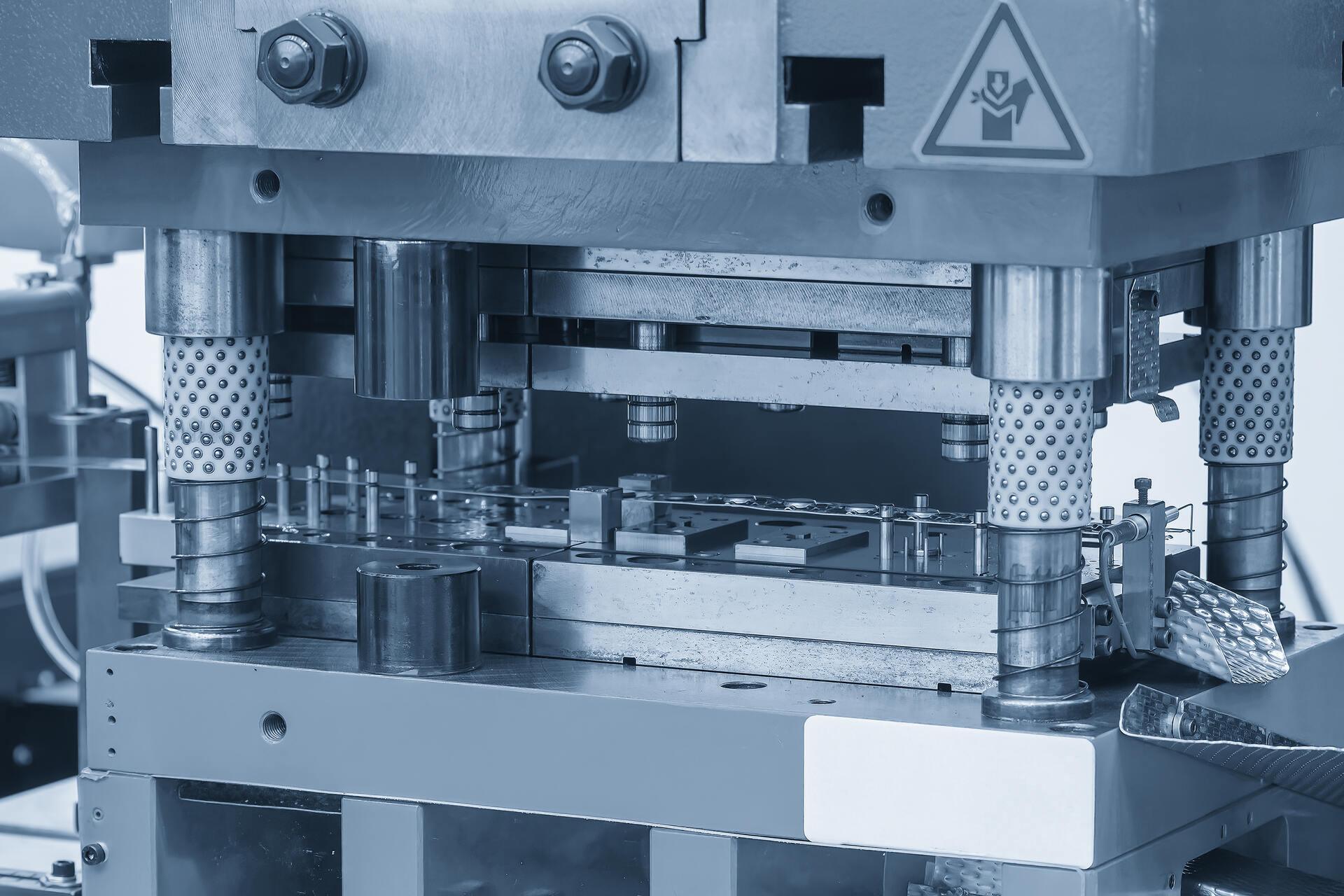
3. Mistake #2: Improper Stamping Techniques and Tooling
3.1 The Critical Role of Precision Stamping in Lamination Assembly
In lamination stack assembly, precision stamping is essential. Accurate stamping produces laminations with clean, smooth edges and exact dimensions. This ensures that each piece fits perfectly in the final stack. Even small deviations can disrupt the magnetic flux, leading to energy losses. Utilizing advanced stamping equipment that consistently maintains pressure and speed is key to achieving the desired precision.
3.2 Pitfalls in Stamping Processes and Tool Maintenance
Poor stamping techniques and inadequate tool maintenance can lead to irregular laminations. Worn or uncalibrated tools often result in uneven edges and burrs, making proper alignment during assembly more difficult. These imperfections can compromise the performance of the motor core. Inconsistent stamping pressure further exacerbates these issues, contributing to higher core losses.
Regular inspections and precise calibrations are vital. A strict maintenance schedule helps ensure that tooling remains in optimal condition. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of defects in the lamination stack assembly. Ultimately, investing in quality stamping techniques and proper tool upkeep is crucial for maintaining efficiency and reliability in electric motor manufacturing.
4. Mistake #3: Lack of Robust Quality Control and Inspection Procedures
4.1 The Necessity of Rigorous Inspection Protocols
Quality control is the backbone of any reliable lamination stack assembly. Thorough inspections should identify dimensional variances, surface flaws, and other deviations that can undermine motor performance. For instance, manufacturers can use digital micrometers to verify lamination thickness against specified tolerances and apply burr measurement tools to ensure edges meet height requirements.
Real-time monitoring systems can also employ laser sensors to measure stack height or detect alignment irregularities, allowing immediate corrections. Additionally, using eddy current or ultrasonic testing methods can help reveal hidden defects—such as cracks or deformations—early in the production cycle. By defining specific checkpoints for each stage, teams can promptly isolate and address issues, reducing waste and preventing late-stage failures.
4.2 Consequences of Insufficient Quality Control Measures
When inspection protocols lack detail or frequency, defects in lamination stack assembly can escalate quickly. Misaligned laminations or excessive burrs, for example, might increase core losses and lead to higher operating temperatures, reducing the motor’s efficiency and lifespan. Over time, these issues can cause unexpected motor failures, impacting both production schedules and end-user satisfaction.
Insufficient quality checks also make it difficult to trace recurring defects to their root causes. Without systematic testing—like burr height measurements, stack height verifications, and nondestructive evaluation—teams may face repeated production setbacks. This inefficiency not only strains resources but can also damage a company’s reputation when customers encounter performance inconsistencies or premature failures. Robust inspection protocols, backed by appropriate measuring tools and real-time data, are thus essential for building confidence in the final product.
5. Mistake #4: Poor Process Optimization and Parameter Management
5.1 The Importance of Process Optimization in Manufacturing
In lamination stack assembly, consistent process parameters can make all the difference in achieving high-quality outcomes. Proper optimization involves defining exact settings for stamping speed, press force, and even temperature control to ensure laminations remain dimensionally accurate. For instance, adjusting the press force to account for variations in material thickness can help prevent burr formation or misalignment during stacking. Real-time data collection—such as monitoring line speed and die temperature—can also alert teams to irregularities before they escalate.
Beyond stamping, process optimization may include fine-tuning stacking sequences or adjusting adhesive application methods (where applicable). These considerations help manufacturers minimize wasted material, reduce production time, and maintain a steady flow of quality products. Establishing a systematic approach, supported by data-driven insights, ensures the lamination stack assembly remains consistent from one production run to another.
5.2 Common Parameter Management Errors and Their Impact
When process settings are not systematically maintained or adapted to material variations, issues can quickly arise. Inadequate or excessive stamping pressure may lead to uneven edge geometry, making it difficult to achieve uniform stacking. Similarly, failing to adjust punch-to-die clearance for different steel grades can result in higher burr heights and an overall decline in assembly quality.
Unregulated thermal conditions can also cause inconsistencies, especially if laminations experience minor expansions or warping. Overlooking these subtleties can disrupt alignment and increase core losses once the motor is in operation. Without a structured process control system—featuring scheduled audits, standardized documentation, and performance tracking—manufacturers risk recurring defects and underperforming motor cores.
By fine-tuning and regularly reviewing process parameters, companies can optimize their lamination stack assembly for efficiency and reliability. A commitment to continuous improvement not only preserves quality standards but also strengthens overall competitiveness in the electric motor market.
6. Mistake #5: Ineffective Communication and Collaboration with Stakeholders
6.1 The Impact of Cross-Functional Communication on Assembly Quality
In the context of lamination stack assembly, clear and consistent communication among various stakeholders—such as design teams, production personnel, and suppliers—is essential for minimizing errors. When departments operate in silos, crucial details about material specifications, dimensional tolerances, or tool maintenance schedules can be overlooked. This may lead to frequent rework, increased scrap rates, and reduced overall efficiency.
6.2 Strategies for Enhancing Collaboration and Avoiding Missteps
Establishing regular touchpoints—like weekly progress meetings or electronic status updates—helps each party stay informed about changes in production parameters or emerging technical concerns. Documenting critical instructions in a centralized system can also foster transparency and reduce misunderstandings. In addition, involving suppliers early in the design phase allows them to provide insight on feasible material substitutions or improved tooling solutions. By proactively sharing data on performance metrics or quality check results, teams can promptly identify inconsistencies in lamination stack assembly and take corrective actions. Adopting these collaborative measures does not guarantee absolute error-proof outcomes, but it can significantly lower the risk of misaligned objectives and unforeseen production challenges.
Further Reading: