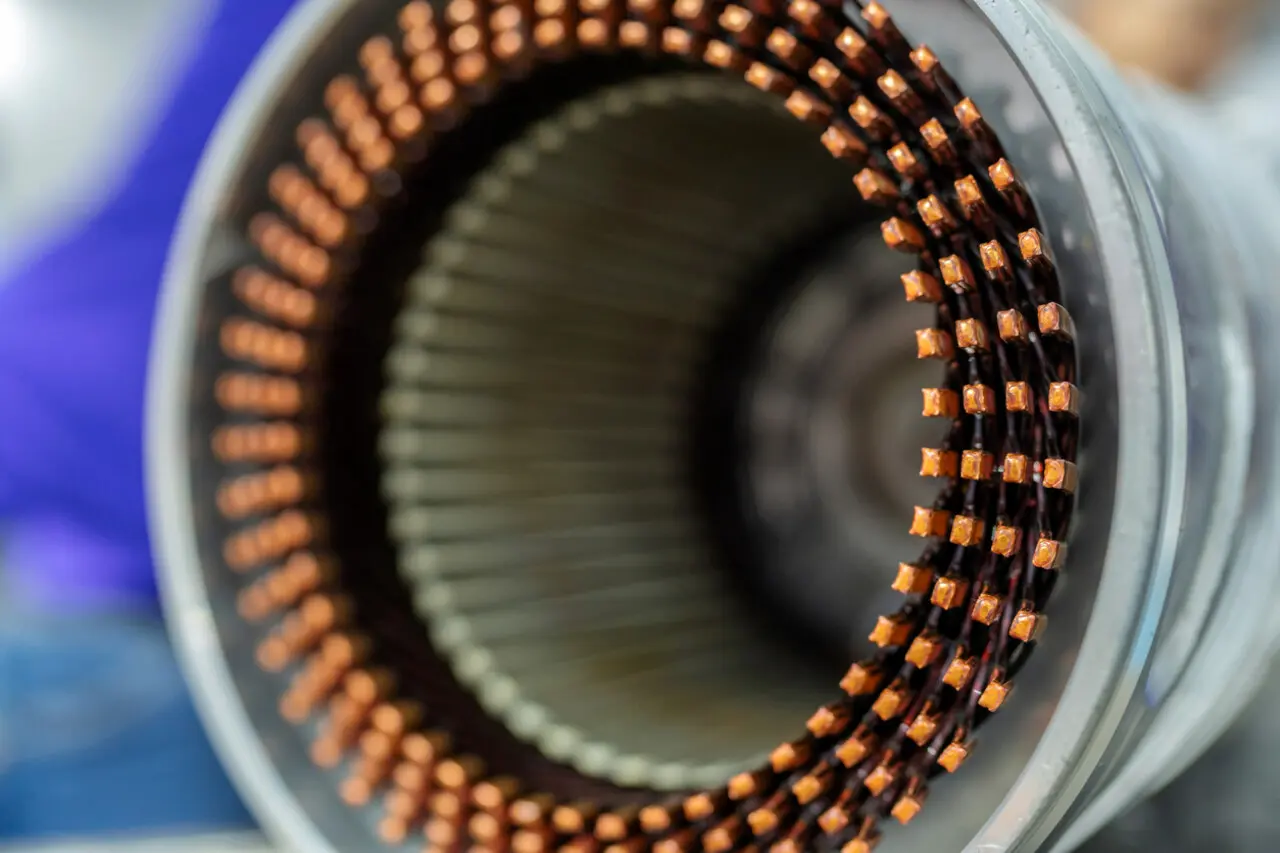
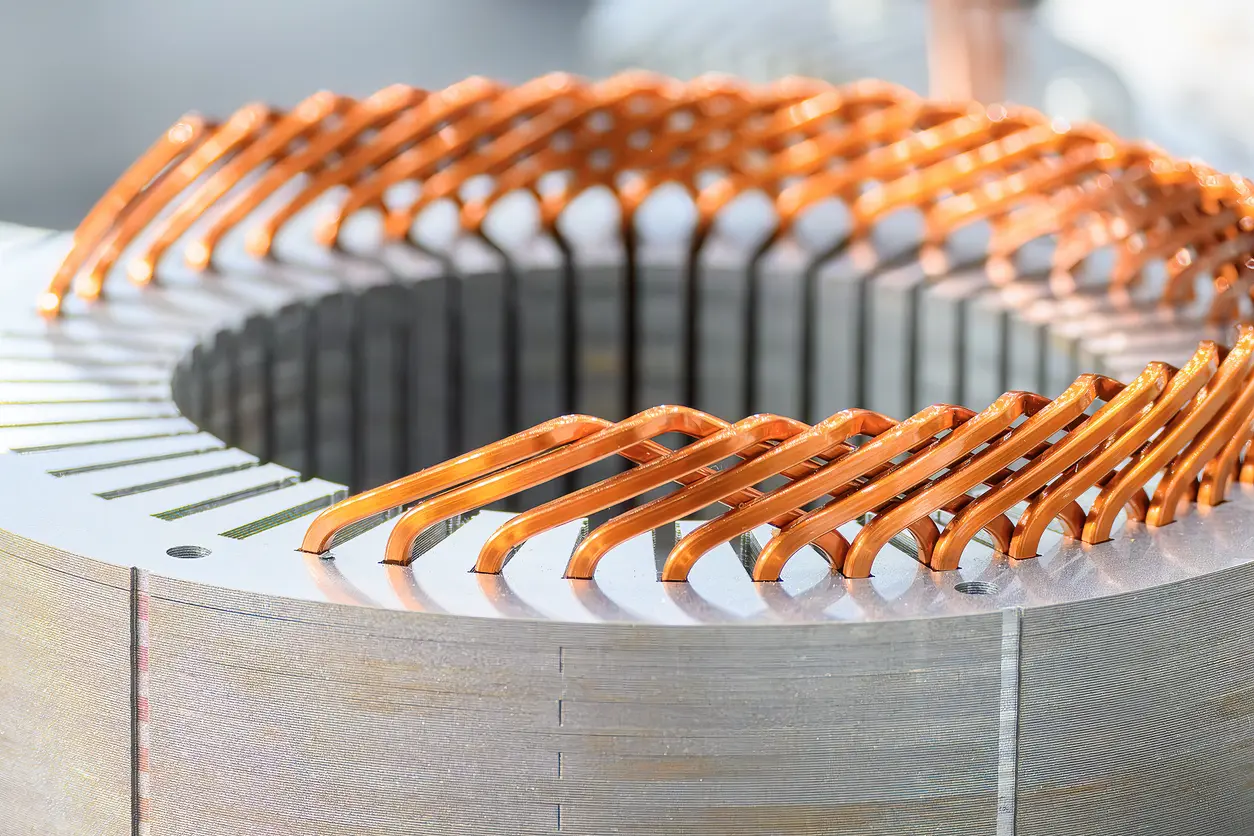
Uncover the three most critical mistakes that jeopardize Frameless Torque Motor Core stacking and compromise motor performance. Learn conservative yet effective strategies to ensure optimal lamination quality, precise alignment, and robust stress management for high-reliability motors.
1. Introduction
1.1 Overview of Frameless Torque Motor Core Stacking
Frameless torque motors are designed without the typical housing or shaft components, allowing for direct integration into various mechanical assemblies. In such motors, the lamination stack—often referred to as the frameless torque motor core stacking—forms the foundation for electromagnetic efficiency and torque generation. Each lamination in the stack is carefully manufactured to specific thickness and material standards so that, when combined, they create an optimized magnetic circuit.
While many industries have recognized the advantages of frameless motors—such as reduced footprint and improved torque density—there is a measured need to maintain precision throughout the stacking process. Deviations in lamination quality, misalignment, or suboptimal bonding can all degrade a motor’s performance. As a result, a conservative, quality-focused approach to frameless torque motor core stacking is generally recommended to ensure both reliability and consistent output over time.
1.2 Significance in Various Industries
Frameless torque motors are employed in an array of high-precision applications, from robotics and aerospace systems to advanced medical equipment and machine tools. In each of these fields, even small missteps in frameless torque motor core stacking can contribute to inefficiencies like increased losses, undue heat generation, and compromised torque delivery.
Given that these industries often operate under strict tolerance and safety requirements, ensuring consistent lamination thickness and alignment is not merely a technical preference but a fundamental necessity. Overlooking any aspect of the stacking process can result in unforeseen operational setbacks, potential downtime, or inflated maintenance costs. By adhering to best practices and remaining cautious about each step, stakeholders across various sectors can leverage the benefits of frameless torque motors while minimizing the risks associated with improper lamination stack assembly.
2. Mistake #1: Overlooking Material Quality and Thickness Accuracy
2.1 Importance of Material Selection
Choosing the correct steel or alloy for frameless torque motor core stacking is a crucial step in ensuring optimal performance. The magnetic properties of the lamination material—such as permeability and low core losses—directly influence motor torque, heat generation, and energy efficiency. In addition, consistent metallurgical quality helps maintain dimensional accuracy during manufacturing and throughout the motor’s operational life. Although it may be tempting to focus on cost alone, a balanced approach that considers both affordability and long-term reliability usually proves more prudent. By carefully vetting material suppliers and adhering to established industry standards, one can build a more dependable foundation for torque motor cores.
2.2 Consequences of Inaccurate Lamination Thickness
When lamination thickness deviates from specified tolerances, the entire frameless torque motor core stacking process can suffer. Even minor variations can result in misaligned magnetic flux paths, which may hamper the motor’s torque-generating capability. Thicker laminations tend to increase eddy current losses, while thinner laminations can introduce unwanted air gaps or structural inconsistencies. Over time, these inefficiencies may lead to elevated heat levels, reduced motor life, and compromised overall performance. A conservative outlook suggests that controlling thickness accuracy is essential for safeguarding both the initial performance and the long-term viability of high-precision motors.

2.3 How to Avoid This Mistake
To mitigate risks, implementing routine inspections and employing precise measurement tools—such as micrometers and laser scanners—can help verify lamination thickness against specified benchmarks. Equally critical is sourcing raw materials from reputable suppliers who adhere to consistent production and quality protocols. Some organizations also integrate statistical process control (SPC) techniques to track variations throughout large-scale production runs. By diligently focusing on measurement accuracy, supplier qualifications, and adherence to recognized standards, stakeholders can significantly reduce the likelihood of errors in frameless torque motor core stacking and maintain a reliable basis for motor functionality.
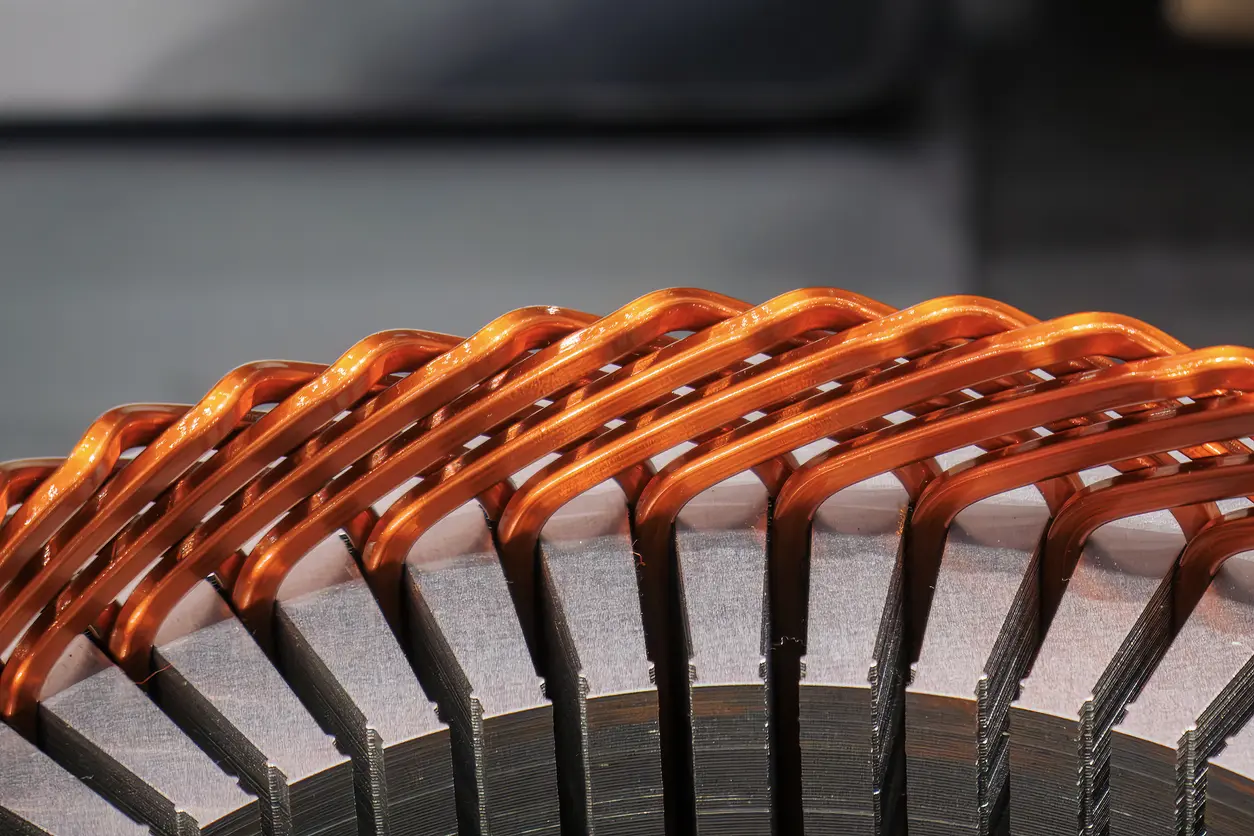
3. Mistake #2: Improper Stacking Techniques Leading to Misalignment
3.1 The Critical Role of Alignment in Frameless Torque Motors
Accurate alignment in frameless torque motor core stacking plays a pivotal role in optimizing the magnetic flux path and achieving targeted torque output. When laminations are properly aligned, the motor can operate more consistently, with reduced vibration and lower risk of uneven wear. Some industry observers note that even slight deviations in alignment can cause significant imbalances, translating into noise, energy loss, and eventual damage to internal components. In many high-precision settings—ranging from robotics to specialized medical equipment—maintaining alignment is viewed as an essential safeguard for reliable long-term motor performance.
3.2 Common Causes of Misalignment
Misalignment during frameless torque motor core stacking often stems from a mix of factors, including inadequate tooling fixtures, insufficient inspection protocols, and human error. In certain production lines, reliance on manual or partially automated processes can increase the likelihood of laminations slipping out of place. Small burrs or irregularities on the edges of each lamination may also contribute to incremental shifts when stacking a large number of sheets. Without thorough oversight, these minor flaws accumulate and result in noticeable misalignment, which can diminish the electromagnetic properties essential for efficient torque generation.
3.3 Best Practices for Precise Stacking
A more prudent approach to minimizing misalignment incorporates multiple layers of quality checks and robust tooling solutions. Some manufacturers employ precision jigs or automated assembly systems designed to maintain uniform pressure and orientation, thereby reducing variations due to operator handling. Periodic calibration of these fixtures can also be beneficial, ensuring that dimensional tolerances remain within acceptable limits. Additionally, incorporating automated vision or laser-based sensors can detect slight deviations during stacking, prompting immediate corrective actions. While no single method guarantees absolute perfection, adopting a conservative, multi-faceted quality control strategy can considerably enhance overall alignment and bolster the reliability of frameless torque motor core stacking processes.
4. Mistake #3: Neglecting Thermal and Stress Factors
4.1 The Impact of Heat on Lamination Stacks
Thermal management is a critical consideration in frameless torque motor core stacking, as excessive heat can compromise material properties and degrade performance over time. Even subtle temperature fluctuations can cause metal laminations to expand and contract, leading to internal stresses and potential misalignment within the stack. In motors where precise torque and efficiency are paramount—such as those used in aerospace or medical applications—uncontrolled heat buildup may generate unwelcome side effects. These could include higher eddy current losses, reduced insulation effectiveness, and premature wear on other motor components. Consequently, designers and manufacturers often recommend conservative design margins to account for varying thermal loads.
4.2 Stress Points and Their Effect on Motor Performance
Beyond thermal factors, mechanical stress exerted during assembly or operation can also affect frameless torque motor core stacking. In particular, uneven clamping pressure or improper bonding methods may create localized stress points that weaken the laminate bonds, risking microcracks or distortions. In turn, such structural issues can escalate into vibration, noise, or compromised magnetic flux paths. While some of these concerns might only emerge after prolonged operation, they can still undercut a motor’s long-term reliability and throughput. Acknowledging this possibility, many engineering teams treat stress prevention as a top priority, especially when motors are destined for critical tasks requiring high uptime and minimal service interruptions.
4.3 Proven Methods to Mitigate Thermal and Mechanical Stress
To safeguard lamination stacks against heat-related failures and mechanical deformations, several approaches may be employed. Careful selection of bonding techniques—whether it be self-bonding, interlocking, adhesive bonding, or laser welding—can help maintain the structural integrity of laminations. Additionally, implementing heat-resistant materials or specialized coatings ensures that frameless torque motor core stacking remains intact during temperature spikes or rapid thermal cycles. In some advanced designs, engineers may incorporate stress-relief notches or carefully placed gaps to accommodate thermal expansion. By combining robust design methods with meticulous assembly practices, manufacturers can more effectively minimize risk and uphold consistent motor performance.
5. Additional Considerations for Optimal Frameless Torque Motor Core Stacking
5.1 Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring rigorous quality control is often seen as essential for maintaining consistent results in frameless torque motor core stacking. This typically involves a combination of dimensional checks, such as stack height and runout measurements, to verify that the assembly meets prescribed tolerances. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods—like ultrasonic or eddy current inspections—can also help identify internal defects or delamination issues before they affect the motor’s operation. Furthermore, documenting each phase of the testing process provides a traceable record that can be referenced if questions of reliability or performance arise later. By placing emphasis on sound inspection techniques, manufacturers and end users can better anticipate potential issues and take timely corrective actions.
5.2 Production Scalability and Customization
Another important aspect to consider is how easily core stacking processes can scale to different production volumes or unique design requirements. While smaller batches may allow for extensive manual intervention and checks, larger runs call for automated or semi-automated systems that can handle a high throughput without compromising on precision. Certain projects might also necessitate specialized shapes, materials, or bonding methods to meet unique performance targets. In such cases, having flexible tooling and adaptable processes can prove beneficial. A conservative approach to scaling—one that balances throughput with meticulous quality standards—helps maintain a consistent build quality, even when product lines or order sizes fluctuate.

5.3 Global Supply Chain and Logistical Factors
When considering global production or assembly arrangements, it is prudent to account for how shipping, handling, and storage conditions could influence frameless torque motor core stacking. Prolonged transit times, shifts in humidity, or fluctuating temperatures may introduce subtle risks for material corrosion or warping. Working with trusted suppliers that follow stringent packaging and transport guidelines can mitigate these variables. By paying close attention to logistical details, stakeholders help protect the integrity of lamination stacks, thereby supporting consistent motor performance across diverse operating environments.
Further Reading:
https://www.asnt.org/what-is-nondestructive-testing/methods/electromagnetic-testing