1. Introduction
1.1 Defining Frameless Motor Core Lamination
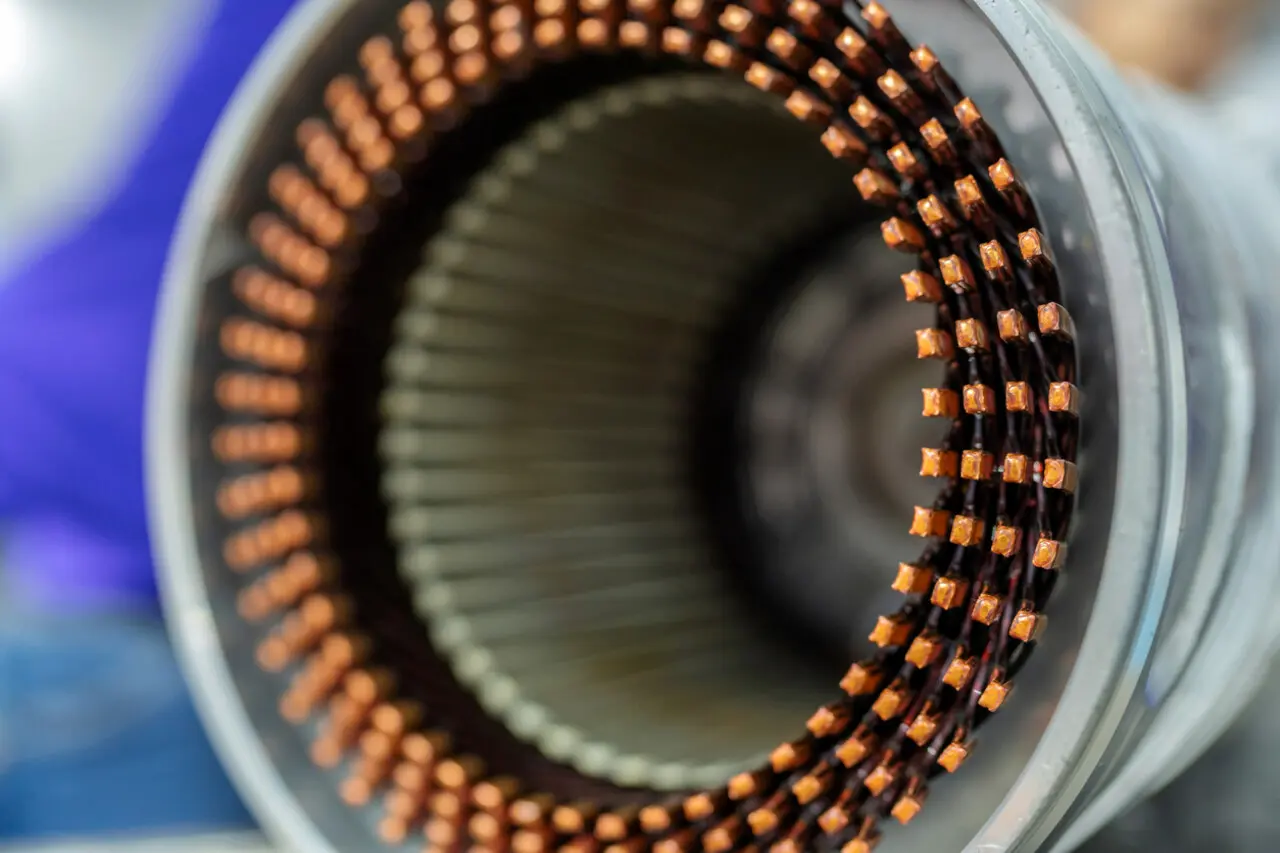
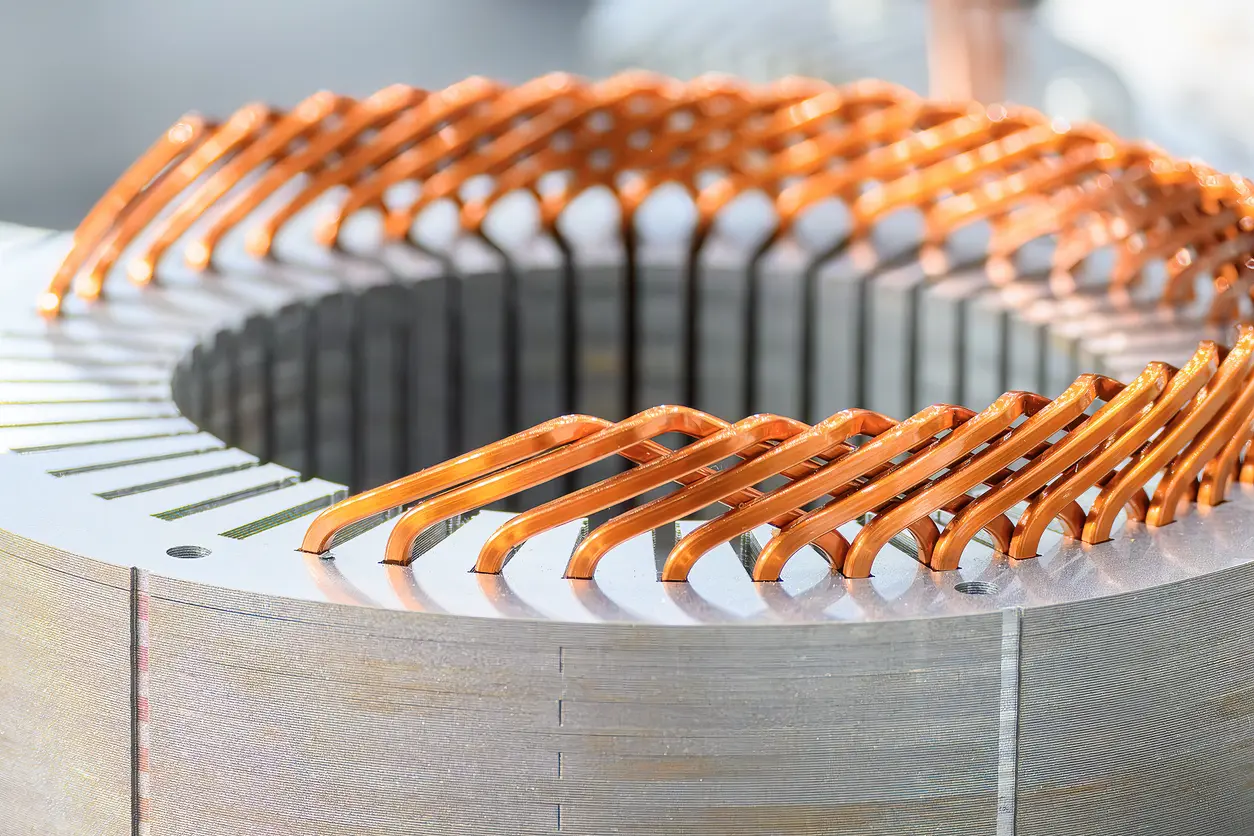
Frameless motor core lamination refers to the fabrication and assembly of stator and rotor laminations without a traditional external housing or frame. In a typical electric motor, the frame or casing not only protects the internal components but also helps with heat dissipation. By contrast, frameless motors integrate the rotor and stator elements directly into the device or machine structure. This design approach can be particularly useful in applications that demand optimized space usage, improved thermal performance, and higher efficiency.
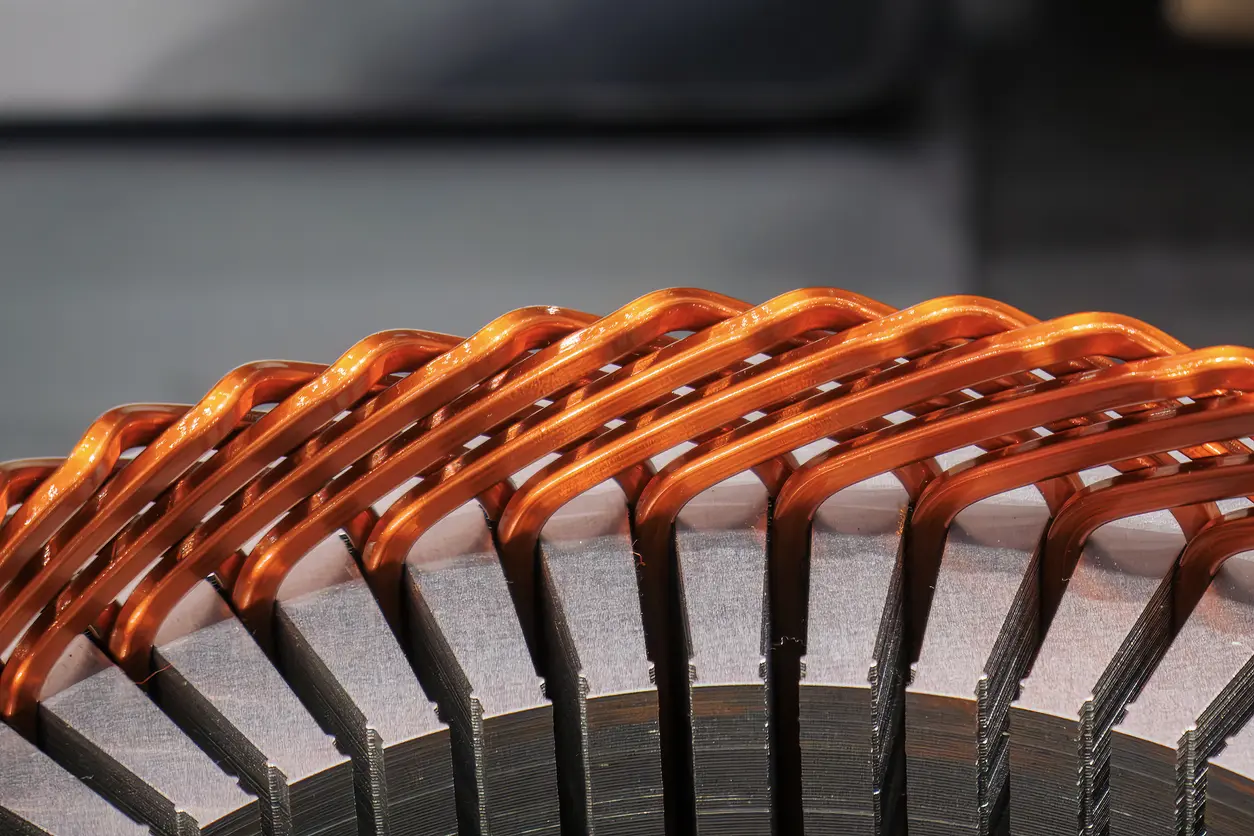
When we talk about “frameless motor core lamination,” we are addressing the process of stacking thin steel sheets—often coated with insulation—to form the core of both the rotor and stator. These laminated stacks minimize eddy current losses, enabling better power output and energy efficiency. For end-users, the key takeaway is that frameless motors offer an opportunity to tailor the motor design for specific applications where conventional motors might be too bulky or less adaptable.
1.2 Overview of Growing Applications
Frameless motor core lamination has steadily gained traction across multiple industries. Robotics and industrial automation are prime examples, where smaller, lighter motors are often critical to achieving greater dexterity and speed. In the medical field, frameless designs prove beneficial in devices requiring compact footprints and precise control, such as surgical robots and diagnostic equipment.
Moreover, the ongoing development of humanoid robots has brought renewed attention to frameless motors. In these advanced systems, engineers aim to replicate human-like movements without increasing the robot’s overall weight. By integrating frameless motor core lamination directly into joint assemblies, designers can reduce bulk and enhance power efficiency. This concept also extends to aerospace projects, drones, electric vehicles, and other emerging technologies where lightweight and high-performance motors are increasingly essential.
Overall, the growing interest in frameless motor core lamination signals a shift toward more flexible, customized solutions that address both performance demands and spatial constraints.
2. Advantage #1: Enhanced Power Density
2.1 What Is Power Density and Why It Matters
Power density, in the context of electric motors, is a measure of how much power can be generated relative to the overall size or weight of the motor. Higher power density often translates to better performance and improved efficiency, especially in applications where space and weight are critical factors. By leveraging frameless motor core lamination, designers are able to minimize unused space and optimize the electromagnetic characteristics within the stator and rotor. This approach can lead to tighter magnetic coupling between the rotor and stator, resulting in greater torque output per unit of mass. Although the specific gains may vary by application, the overall benefit is typically a more compact yet capable motor solution.
2.2 Real-World Impact
In real-world scenarios, enhanced power density can yield tangible advantages across various industries. For instance, industrial robots benefit from motors that deliver robust torque without significantly increasing the weight of the robotic arm. This can improve speed, precision, and handling capacity. In aerospace or drone applications, reducing the size and mass of onboard motors can make a substantial difference in flight range, maneuverability, and energy consumption. Likewise, portable medical devices—such as surgical robots—are increasingly looking toward frameless motor core lamination to maximize output and maintain a manageable footprint. These benefits often go hand-in-hand with increased design flexibility, which allows engineers to create highly specialized systems suited to demanding conditions.
2.3 Practical Considerations
Despite these clear advantages, the pursuit of higher power density must be balanced with practical considerations. For example, the materials used in frameless motor core lamination must effectively handle heat to avoid thermal overload. Additionally, rigorous alignment and assembly processes are required to ensure that the stator and rotor maintain optimal clearance. Furthermore, designers should be prepared for the potential need for customized solutions, since off-the-shelf components may not always meet the unique geometric and performance requirements of high-density applications. By acknowledging these factors early, projects can reap the full benefits of enhanced power density while minimizing potential hurdles.3. Advantage #2: Improved Efficiency
3. Advantage #2: Improved Efficiency
3.1 Energy Efficiency Explained
Energy efficiency in electric motors generally refers to how effectively a motor converts electrical power into mechanical output. By utilizing frameless motor core lamination, engineers can reduce certain inefficiencies found in traditional motor designs. In a conventional motor with a bulky frame, heat dissipation may be less direct, which can lead to additional losses over time. Frameless motors, on the other hand, have their stator and rotor components integrated more seamlessly into the machine’s structure. As a result, less energy is wasted in overcoming mechanical or thermal obstacles. Although specific efficiency gains vary by application, many users find that frameless motors can deliver comparable or superior performance with less power consumption.
3.2 Thermal Management Benefits
Effective thermal management is a significant contributor to motor efficiency. Excess heat, if not handled properly, can increase resistance within the stator windings and lead to premature wear of components. Because frameless motor core lamination eliminates a separate housing, there is typically a more direct path for heat to escape. This design can help maintain optimal operating temperatures, ultimately preserving the motor’s performance and extending its service life. Furthermore, better heat dissipation allows for higher continuous torque outputs without the risk of overheating. While each application has different cooling requirements, frameless motors often offer greater flexibility for incorporating custom cooling solutions that match specific operational demands.
3.3 Positive Environmental Impact
Improved efficiency not only leads to cost savings but also yields environmental benefits. In many industrial or commercial settings, motors operate for extended periods. Even modest efficiency gains can translate into noticeable reductions in energy consumption. By adopting frameless motor core lamination, companies may lower their carbon footprint while enhancing productivity. Additionally, less frequent maintenance and fewer component replacements can contribute to a more sustainable operation overall. Although there are varying degrees of efficiency improvements depending on design and application, these collective benefits make frameless motors an appealing choice for forward-thinking organizations.
4. Advantage #3: Reduced Weight and Size
4.1 Lightweight Construction
One of the most notable characteristics of frameless motor core lamination is the absence of an external housing, which can significantly lower the overall motor weight. By building the rotor and stator directly into the machine’s structure, engineers effectively eliminate extra material and reduce unnecessary mass. This streamlined arrangement is not only beneficial in terms of total motor weight, but it may also optimize the power-to-weight ratio.
In many cases, this advantage can be especially helpful in mobile or airborne applications, such as drones and small aircraft, where every gram counts. While the exact amount of weight reduction will vary depending on the motor’s size and design parameters, the core principle of housing-free integration remains a key reason why some industries favor frameless configurations.
4.2 Compact Design in Action
Beyond weight savings, a frameless setup generally has a smaller footprint compared to a conventional motor with a metal frame. The compact nature of frameless motor core lamination allows manufacturers and system integrators to fit motors into tighter spaces without compromising functionality. This level of adaptability often leads to more creative design possibilities, since engineers can rearrange internal components to meet specific dimensional requirements. As a result, industries such as medical device manufacturing, which relies on compact yet precise instruments, can greatly benefit from the minimized form factor. Moreover, smaller motor sizes can lower overall product dimensions, potentially reducing both material costs and shipping expenses.
4.3 Impact on Next-Generation Robotics
Reduced weight and a smaller profile are especially advantageous for next-generation robotics, including humanoid platforms. When designing a robotic arm or leg, excess weight can limit agility and increase energy consumption during movement. By adopting frameless motor core lamination, robot developers can incorporate motors that provide sufficient torque without adding undue bulk. This helps achieve a balance between power output and maneuverability, making it feasible to replicate complex human-like motions. As humanoid robots become more prevalent across various sectors, continued advances in lightweight, frameless motor technologies could drive further innovation while maintaining reliable performance.
5. Advantage #4: Design Flexibility and Customization
5.1 Large Bore and Unique Mounting Options
One of the standout features of frameless motor core lamination is the ability to incorporate a larger bore. This design aspect can be extremely helpful for engineers who need to accommodate additional components, such as wiring harnesses, fluid lines, or even optical systems, through the center of the motor.
By removing the traditional motor housing, designers gain more freedom in positioning and securing the rotor-stator assembly directly onto the machine’s structure. Although some projects may call for careful dimensional analysis to ensure proper clearance and alignment, the potential for streamlined installations can be a compelling draw for businesses looking to optimize their device layouts.
5.2 Tailoring Performance to Specific Applications
Frameless motors lend themselves well to customization because manufacturers can adjust various parameters—such as stator winding density, rotor magnet arrangement, and lamination materials—to achieve targeted performance goals.
These goals might include higher torque, faster speeds, or improved thermal management. For instance, an application in robotics might call for precise torque control at low speeds, while a drone propulsion system may prioritize rapid acceleration and reduced weight.
With frameless motor core lamination, engineers can often fine-tune the electromagnetic design to match exact specifications. While such customization may require detailed planning and potential upfront investment, the result can be a far more efficient and reliable motor that fits seamlessly into specialized or compact environments.
5.3 Scalability for Future Innovations
As industries evolve, product requirements frequently shift, necessitating versatile motor solutions that can adapt to new challenges. The modular nature of frameless designs allows developers to scale motor size, adjust coil configurations, or experiment with emerging materials for improved performance.
For example, if a robotics platform is upgraded with more advanced sensors or an expanded range of motion, the motor design can likewise be refined to accommodate these enhancements. Although no single approach guarantees universal success, frameless motor core lamination provides an adaptable foundation upon which organizations can build, modify, and innovate as their technological needs grow.
6. Advantage #5: Precision and Reliability
6.1 Direct Mounting for Better Alignment
One of the key benefits of frameless motor core lamination is the opportunity to mount the motor’s stator and rotor directly onto the host structure. When components are built this way, there is less reliance on secondary housings or support brackets, which can sometimes introduce misalignment. With proper engineering, direct mounting ensures more accurate concentricity between the rotor and stator, helping to maintain stable performance over the motor’s operating range. Although it requires careful planning and execution, this arrangement can enhance precision, reduce vibration, and improve overall motor responsiveness in environments that demand reliable output.
6.2 Durability in Challenging Environments
Because frameless designs eliminate extra hardware, they often have fewer points of potential failure. This can be advantageous in settings where dust, moisture, or mechanical impact would normally pose a concern. In industrial automation, for example, motors may be subjected to frequent start-stop cycles or exposed to abrasive particles. A frameless motor core lamination system—properly sealed and integrated—can offer robust performance in these conditions, as it reduces the number of external components that could degrade over time. Nevertheless, selecting the right materials and coatings remains essential to protect the lamination stack from corrosion and wear, ensuring that the motor retains its reliability in demanding applications.
6.3 Importance for High-Stakes Applications
Precision and reliability are especially critical in fields such as medical robotics, aerospace, and defense. In these areas, even minor deviations can have serious implications, from compromised safety to reduced mission success rates. By employing frameless solutions, engineers can harness direct torque transmission and fine-tuned alignment, which may help meet stringent performance benchmarks. While such systems do require thorough testing and potential investment in specialized components, the payoff can be substantial. Over time, a properly engineered frameless motor core lamination can offer consistent, dependable operation that justifies its role in pivotal applications.
Further Reading:
https://www.alvaindustries.com/post/an-engineers-guide-to-frameless-motors