1. Introduction to Permanent Magnet Core Lamination
1.1 What Is Permanent Magnet Core Lamination?
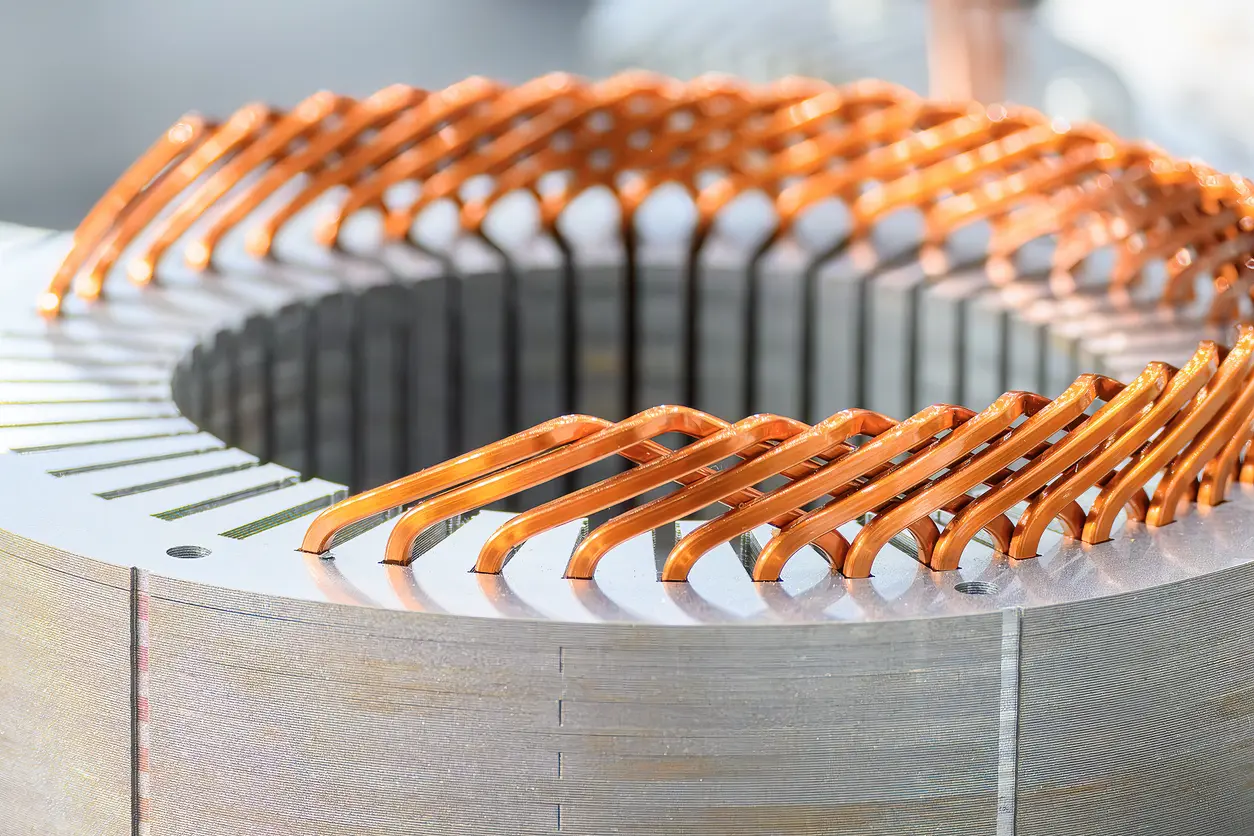
Permanent magnet core lamination refers to the process of stacking thin, insulated metal sheets (often made of silicon steel) to form the core of an electric motor that utilizes permanent magnets. This layered structure is designed to reduce eddy current losses, which can occur when a solid metal core is subjected to rapidly changing magnetic fields. By segmenting the core into multiple lamination sheets, the electrical conductivity across each layer is minimized, helping improve overall efficiency and performance.
In many modern applications—such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, and industrial robots—designers rely on permanent magnet core lamination for its potential to deliver high torque density and better energy efficiency. Although different fabrication methods (like wire-edm cutting, stamping, and self-bonding) can be used, each approach aims to maximize material quality and minimize the impact of heat or mechanical stress on the metal sheets. As a result, this lamination process plays a crucial role in achieving a balance between performance, durability, and cost.
1.2 Key Benefits of PM Core Lamination
One of the main benefits of permanent magnet core lamination lies in its ability to significantly reduce heat and energy losses. In practice, a well-laminated core helps minimize the undesirable effects of eddy currents, leading to lower operating temperatures and potentially prolonging the lifespan of the motor. Furthermore, laminated cores often exhibit reduced vibration and acoustic noise, which can be an essential factor in sensitive environments like medical equipment or laboratory settings.
Additionally, permanent magnet core lamination enables greater design flexibility. Engineers can optimize slot shapes, lamination thickness, and magnet placement to achieve specific performance goals or adapt to various industry requirements. For instance, an electric vehicle manufacturer might prioritize high torque at low speeds, while a robotics company may seek extremely precise control and motion. In both cases, carefully engineered laminations help refine motor characteristics, ultimately benefitting efficiency, reliability, and overall operational effectiveness.

2. Choose the Right Lamination Material
2.1 Importance of Material Selection
When it comes to permanent magnet core lamination, selecting the right material is a critical step that can greatly influence your motor’s overall efficiency and lifespan. Engineers commonly opt for electrical steels—such as silicon steel or iron-cobalt alloys—because these materials strike a balance between magnetic permeability and electrical resistivity. A higher silicon content, for instance, may help reduce eddy current losses; however, it can also affect the steel’s ductility and ease of manufacturing. As a result, companies in various industries—from automotive to aerospace—tend to evaluate both the short-term and long-term trade-offs of each material choice.
Beyond basic composition, lamination thickness also plays a considerable role. Thinner laminations can minimize eddy current loops, but they may raise production costs due to the higher volume of sheets needed. In real-world applications, some electric vehicle manufacturers have found that ultra-thin laminations can offer superior torque density, albeit with added complexity in processing and assembly. By carefully matching material properties to performance goals, designers can achieve a custom permanent magnet core lamination that meets specific operational requirements without overshooting budget constraints.
2.2 Testing and Certifications
Once a suitable material is chosen, comprehensive testing and certifications help ensure the lamination will perform as intended. Manufacturers often rely on industry standards like ASTM A677 or A683 for electrical steels, verifying core loss and permeability properties under controlled conditions. Additionally, ISO 9001 certification can serve as a baseline for quality management, offering customers a degree of reassurance that the production process meets recognized benchmarks.
In certain high-performance applications—such as medical equipment or aerospace components—more rigorous or specialized tests may be conducted to confirm thermal stability and mechanical strength. For example, non-destructive testing (NDT) methods can identify hidden cracks or inconsistencies in the lamination sheets. Through methodical testing and careful documentation, companies can maintain consistent, reliable permanent magnet core lamination quality, ultimately benefiting end users in demanding real-world environments.
3. Optimize the Lamination Process
3.1 Cutting Techniques
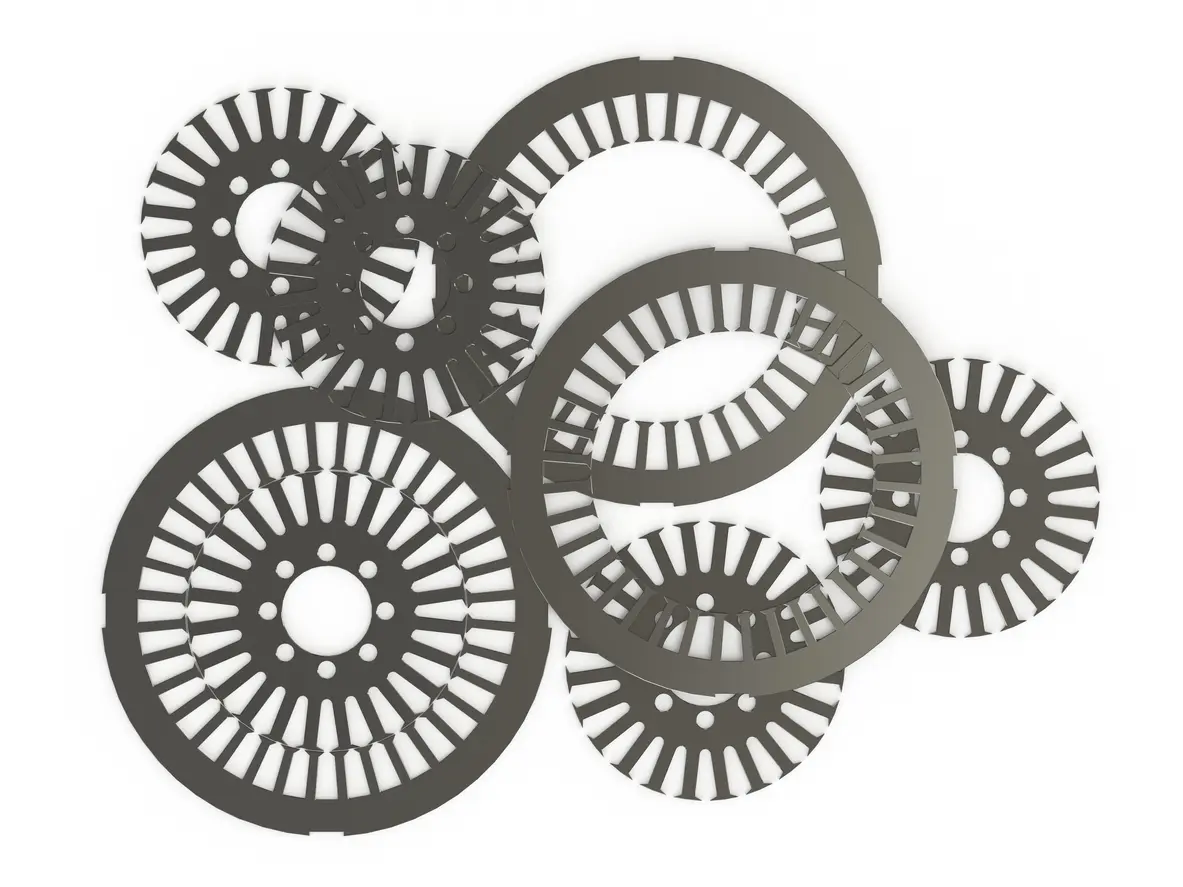
When focusing on permanent magnet core lamination, the method of cutting lamination sheets can substantially affect manufacturing efficiency and motor performance. Traditional stamping processes remain popular due to their cost-effectiveness and rapid production cycles. This approach is often preferred in high-volume scenarios—like automotive manufacturing—where meeting strict timelines and budget targets is essential. However, stamping can introduce stress at the edges of the laminations if not carefully managed.
For projects requiring exceptionally precise tolerances, laser cutting is another viable option. Although somewhat more expensive, this method can produce complex geometries and tight clearances without creating excessive mechanical strain. Some advanced manufacturers have even experimented with alternative techniques, such as waterjet cutting or electrical discharge machining (EDM), to control heat-affected zones and maintain optimal magnetic properties. In each of these cases, the goal remains the same: reduce burrs and preserve the integrity of every lamination sheet to ensure consistent performance.

3.2 Stacking and Bonding Methods
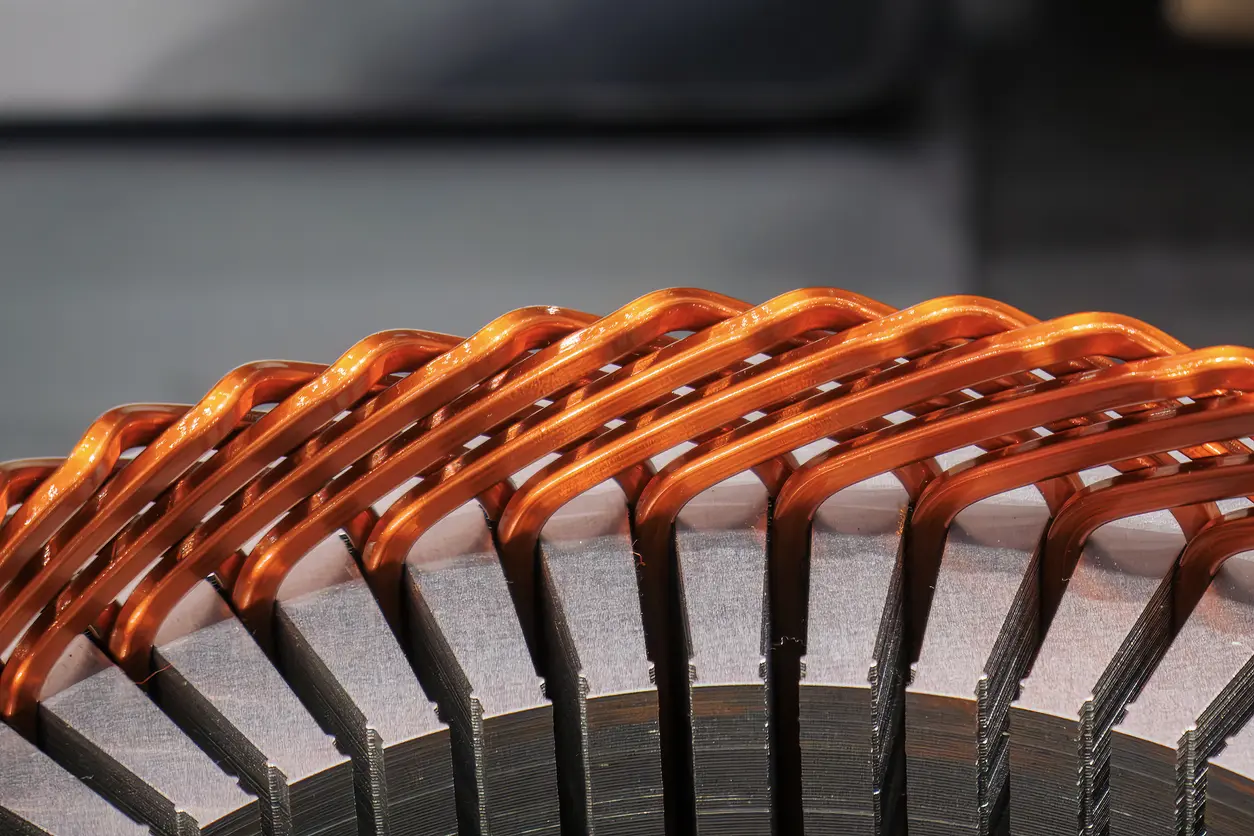
After the lamination sheets are cut, the next step is stacking them in a way that supports the best possible magnetic flux path and minimizes internal losses. Depending on the specific application—be it an electric vehicle drive motor or a high-precision robotic actuator—engineers may utilize interlocking features, adhesives, or welding techniques. Interlocking methods can speed up production while retaining accurate alignment, but adhesives might offer superior insulation and lower noise in specific operating conditions.
Bonding methods can also vary significantly based on material choice. For instance, using a high-temperature epoxy in aerospace applications can help ensure stable performance under harsh thermal cycles. In contrast, ultrasonic welding might be favored for certain industrial motors, providing a strong mechanical bond without introducing high levels of heat. By carefully selecting cutting and stacking approaches, it becomes possible to create a permanent magnet core lamination that balances durability, precision, and overall efficiency for a broad range of end-use scenarios.
4. Enhance Thermal Management
4.1 Lamination Coatings and Insulation
Effective thermal management is crucial in permanent magnet core lamination, as excessive heat can lead to reduced motor efficiency and potential magnet demagnetization. One of the primary methods to control heat buildup involves applying specialized coatings and insulation on each lamination layer. Coatings typically consist of epoxy or inorganic compounds that serve multiple purposes: they reduce inter-laminar eddy currents, enhance electrical insulation, and help maintain a stable thermal environment around the core.
The thickness of these coatings can vary based on the motor’s performance requirements. For instance, aerospace applications might favor ultra-thin insulation layers to keep overall weight low, while industrial motors could require slightly thicker coatings for added durability under higher thermal loads. In either case, careful selection of coating materials and application processes can lead to consistent heat distribution across the laminated stack, reducing the likelihood of localized hotspots. Real-life examples include manufacturers who have successfully tested phosphate-based coatings to achieve a balance between corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity—particularly beneficial in environments with high humidity or frequent temperature fluctuations.
4.2 Cooling Strategies and Ventilation
Beyond coatings, an effective cooling strategy is essential to safeguard permanent magnet core lamination from thermal stress. Many designs incorporate simple yet efficient methods like axial or radial ventilation channels, ensuring steady airflow across the lamination stack. This approach can dissipate heat generated by eddy currents and magnetic hysteresis, maintaining more stable operating temperatures. In high-power motors—such as those used in electric vehicles—engineers often add forced-air or liquid-cooling systems to handle the added thermal load.
In certain advanced robotics applications, design teams may introduce strategically placed cooling ducts or fluid channels directly within the motor housing. By combining proper airflow design with effective insulation layers, these systems help maintain optimal temperatures even under demanding operating cycles. Although such solutions can increase manufacturing complexity, they often pay off by extending motor life and sustaining higher performance over prolonged service intervals.
5. Continuous Quality Assurance and Testing
5.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods
Quality assurance plays a vital role in maintaining optimal performance of any permanent magnet core lamination design. By employing various Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) techniques, manufacturers can detect internal defects—such as cracks, delamination, or excessive burrs—without causing damage to the lamination stack itself. Common NDT methods include ultrasonic testing, eddy current inspection, and radiographic examination. For instance, ultrasonic testing uses high-frequency sound waves that travel through the lamination layers, reflecting back when they encounter material imperfections. This approach allows engineers to pinpoint problematic areas early in the production process, avoiding costly rework or field failures.
Real-world applications often illustrate the value of thorough NDT. In high-end electric motors for aerospace or medical systems, any minor defect can compromise safety or precision. Therefore, these industries frequently incorporate multiple inspection stages during and after lamination assembly. Some manufacturers leverage automated NDT solutions—featuring robotic scanning arms and advanced imaging software—to achieve a higher degree of consistency and repeatability. The insights gained from such testing can guide immediate adjustments on the production line, helping preserve the integrity of each permanent magnet core lamination.
Further Reading and More Info: